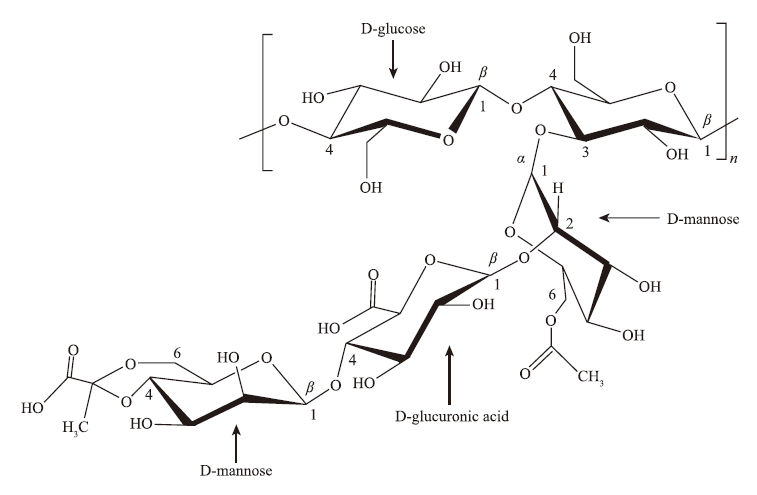
Xanthan gum is a kind of extracellular polysaccharides produced by xanthomonas. It is a heteropolysaccharide polymer with high molecular weight formed by a series of five-sugar residues repeating units. Xanthan gum and its derivatives are widely used in various industries such as daily-use chemical industry, food processing industry, pharmaceutical industry, water treatment, and oil exploitation, due to their excellent stability, thickening ability, emulsifying ability, suspensibility, rheological property, acid resistance, base resistance, heat resistance, salt resistance, and other fit properties. In this paper, the chemical structure, the main physicochemical properties, the production methods, and the modification technologies of xanthan gum, as well as the properties, the preparation, separation and purification methods of xanthan gum oligosaccharides are briefly presented. Furthermore, the application status of xanthan gum and its modified products, the current problems in xanthan gum production, and the future prospects for the development of xanthan gum are also mentioned in this paper.