


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 376-384.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-2806.2024.04.002
• Basic research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenjie Ding1,Jing Shen1,Xiaona Dong1,Zhiping Du1,*( ),Shujun Wang2
),Shujun Wang2
Received:2024-01-06
Revised:2024-03-18
Online:2024-04-22
Published:2024-04-26
Contact:
*Tel.: +86-13934596308, E-mail: CLC Number:
Wenjie Ding, Jing Shen, Xiaona Dong, Zhiping Du, Shujun Wang. Preparation of AC@Fe3O4 and its adsorption of emulsion from water[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(4): 376-384.
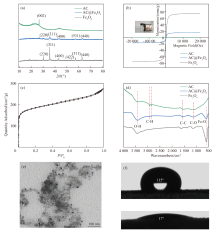
Fig. 2
Characterization of structure, composition and magnetic properties. (a) XRD patterns of AC, Fe3O4 and AC@Fe3O4; (b) VSM diagrams of AC, Fe3O4 and AC@Fe3O4; (c) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of AC@Fe3O4; (d) IR analyses of AC, Fe3O4 and AC@Fe3O4;(e) TEM image of AC@Fe3O4; (f) contact angles of water and oil on AC@Fe3O4"
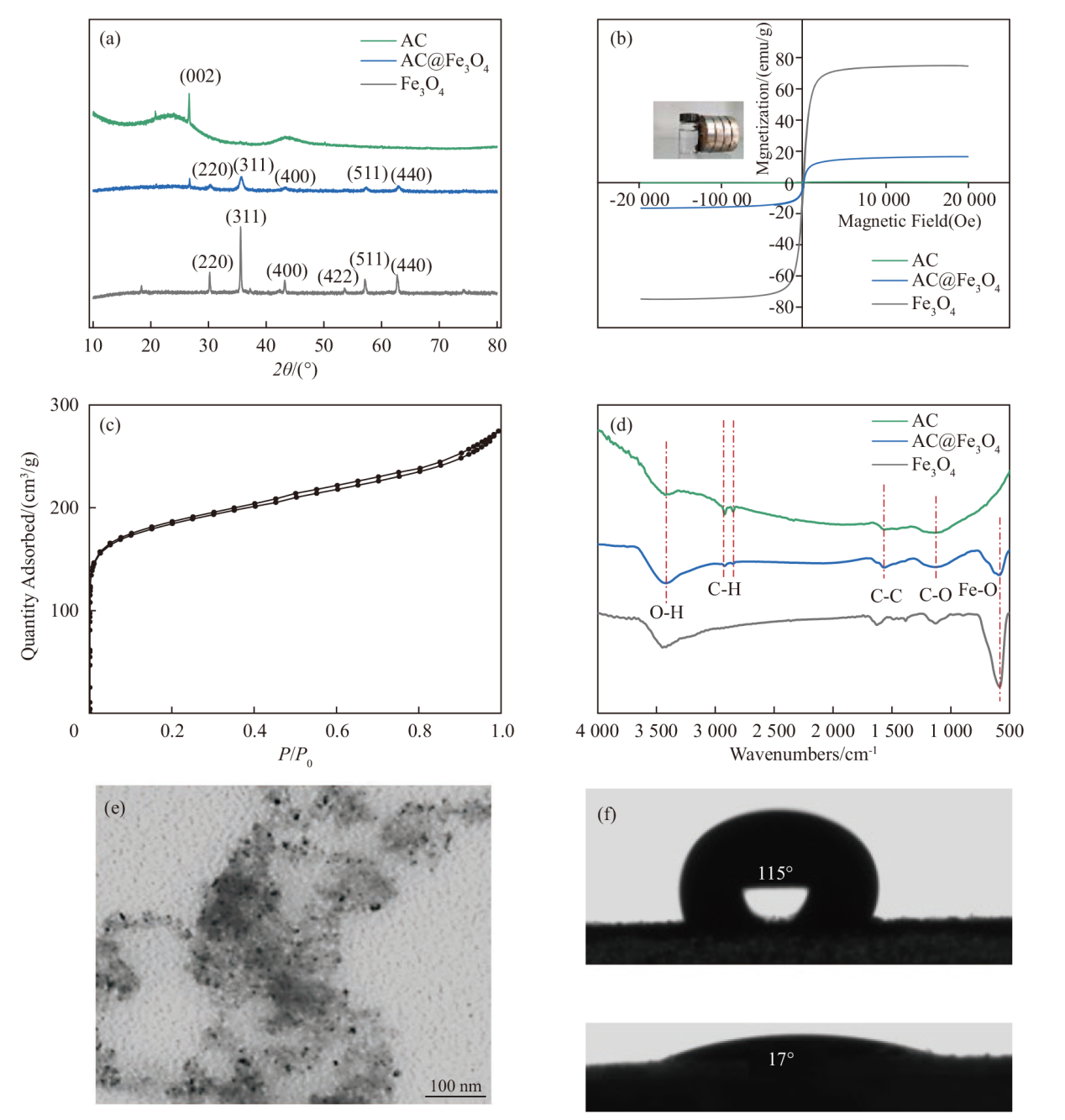
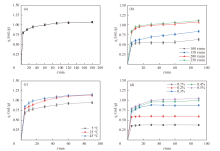
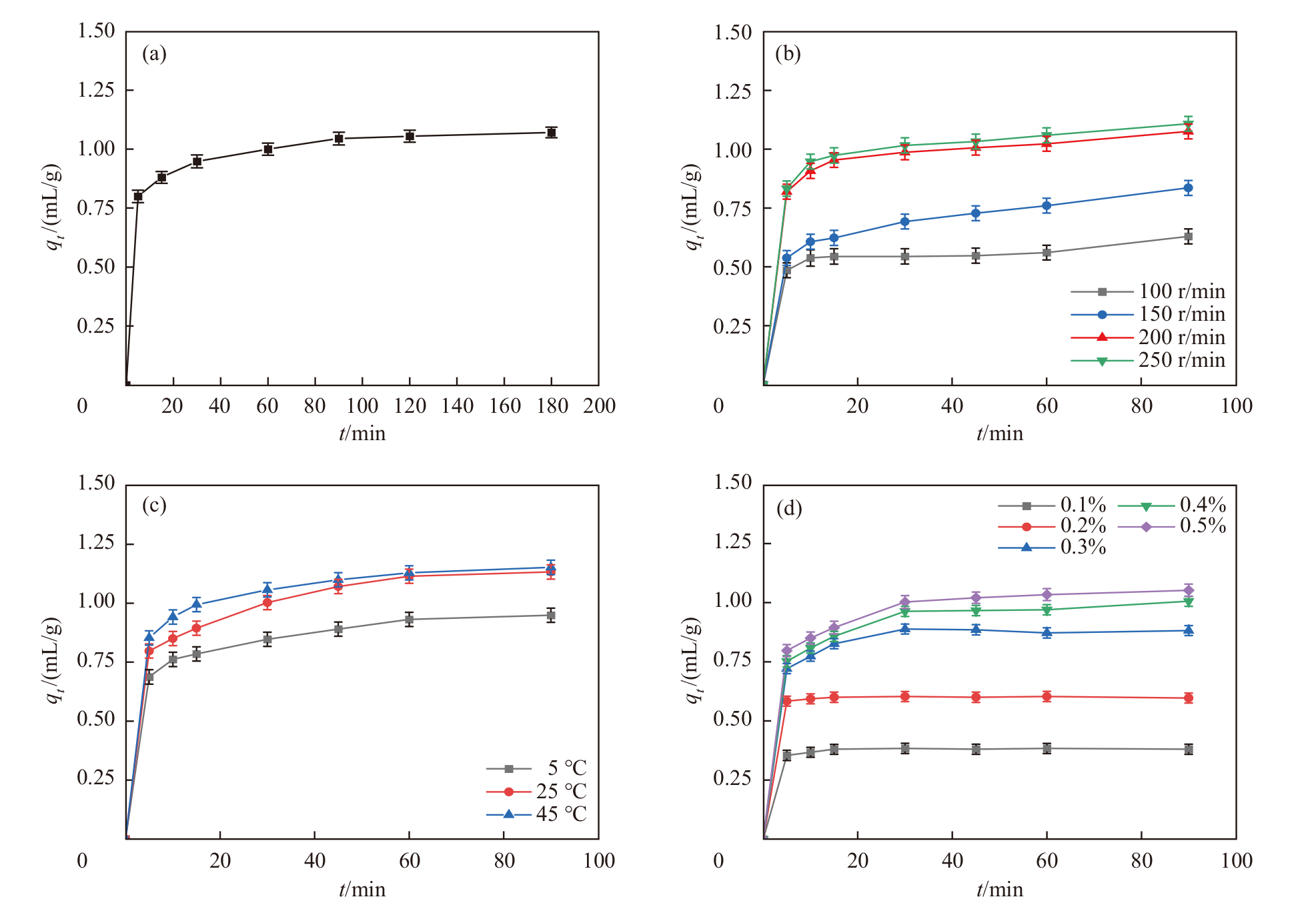
