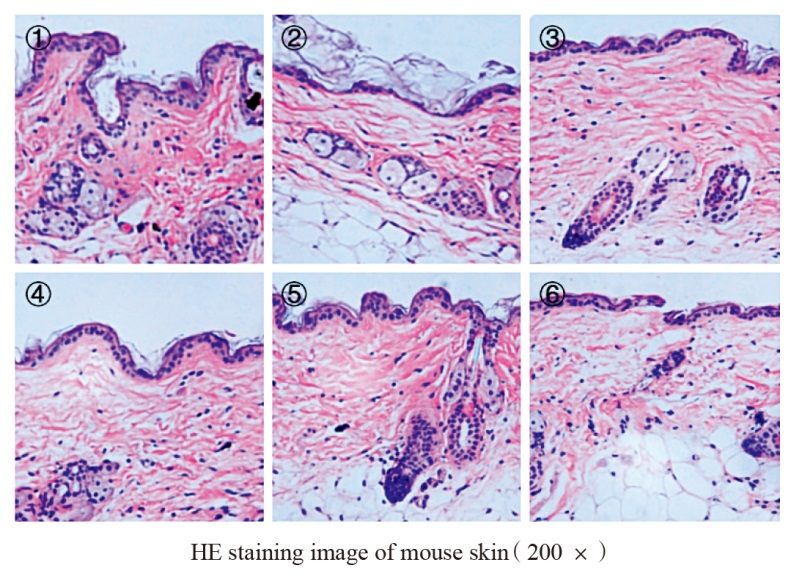
The study aimed to investigate the anti-aging and antioxidant effects of isosinensetin (ISO) on skin aging mice induced by D-galactose (D-gal). The mice were divided into 6 groups (n=12): C group, D-gal group, D-gal+L-ISO group, D-gal+M-ISO group, D-gal+H-ISO group and D-gal+H-ISO+ML385 group. The skin aging mouse model was established by subcutaneous injection of D-gal of 1 g/ (kg·d) into the back of mice for 6 weeks. From the day of D-gal injection, mice in C group and D-gal group were applied with snow cream on their back depilation area, while mice in D-gal+L-ISO group, D-gal+M-ISO group and D-gal+H-ISO group were applied with 50, 100 and 200 mg/kg isosinensetin cream, respectively. The mice in D-gal+H-ISO+ML385 group were applied with 200 mg/kg isosinensetin cream and intraperitoneally injected with 30 mg/(kg·d) nuclear factor E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) inhibitor ML385. The application amount was 2 mg/cm2. After 6 weeks of transdermal administration, the body weight, skin water content, skin antioxidant index, hydroxyproline (HYP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) levels were measured. The skin morphology was observed by HE staining. The transcriptional levels of COL1A1, COL3A1, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) -1 and MMP-3 in skin were detected by RT-qPCR. The protein levels of Nrf2 (nucleus), Kelch-like ECH associated Protein 1 (Keap1) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in skin were detected by Western blotting. The results show that all three doses of isosinensetin increases skin water content, improves skin morphology, increases superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) levels, decreases malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, increases HYP and HA levels, increases COL1A1 and COL3A1 mRNA levels, decreases MMP-1 and MMP-3 mRNA levels, increases Nrf2 (nucleus) and HO-1 protein levels, and decreases Keap1 protein levels in skin aging mice (P<0.05). ML385 attenuates the anti-aging and antioxidant effects of isosinensetin (P<0.05). In short, transdermal administration of isosinensetin can improve the anti-aging and antioxidant ability of D-gal-induced skin aging mice by activating Nrf2 pathway.