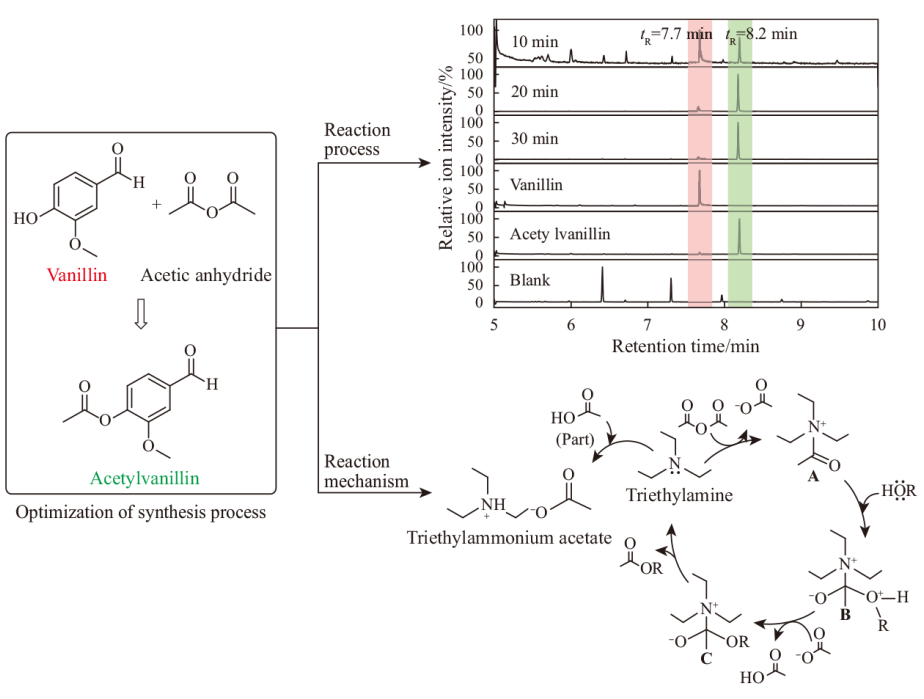
Acetylvanillin (4-acyloxy-3-methoxy-benzaldehyde) is an important vanillin derivative, which has strong milk fragrance. It is an intermediate produced in the reaction process of synthesizing vanillin from eugenol, isoeugenol and other raw materials. It is often used as flavoring agent in various dairy products (such as modulated milk powder, fresh milk, yogurt, etc.), biscuits, beverages, cosmetics (perfume), tobacco, wine, food packaging, feed, etc. Due to the structural characteristics of various functional groups (-CHO, AcO-, MeO-) on the benzene ring of acetylvanillin, it can undergo a variety of chemical reactions. Therefore, it is also widely used in the preparation of drugs and other fine chemicals as an important organic intermediate. At present, the chemical synthesis of acetylvanillin mainly takes vanillin as raw material, and it is prepared by acylation reagents such as anhydride and acyl chloride at room temperature following strong alkali or catalyst. However, this process has some shortcomings, such as incomplete reaction, long time of esterification, complicated post-treatment, corrosion in equipment, and difficult access to catalyst. In this work, the effects of experimental conditions on the yield were investigated, including the ratios of raw materials, the solvents, alkaline reagents and reaction time, and the optimization of synthesis process and the analysis of reaction process were carried out. Vanillin and acetic anhydride were used as raw materials. The reaction process of acetylvanillin was analyzed and characterized by capillary melting point method, FT-IR and GC-MS/MS. The results showed that, the optimized synthesis conditions of acetylvanillin were as follows. The molar ratio of raw materials n(vanillin) : n(acetic anhydride) : n(triethylamine) was 1:1.3:0.5; the reaction time at room temperature was 0.5 h, and the yield was 99.0%. The catalytic effect of triethylamine as the catalyst in the reaction process was discussed, and its catalytic mechanism was speculated. This process had the advantages of mild reaction conditions, short reaction time, high yield, low cost and easy availability of raw materials, and simple operation. This study could provide reference for the optimization of synthesis process, analysis method and basic theoretical research.