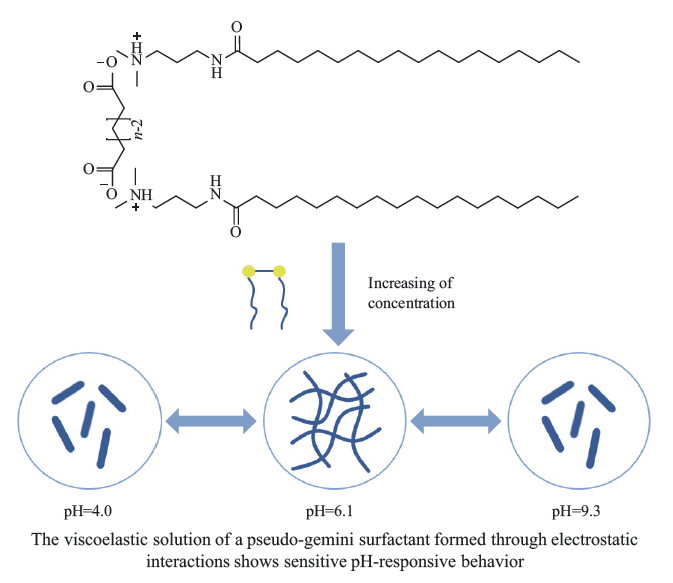
Three pseudo-gemini surfactants (2C18N3N/XA, XA=SA, GA and AA) were formed by non-covalently connecting dibasic acid(HOOC (CH2) nCOOH, n=2, 3 and 4, abbreviated as SA, GA and AA, respectively) with long-chain tertiary amine (C17H35CONHCH2CH2CH2N (CH3) 2) in the molar ratio of 1:2 through electrostatic interactions. The whole process had avoided any complicated synthetic procedures. The surface activity and rheological properties of the surfactants were investigated. The critical micelle concentration (cmc) of 2C18N3N/GA was 4.60×10-5 mmol/L, which was significantly lower than that of conventional gemini surfactants, indicative of strong aggregation ability. 2C18N3N/SA and 2C18N3N/AA also had low cmc values. These surfactants could form wormlike micelles when the concentrations were above 50 mmol/L, exhibiting viscoelastic behavior, and the viscoelastic solutions thereof had good temperature and shear resistance. Due to the tertiary amine group in the pseudo-gemini surfactant, it exhibited pH-responsive properties. It was found that when the pH was 6.1, the viscosity of the solution was very high, whereas when the pH was 4.0 or 9.3, the viscosity rapidly decreased. Furthermore, the pseudo-gemini surfactant was also responsive to temperature. With the increase of temperature, the viscosity of the system rapidly increased. At 60 ℃, the zero-shear viscosity of 2C18N3N/GA at 300 mmol/L could be as high as 11 967.73 Pa·s. These surfactants were simple to be prepared and showed excellent performance, which expanded the range of preparation and application of novel surfactants.