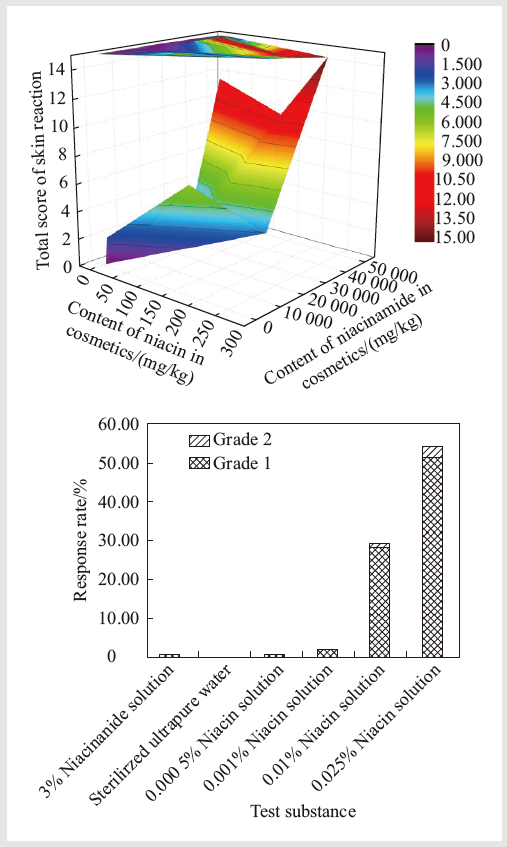
To investigate the main causes of skin adverse reactions caused by niacinamide cosmetics, niacin and niacinamide patch test in healthy volunteers, and niacinamide cosmetics stability test were conducted. Niacinamide cosmetics were selected to perform patch test on healthy volunteers, and the content of niacin and niacinamide were measured. Subsequently, patch tests of niacin solution with different content (0.000 5%, 0.001%, 0.01%, 0.025%) and 3% niacinamide solution were carried out, and the stability test of niacinamide cosmetics was carried out. The results are shown as following: among 45 kinds of niacinamide cosmetics selected, 17 kinds of them cause skin reactions by patch test (accounting for 37.8% of the total), and niacin is detected in 41 kinds (accounting for 91.1%) with the content of 0.000 15%-0.026 6%. Self-established skin reaction scoring method is used for scoring, and the total score of skin reaction is significantly positively correlated with the niacin content (r=0.406, P=0.006), but not significantly correlated with the niacinamide content (r=0.099, P=0.517). There are no significant differences among skin irritation of 0.000 5% niacin solution, 0.001% niacin solution, 3% niacinamide solution and the negative control (P>0.05). There are significant differences between skin irritation of 0.025% niacin and the negative control, or between skin irritation of 0.01% niacin and the negative control (P<0.05). Niacinamide cosmetics are placed at 25 ℃ for 8 weeks and the content of niacin are stable, while niacin content are gradually increased at 55 ℃ for 8 weeks. Hence, niacin is potentially irritating to healthy human skin, and the degree of irritation worsens with the increase of the content. In addition, for niacinamide cosmetics, part of niacinamide slowly hydrolyze to niacin under high temperature, which may cause adverse reactions on the skin of the sensitive consumers.