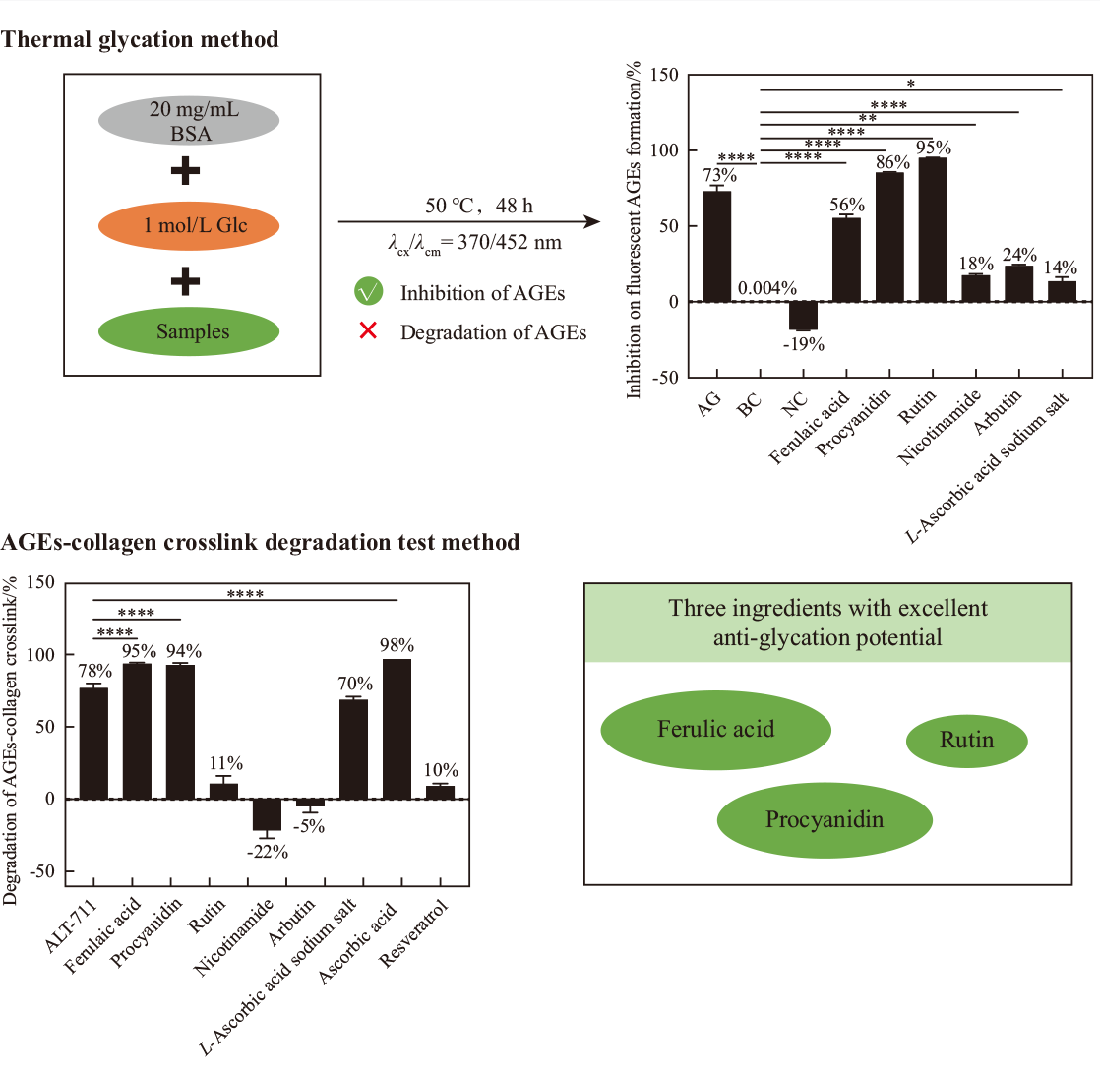
In response to the increasing demand for anti-glycation ingredient screening, existing biochemical anti-glycation evaluation systems(in vitro), anti-glycation cell models and human efficacy evaluation methods have extended lead times and high costs. They are not suitable for large-scale primary screening of ingredients. An in vitro efficacy evaluation model with short experimental lead time, low cost, simple operation, and good reproducibility for preliminary screening of anti-glycation ingredients is urgently needed. In this study, we optimized the in vitro biochemical anti-glycation evaluation system based on the thermal glycation method and investigated the suitability of the screening of AGEs (advanced glycation end products) and degraded fluorescent AGEs by testing eight ingredients, including ferulic acid, procyanidins, rutin and L-ascorbic acid. The screening results were compared with the results of the AGEs-collagen cross-linkage disruption experiments that have been published to test the degradation ability of AGEs, and the screening ability, advantages and limitations of the system were discussed and analyzed. We confirm that the better conditions in building the model are: a reaction system consisting of 20 mg/mL BSA, 1 mol/L glucose, and 0.1 mol/L PBS buffer, a reaction temperature of 50 ℃, an incubation time of 48 h, and a detection wavelength of λex/λem=370/452 nm. In the test of inhibition/degradation of fluorescent AGEs, ferulic acid, procyanidin and rutin solutions at the tested content of 2% achieve 56%, 86% and 95% inhibition, respectively, with good anti-glycation effect, and ferulic acid and rutin show a trend of potential degradation of AGEs. The optimized system, though, has some limitations in the application of degrading fluorescent AGEs, compared with the method of AGEs-collagen cross-link disruption ability test, in terms of control system setting and experimental results. However, in the screening of ingredients for the inhibition of fluorescent AGEs, the stability and authenticity of the results are good, and the test cycle is significantly shortened, which provides a rapid, stable and economic cost-saving technical platform for the screening of anti-glycation efficacy additives and the development of related products.