


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 161-167.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-2806.2024.02.006
• Development and application • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhen Xie1,Wei Huang2,Jinsong Zhang1,Shuhuai Chen1,Linji Qu1,Rong Kuang1,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-14
Revised:2024-01-29
Online:2024-02-22
Published:2024-02-28
Contact:
* Tel.: +86-13989899796, E-mail: CLC Number:
Zhen Xie, Wei Huang, Jinsong Zhang, Shuhuai Chen, Linji Qu, Rong Kuang. Study on biomarkers of corneal injury in the evaluation of eye irritation of cosmetics[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 161-167.
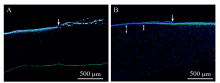
Fig. 1
Results of corneal fluorescence staining for the positive control group(A:3 h post-exposure, B: 24 h post-exposure. The arrow shows the location of the abrupt change in phalloidin staining, i.e., the edge of the exposed area of the cornea bounded by the dosing ring; the double-headed arrow shows the absence of phalloidin staining in the corneal stromal cells, and the thickness of the staining defect indicated by the double-headed arrow appears to increase slightly the closer to the central cornea)"
Tab. 2
Epithelial and stromal DOI measurements for different concentration and post-exposure time groups (n=3)"
| 组别 | 后暴露时间/h | 上皮厚度/μm | Epi DOI/% | 基质厚度/μm | Stromal DOI/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| NC | 3 | 39.8 | 2.7 | NA | NA | / | / | NA | NA | |||
| 24 | 39.0 | 3.8 | NA | NA | / | / | NA | NA | ||||
| PC | 3 | 12.7 | 6.0 | 68.1 | 15.0 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 24 | 17.0 | 0.3 | 56.4 | 0.8 | 586.7 | 27.3 | 21.8 | 3.6 | ||||
| 编号2 10% 稀释组 | 3 | 40.8 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 24 | 41.8 | 1.6 | 0 | 0 | / | / | / | / | ||||
| 编号2不稀释组 | 3 | 33.1 | 2.0 | 16.7 | 5.0 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 24 | 37.2 | 1.3 | 4.5 | 3.4 | / | / | / | / | ||||
| 编号13 10%稀释组 | 3 | 21.5 | 0.9 | 45.9 | 2.4 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 24 | 36.5 | 1.6 | 6.5 | 4.1 | / | / | / | / | ||||
| 编号13不稀释组 | 3 | 14.1 | 3.6 | 64.5 | 9.0 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 24 | 24.1 | 2.1 | 38.1 | 5.4 | / | / | / | / | ||||
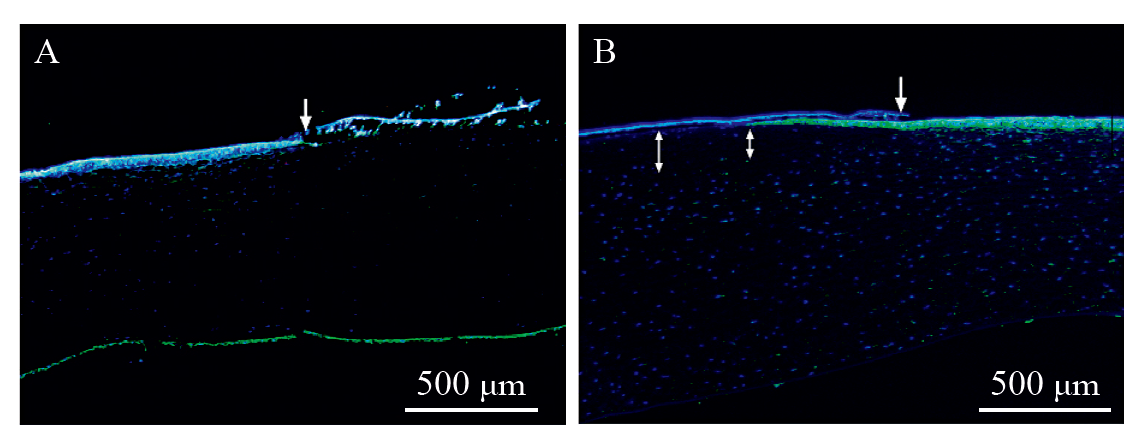
Fig. 3
Fluorescence staining results of the test materials in isolated rabbit corneas (Corneal exposure to subject #8 followed by exfoliation of the epithelium (arrow). Positive control and subject #14 have a significant absence of phalloidin staining in the anterior stroma (double arrows), indicating that the damage extends to the stroma)"

Tab. 3
In vitro epithelial and stromal DOI measurements (n=3)"
| 组别 | 上皮厚度/μm | Epi DOI/% | 基质厚度/μm | Stromal DOI/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||||
| NC | 40.5 | 0.9 | NA | NA | / | / | NA | NA | |||
| PC | 16.9 | 1.5 | 58.3 | 3.7 | 442.6 | 15.5 | 26.9 | 2.6 | |||
| 1 | 38.7 | 0.8 | 4.6 | 2.0 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 2 | 37.8 | 1.9 | 6.7 | 4.6 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 3 | 37.1 | 2.3 | 8.3 | 5.7 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 4 | 8.8 | 4.3 | 78.2 | 10.5 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 5 | 33.0 | 1.9 | 18.5 | 4.7 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 6 | 11.2 | 2.4 | 72.3 | 5.9 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 7 | 22.7 | 3.5 | 44.0 | 8.6 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 8 | 12.0 | 2.2 | 70.4 | 5.4 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 9 | 38.9 | 1.1 | 4.0 | 2.6 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 10 | 50.0 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 11 | 29.5 | 3.4 | 27.1 | 8.4 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 12 | 30.4 | 1.5 | 25.0 | 3.7 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 13 | 18.5 | 5.6 | 54.3 | 13.8 | / | / | / | / | |||
