


日用化学工业(中英文) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 508-515.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-2806.2025.04.013
杨武成1,3,谢宇1,2,魏剑1,2,范瑞芳3,*( ),谭建华1,2,*(
),谭建华1,2,*( ),席绍峰1,2
),席绍峰1,2
收稿日期:2024-05-08
修回日期:2025-03-27
出版日期:2025-04-22
发布日期:2025-04-28
基金资助:
Wucheng Yang1,3,Yu Xie1,2,Jian Wei1,2,Ruifang Fan3,*( ),Jianhua Tan1,2,*(
),Jianhua Tan1,2,*( ),Shaofeng Xi1,2
),Shaofeng Xi1,2
Received:2024-05-08
Revised:2025-03-27
Online:2025-04-22
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要:
在皮肤研究领域,共聚焦拉曼光谱是一项新兴的分析技术。它可以用于皮肤生理学分析,获得有关皮肤分子组成和结构的数据,并且该技术还具有高空间分辨率、非侵入性以及无需提前对目标物质进行标记(如使用荧光染料标记)的优点。基于以上优点,这项技术具有成为实验室标准化分析技术的巨大潜力。但共聚焦拉曼光谱技术目前仍处在一个不断发展和完善的阶段,文章介绍了共聚焦拉曼光谱的原理,重点强调了该技术的优点,并概述了共聚焦拉曼光谱技术在皮肤研究,特别是皮肤屏障功能和活性物质经皮吸收研究中的应用。同时分析了共聚焦拉曼光谱的局限性,并展望了共聚焦拉曼光谱的未来发展趋势。
中图分类号:
杨武成, 谢宇, 魏剑, 范瑞芳, 谭建华, 席绍峰. 共聚焦拉曼光谱在皮肤屏障功能评估和经皮吸收研究中的应用[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2025, 55(4): 508-515.
Wucheng Yang, Yu Xie, Jian Wei, Ruifang Fan, Jianhua Tan, Shaofeng Xi. Application of confocal Raman spectroscopy in the evaluation of skin barrier function and permeability[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2025, 55(4): 508-515.
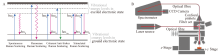
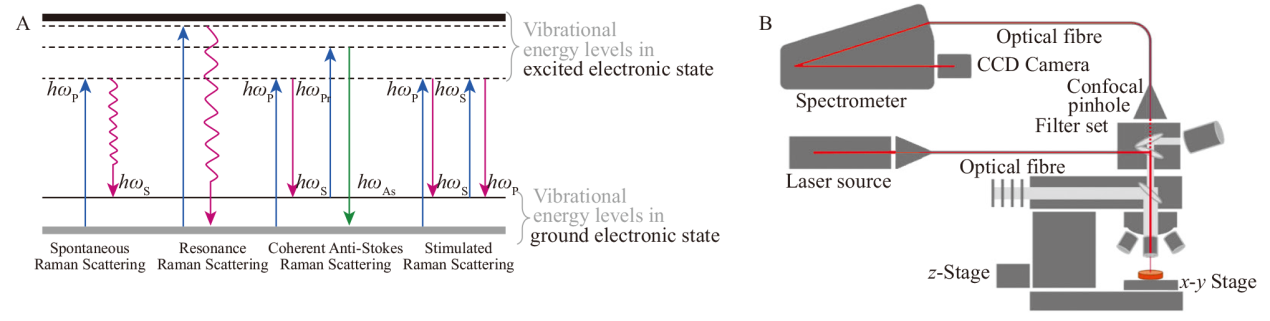
图1
不同类型散射能级示意图(A);共聚焦拉曼光谱成像原理示意图,红线表示激光通路以及收集拉曼散射的过程(B)[10,12] hωp:激发光子;hωs:斯托克斯光子;hωAs:反斯托克斯光子;Vibrational energy levels in excited electronic state:激发态的振动能级;Spontaneous Raman scattering:自发拉曼散射;Resonance Raman scattering:共振拉曼散射;Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS):相干反斯托克斯拉曼散射;Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS):受激拉曼散射;Laser source:激光器;Optical fibre:光纤;Spectrometer:光谱仪;Filter set:过滤器;Confocal pinhole:共聚焦针孔;CCD Camera:电荷耦合器件相机"
| [1] |
Rajkumar J, Chandan N, Lio P, et al. The skin barrier and moisturization: function, disruption, and mechanisms of repair[J]. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 2023, 36(4): 174-185.