Fig. 3
Adsorption properties of AC@Fe3O4 for coal-mining hydraulic support emulsion in water. (a) Effect of adsorption time on the adsorption capacity of AC@Fe3O4; (b) effect of oscillation rate on the adsorption capacity of AC@Fe3O4; (c) effect of temperature on the adsorption capacity of AC@Fe3O4; (d) effect of emulsion volume fraction on the adsorption capacity of AC@Fe3O4"
Tab. 3
Parameters of adsorption kinetics for emulsion on AC@Fe3O4 surface"
| φ(乳液)/% | 伪一级动力学 | 伪二级动力学 | 实际qe /(mL/g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | qe /(mL/g) | R2 | k2 | qe /(mL/g) | R2 | |||
| 0.1 | 0.023 | 0.041 | 0.18 | 1.81 | 0.38 | 0.999 | 0.38 | |
| 0.2 | 0.039 | 0.064 | 0.11 | 1.92 | 0.61 | 0.999 | 0.60 | |
| 0.3 | 0.041 | 0.190 | 0.43 | 1.47 | 0.89 | 0.998 | 0.88 | |
| 0.4 | 0.048 | 0.420 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 1.03 | 0.996 | 1.01 | |
| 0.5 | 0.044 | 0.520 | 0.78 | 0.52 | 1.09 | 0.998 | 1.07 | |
| [1] | Du Guoyong, Yang Yue, Wang Yonghong. A review of oily wastewater by adsorption[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021, 50 (9) : 2490-2495. |
| [2] | Hong Ke, Mo Chenjian, Zhu Saichang. Research progress on demulsification and subsequent treatment technology of emulsion wastewater[J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2016 (3) : 44-45. |
| [3] | Tian Yongda, Li Ze, Pan Bintao, et al. Research progress of emulsified oil wastewater treatment technology[J]. Chemical Engineering & Equipment, 2018 (8) : 295-296. |
| [4] | An Rui, Zhao Qing. Progress in the adsorption of triclosan in aqueous solution[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53 (8) : 945-953. |
| [5] |
Jiang Yong, Xie Qiang, Zhang Yanhai, et al. Preparation of magnetically separable mesoporous activated carbons from brown coal with Fe3O4[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2019, 29 (3) : 513-519.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2019.01.002 |
| [6] |
Hao Zheng, Wang Changhui, Yan Zaisheng, et al. Magnetic particles modification of coconut shell-derived activated carbon and biochar for effective removal of phenol from water[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 211: 962-969.