| 14 | 17.5 | 0.2 | 56.7 | 0.5 | 448.4 | 30.7 | 29.6 | 4.8 | |||
Tab. 4
In vivo epithelial and stromal DOI measurements (n=3)"
| 组别 | 上皮厚度/μm | Epi DOI/% | 基质厚度/μm | Stromal DOI/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | Mean | SD | Mean | ||||
| NC | 41.5 | 0.6 | NA | NA | / | / | NA | NA | |||
| 1 | 43.4 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 42.8 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 3 | 38.9 | 0.7 | 6.3 | 1.6 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 4 | 14.3 | 0.2 | 65.6 | 0.5 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5 | 36.9 | 2.6 | 11.2 | 6.3 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 6 | 20.8 | 5.7 | 49.9 | 13.8 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 7 | 30.3 | 3.4 | 27.0 | 8.1 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 8 | 20.7 | 1.8 | 50.1 | 4.3 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 9 | 38.9 | 1.0 | 6.3 | 2.4 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 10 | 49.3 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 11 | 19.6 | 0.9 | 52.8 | 2.1 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 12 | 29.1 | 4.0 | 29.9 | 9.6 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | / | / | 0 | 0 | |||
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 553.6 | 7.8 | 11.4 | 1.3 | |||
| [1] | OECD. Test Guideline No.405: Acute Eye Irritation/Corrosion [S]. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2012. |
| [2] | OECD. Test Guideline No.160: Guidance Document on the Collection of Eye Tissues for Histological Evaluation and Collection of Data [S]. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2018. |
| [3] |
Lebrun S, Xie Y, Chavez S, et al. An in vitro depth of injury prediction model for a histopathologic classification of EPA and GHS eye irritants[J]. Toxicol in Vitro., 2019, 61: 104628.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104628 |
| [4] | Cater K C, Harbell J W. Prediction of eye irritation potential of liquid and granular laundry detergent formulas using the bovine corneal opacity and permeability (BCOP) assay[J]. Cutaneous & Ocular Toxicology, 2013, 32 (3) : 210-221. |
| [5] | Xie Zhen, Chen Shuhuai, Liu Lu, et al. Evaluation of eye irritation of shampoos, shower gel and facial cleansers using Bovine Corneal Opacity and Permeability Assay based on biomarkers of cell viability[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51 (2) : 109-114. |
| [6] | National Medical Products Administration. Safety and technical standards for cosmetics (2015 Edition) [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015: 493-495. |
| [7] |
Xie Z, Ye K, Chen S H, et al. Cellular viability and death biomarkers enables the evaluation of ocular irritation using the bovine corneal opacity and permeability assay[J]. Toxicol Lett., 2021, 340: 52-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.01.004 pmid: 33421553 |
| [8] |
Lebrun S, Xue Y, Chavez S, et al. An in vitro depth of injury prediction model for a histopathologic classification of EPA and GHS eye irritants[J]. Toxicol in Vitro., 2019, 61: 104628.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104628 |
| [9] | OECD. Test Guideline No. 437: Bovine Corneal Opacity and Permeability Test Method for Identifying i) Chemicals Inducing Serious Eye Damage and ii) Chemicals Not Requiring Classification for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage [S]. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2020. |
| [10] | Xie Zhen, Chen Shuhuai, Liu Lu, et al. Predictive value of bovine corneal opacity and permeability test in combination with histopathology in eye irritation of cosmetic products[J]. China Medical Herald, 2021, 18 (4) : 14-17. |
| [11] |
Furukawa M, Skakibara T, Itoh K, et al. Histopathological evaluation of the ocular-irritation potential of shampoos, make-up removers and cleansing foams in the bovine corneal opacity and permeability assay[J]. J. Toxicol. Pathol., 2015, 28 (4) : 243-248.
