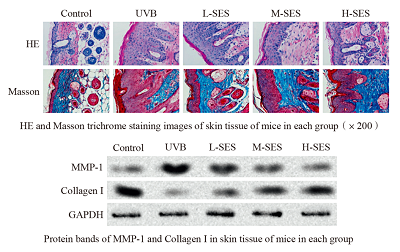
The study aimed to reveal the effect of Sesamolin (SES) on skin photoaging mice induced by ultraviolet B (UVB). Mice were randomly divided into five groups (n=12): control group, UVB group, low dose SES group (L-SES), medium dose SES group (M-SES) and high dose SES group (H-SES). Mice in control group were not irradiated with UVB, while mice in other groups were irradiated with UVB for 8 weeks. In addition, from the day of irradiation, mice in L-SES group, M-SES group and H-SES group were administrated with 0.5 mL Sesamolin solution of 20, 40 and 80 mg/(kg·d), respectively, for a total of 8 weeks. After administration, the water content of epidermis of mice in each group was measured. Skin morphology was evaluated by HE staining and collagen deposition was evaluated by Masson trichrome staining. The levels of oxidative stress indexes (SOD, CAT, GSH-Px and MDA) in skin tissue were measured. The mRNA or protein levels of MMP-1, Collagen I, Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1 and AQP3 in skin tissue were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blotting. Compared with UVB group, the water content of epidermis in L-SES group, M-SES group and H-SES group increases, the thickness of epidermis decreases, the skin lesion alleviates, the collagen fibers arrange neatly, the collagen density increases, the expression levels of MMP-1 mRNA and protein decrease, the expression levels of Collagen I mRNA and protein increase, the levels of SOD, CAT and GSH-Px increase, the level of MDA decreases, and the relative expression levels of mRNA and protein in Nrf2 and HO-1 increase, the relative expression levels of Keap1 mRNA and protein decrease, while the relative expression levels of mRNA and protein of AQP3 increase (P<0.05). Sesamolin can increase the water content and antioxidant capacity of mouse epidermis in a dose-dependent manner and reduce skin injury. The mechanism may be related to the up-regulation of AQP3 expression and activation of Nrf2 signal pathway.