doi: S0045-6535(18)31513-3 pmid: 30119027 |
| [7] | Wang Gen, Gao Ge, Yang Shengjiong, et al. Magnetic mesoporous carbon nanospheres from renewable plant phenol for efficient hexavalent chromium removal[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 310. DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110623. |
| [8] |
Zhang Xiaofang, Li Yuhuan, He Yang, et al. Preparation of magnetic activated carbon by activation and modification of char derived from co-pyrolysis of lignite and biomass and its adsorption of heavy-metal-containing wastewater[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12 (6) : 665.
doi: 10.3390/min12060665 |
| [9] | Anzai T, Matsuura Y, Sugawara T, et al. Removal of humic acid in water by rice hull magnetic activated carbon and magnetic separation[J]. Ieee Transactions on Applied Superconductivity: A Publication of the Ieee Superconductivity Committee, 2016, 26 (4). DOI: 10.1109/TASC.2015.2512218. |
| [10] |
Kovummal G R, Pattayil A J. Coconut shell based activated carbon-iron oxide magnetic nanocomposite for fast and efficient removal of oil spills[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3 (3) : 2068-2075.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.04.028 |
| [11] |
Luo Hao, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaoyan, et al. A facile route for preparation of magnetic biomass activated carbon with high performance for removal of dye pollutants[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24 (18) : 15599-15608.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9207-y pmid: 28523615 |
| [12] | Sağlam S, Türk F N, Arslanoğlu H. Synthesis of magnetic activated carbon from industrial waste: characterization, tetracycline removal and interpretation of its mechanism[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 2024. DOI: 10.1007/s13399-023-05229-y. |
| [13] | Zhan Huiying. Measuring oil content in waste water using UV-spectrum[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Arts and Science (Natural Sciences), 2007 (1) : 65-66, 69. |
| [14] | Peng Sihan. Research on demulsification and biodegradation of emulsified oil wastewater used for hydraulic supports in mines[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2022. |
| [15] | Zhang Xiaowei. Study on the removal of emulsified oil from coal chemical wastewater[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2021. |
| [16] | Huang Zhouman. Experimental study on the treatment of trace oil in nine drainage[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2008. |
| [17] |
Lü Ting, Chen Yi, Qi Dongming, et al. Treatment of emulsified oil wastewaters by using chitosan grafted magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 696: 1205-1212.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.118 |
| [18] |
Wu Nannan, Xu Dongmei, Wang Zhou, et al. Achieving superior electromagnetic wave absorbers through the novel metal-organic frameworks derived magnetic porous carbon nanorods[J]. Carbon, 2019, 145: 433-444.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.028 |
| [19] |
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Ghaedi M, et al. Novel strategy for synthesis of magnetic dummy molecularly imprinted nanoparticles based on functionalized silica as an efficient sorbent for the determination of acrylamide in potato chips: optimization by experimental design methodology[J]. Talanta, 2016, 154: 526-532.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.04.010 pmid: 27154710 |
| [20] |
Ma Zhiya, Guan Yueping, Liu Huizhou. Synthesis and characterization of micron-Sized monodisperse superparamagnetic polymer particles with amino groups[J]. Journal of Polymer Science part A-Polymer Chemistry, 2005, 43 (15) : 3433-3439.
doi: 10.1002/pola.v43:15 |
| [21] |
Chang Yanping, Ren Cuiling, Qu Jichun, et al. Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4/graphene nanocomposite and investigation of its adsorption performance for aniline and p-chloroaniline[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 261: 504-509.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.08.045 |
| [22] |
Lü Ting, Zhang Shuang, Qi Dongming, et al. Synthesis of pH-sensitive and recyclable magnetic nanoparticles for efficient separation of emulsified oil from aqueous environments[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 396: 1604-1612.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.223 |
| [23] |
Hossein E, Seyyed A A H. Clay/MgFe2O4 as a novel composite for removal of Cr (Ⅵ) from aqueous media[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5 (30) : 9377-9387.