doi: 10.1293/tox.2015-0022 pmid: 26538816 |
| [12] |
Danjo Y, Gipson I K. Specific transduction of the leading edge cells of migrating epithelia demonstrates that they are replaced during healing[J]. Exp. Eye. Res., 2002, 74: 199-204.
pmid: 11950230 |
| [13] | Ashby B D, Garrett Q, Willcox M D P. Corneal injuries and wound healing—review of processes and therapies[J]. Austin J. Clin. Ophthal., 2014, 1 (4) : 1-25. |
| [1] | Jingxuan Liu, Jianming Jin, Hua Wu. Botanical cosmetic ingredients (VII)Research and development of plant antifungal [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 259-266. |
| [2] | Wu Bi, Xiaohong Pan, Xiaoqin Tu, Shuai Yin, Hui Sun. Analysis of the mechanism of anti-sensitive skin effect of cosmetic raw material Stephania tetrandra based on network pharmacology [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 305-312. |
| [3] | Yaoyao Li. Study on the anti-aging and antioxidant effects of isosinensetin [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 313-319. |
| [4] | Liyuan Zhang, Linqi Yan, Qiaoyuan Cheng, Lvye Qi, Rong Wang, Liuqian Huang. Determination of 14 kinds of α-hydroxy acids and hydroxy esters in cosmetics [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 353-359. |
| [5] | Wei Xu, Po Zou, Changyu Li, Ming Yang, Yan Lu, Huiliang Li. Determination of 36 stimulants in cosmetics by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 360-368. |
| [6] | Kangfu Zhou, Yixuan Zhi, Feifei Wang, Yazhuo Shang. New emulsion system and its application in cosmetics (VI)Microemulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 139-148. |
| [7] | Xiaohong Pan, Ziqi Gao, Zhen Chen, Shuai Yin, Haiping Huang, Bin Hu. Discussion on the current situation of research and management on the stability of cosmetic products in China [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 201-208. |
| [8] | Li Lu, Fang Fang, Youlong Feng, Ling Cao. Screening for illegal addition of sulfonamides in cosmetic products using ultra-performance liquid chromatographytriple quadrupoletandem mass spectrometry with precursor ion scanning [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 216-223. |
| [9] | Ren Wang, Yuanyang Wu, Jia Qiao, Linqi Yan, Cen Chen, Liyuan Zhang. Study on phenoxyethanol content in children’s cosmetics on the mark and preliminary risk assessment [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 224-230. |
| [10] | Yixiang Lu, Liting Wu, Jimin Jiang, Hailu Chen, Xuan Huang. Determination of tolnaftate and liranaftate in cosmetics by high performance liquid chromatography and verification by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 231-238. |
| [11] | Liyuan Zhang, Qiaoyuan Cheng, Cen Chen, Zehua Li, Liuqian Huang, Lvye Qi. Determination of 3 kinds of α-hydroxy acids and their esters in cosmetics by high performance liquid chromatography [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 102-106. |
| [12] | Linling Lu, Hui Lu, Chunyan Min, Yefei Qian. Determination of functional components of Glycyrrhizae, Ginseng and Scutellariae in facial masks by UHPLC-MS/MS [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 107-113. |
| [13] | Xu Han, Jiajia Wu, Na Wu, Yazhuo Shang. New emulsion system and its application in cosmetics (V) Janus emulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 24-31. |
| [14] | Feng Liu, Yuanchang Deng, Guohong Ying, Xiaowei Wang. Establishment of duplex-PCR method for rapid detection of Pluralibacter gergoviae [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 45-50. |
| [15] | Yaru Wang, Tingyuan Mo, Hongxia Lai, Yue Zhou, Jiaying Xie, Jianhua Tan. Analysis of the causes of skin irritation of niacinamide cosmetics based on patch test and stability test [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 51-56. |
|