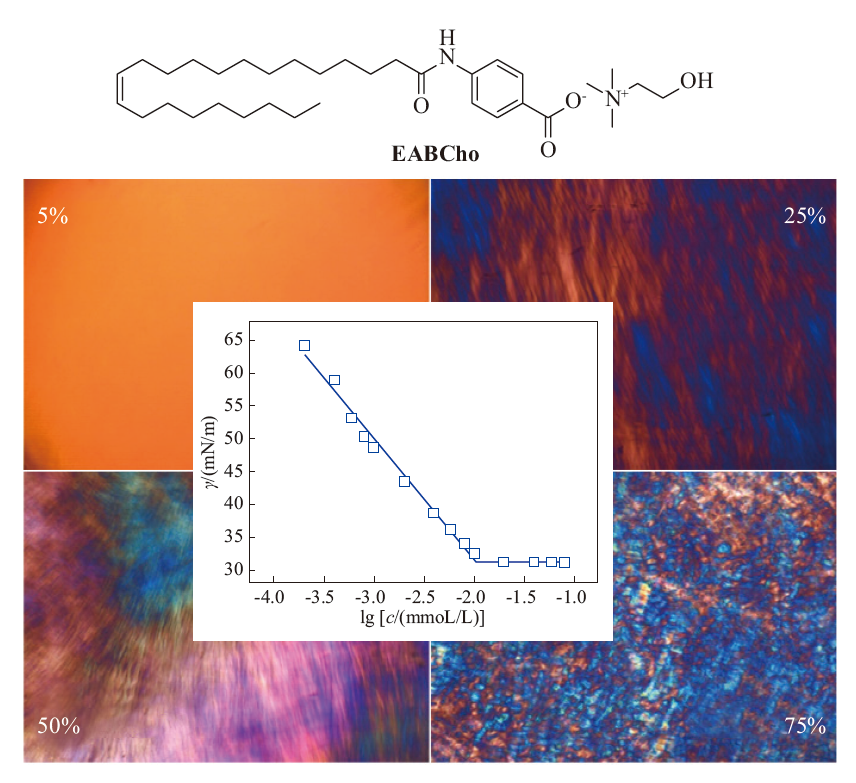
Ionic liquid surfactants (ILSs) are advantageous over traditional amphiphiles because of their adjustable structure and physicochemical properties. However, the improvement of common ILSs in terms of self-assembly and thickening remains a significant challenge. Compared with conventional cationic ILSs, anionic ILSs composed of a long alkyl anion and a relatively small cation have been rarely reported. Due to the simple and readily available raw materials and potential environmental friendliness, fatty-acid-based ionic liquid surfactants have attracted great interest in recent years. In this work, an ILS based on ultra-long-chain fatty acid, namely [erucamide benzoic acid] [choline] (EABCho), was designed and synthesized using erucic acid as raw material. Erucic acid is a leftover material in the processing of rapeseed oil. The molecular structure was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Its fundamental properties including surface activity, thermodynamics of micellization, and phase behavior of aqueous solution were investigated by surface tension, conductivity, polarized optical microscopy and rheology. The results indicated that, EABCho had a critical micelle concentration of only 0.01 mmol/L and a micellization free energy of -59.852 kJ/mol, i.e., the introduction of an ultra-long carbon chain (C22) and benzene ring structure endowed EABCho with strong self-assembly ability which was much stronger than that of the corresponding analogue with short carbon chain. With the increase of concentration, the aqueous solution of EABCho presented micellar phase, hexagonal liquid crystal phase and lamellar liquid crystal phase in sequence, all showing significant gel-like properties. Therefore, it was expected to be used as a rheology regulator in daily chemicals, oil exploration, etc.