doi: 10.1002/slct.v5.30 |
| [24] | Wang Meng, Fu Xinmei, Wang Hanmei, et al. Study on the adsorption behavior of chestnut shells on emulsified oil in oily wastewater[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2022, 48 (7) : 52-57. |
| [25] | Yuan Bo, Wang Liping, Hua Sulan, et al. Complex organoclay adsorbent for treatment of emulsified oily wastewater[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2006, 28 (6) : 448-451. |
| [26] | Zhang Jingfan, Zhang Chengnan, Zhu Yunping, et al. Biodegradation of seven phthalate esters by Bacillus mojavensis B1811[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2018, 132: 200-207. |
| [27] |
Rahmani M, Mabrouki J, Regraguy B, et al. Adsorption of (methylene blue) onto natural oil shale: kinetics of adsorption, isotherm and thermodynamic studies[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 103 (18) : 6495-6509.
doi: 10.1080/03067319.2021.1957466 |
| [28] |
Al-Ghouti M A, Da’ana D A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review[J]. Journal of Hazard Mater, 2020, 393: 122383.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383 |
| [1] | Zilong Liu, Yanxiao Hei, Di Shi, Yufei Xiao, Xue Li. Recent advances of surfactants and their adsorption characteristics in oil recovery [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(4): 457-466. |
| [2] | Yuting Duan, Yingmiao Zhao, Sui Shen, Zhenxi Lu, Bing Liang, Jiapeng Long. Preparation and adsorption properties of porous boron nitride materials [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 273-281. |
| [3] | Shaodi Jin, Xueer Xu, Dongya Gu. Preparation and adsorption performance of tannin cured with triethylenetetramine [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 290-297. |
| [4] | Keyun Hu. Preparation and paramagnetic study of Fe3O4-based core-shell nanostructured materials [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 298-304. |
| [5] | An Rui,Zhao Qing. Progress in the adsorption of triclosan in aqueous solution [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(8): 945-953. |
| [6] | Wu Yuwen, Ma Ling, Chen Timson, Chang Kuan, Wang Jing. Scientific foundations of hair and scalp care (I) Effects of moisture on the properties of hair and the study on moisturizing efficacy [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(1): 8-15. |
| [7] | Zhao Fengtao,Li Xuanjing,Li Enze,Du Zhiping,Li Jianfeng,Shen Jing. Preparation of magnetic nano-Fe3O4 and its application in wastewater treatment [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(8): 882-891. |
| [8] | Wang Haobo,Yi Yun,Fu Chengbing,Liu Fei,Cao Jianxin,Pan Hongyan. Adsorption removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+ from industrial calcium chloride by modified kaolin [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(8): 819-826. |
| [9] | Xuan Chao,Hu Changrong,Yi Yun,Liu Fei,Cao Jianxin,Pan Hongyan. Analysis of phosphorus adsorption performance and adsorption kinetics of phosphogypsum in loess soil [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(6): 606-612. |
| [10] | Zhang Qianjie,Shen Xingliang,Sheng Taotao,Zhang Wanping,Xu Jianying. The interaction of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide-pearl powder and its stabilization of the double phase inversion in emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(5): 468-475. |
| [11] | Zhang Qin,Shi Qiuhong. Application of PoPD-TiO2-GO composite photocatalyst in adsorption and degradation of chemical dye wastewater [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(10): 1088-1093. |
| [12] | Zhi Lifei,Shi Xiufang,Zhang Erzhuang,Li Xiaoming,Wang Hui,Pan Ruili. Adsorption behaviors of didecyl quaternary ammonium salts with different counterions on polytetrafluoroethylene surface [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(8): 725-733. |
| [13] | CHEN Yue,YIN Hong-yao,SUI Xiao-yuan,FENG Yu-jun. Progress in research of the stability of polytetrafluoroethylene dispersion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(5): 457-462. |
| [14] | FU Duo-jiao,ZHOU Yin,CHEN Han-yu,LIU Hong-qin,XU Bao-cai. Advances in research and application of quaternary ammonium Gemini surfactants and their modified clay [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(4): 338-347. |
| [15] | Jin Shaodi,Gu Dongya,Shi Zhichao. Study on the preparation and adsorption properties of β-cyclodextrin/tannin composite microspheres [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(10): 969-974. |
|