doi: 10.1159/000534136 pmid: 37717558 |
| [2] | Egawa M. Raman microscopy for skin evaluation[J]. The Analyst, 2021, 146(4): 1142-1150. |
| [3] | Bouwstra J A, Nădăban A, Bras W, et al. The skin barrier: an extraordinary interface with an exceptional lipid organization[J]. Progress in Lipid Research, 2023, 92: 101252 |
| [4] | Gorzelanny C, Mess C, Schneider S W, et al. Skin barriers in dermal drug delivery: which barriers have to be overcome and how can we measure them?[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2020, 12(7): 684. |
| [5] |
Mohammed D, Yang Q, Guy R H, et al. Comparison of gravimetric and spectroscopic approaches to quantify stratum corneum removed by tape-stripping[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2012, 82(1): 171-174.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.05.018 pmid: 22713518 |
| [6] | Ali S M, Bonnier F, Lambkin H, et al. A comparison of Raman, FT IR and ATR-FT IR micro spectroscopy for imaging human skin tissue sections[J]. Analytical Methods, 2013, 5(9): 2281-2291. |
| [7] | Perticaroli S, Yeomans D J, Wireko F C, et al. Translating chemometric analysis into physiological insights from in vivo confocal Raman spectroscopy of the human stratum corneum[J]. Biochimica Biophysica Acta, 2019, 1861(2): 403-409. |
| [8] | Brzozowski K, Matuszyk E, Pieczara A, et al. Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy in chemistry and life science-development, innovation, perspectives[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2022, 60: 108003. |
| [9] | Serebrennikova K V, Berlina A N, Sotnikov D V, et al. Raman scattering-based biosensing: new prospects and opportunities[J]. Biosensors, 2021, 11(12): 512. |
| [10] | Tancrède-Bohin E, Baldeweck T, Brizion S, et al. In vivo multiphoton imaging for non-invasive time course assessment of retinoids effects on human skin[J]. Skin Research and Technology, 2020, 26(6): 794-803. |
| [11] |
Caspers P J, Lucassen G W, Puppels G J. Combined in vivo confocal Raman spectroscopy and confocal microscopy of human skin[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2003, 85(1): 572-580.
pmid: 12829511 |
| [12] |
Sharma A, Sharma S, Zarrow A, et al. Raman spectroscopy: incorporating the chemical dimension into dermatological diagnosis[J]. Indian Journal of Dermatology, 2016, 61(1): 1-8.
doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.173978 pmid: 26955087 |
| [13] |
Franzen L, Windbergs M. Applications of Raman spectroscopy in skin research—From skin physiology and diagnosis up to risk assessment and dermal drug delivery[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2015, 89: 91-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.04.002 pmid: 25868454 |
| [14] |
Nakagawa N, Matsumoto M, Sakai S. In vivo measurement of the water content in the dermis by confocal Raman spectroscopy[J]. Skin Research and Technology, 2010, 16(2): 137-141.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0846.2009.00410.x pmid: 20456092 |
| [15] | Kourbaj G, Bielfeldt S, Seise M, et al. Measurement of dermal water content by confocal Raman spectroscopy to investigate intrinsic aging and photoaging of human skin in vivo[J]. Skin Research and Technology, 2020, 27(3): 404-413. |
| [16] | Rigal A, Michael-Jubeli R, Nkengne A, et al. Raman confocal microscopy and biophysics multiparametric characterization of the skin barrier evolution with age[J]. Journal of Biophotonics, 2021, 14(9). |
| [17] | Caspers P J, Lucassen G W, Carter E A, et al. In vivo confocal Raman microspectroscopy of the skin: noninvasive determination of molecular concentration profiles[J]. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2001, 116(3): 434-442. |
| [18] | Caspers P J, Lucassen G W, Bruining H A, et al. Automated depth-scanning confocal Raman microspectrometer for rapid in vivo determination of water concentration profiles in human skin[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2000, 31: 813-818. |
| [19] |
Wu J, Polefka T G. Confocal Raman microspectroscopy of stratum corneum: a pre-clinical validation study[J]. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2008, 30(1): 47-56.
doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2494.2008.00428.x pmid: 18377630 |
| [20] |
Egawa M, Kajikawa T. Changes in the depth profile of water in the stratum corneum treated with water[J]. Skin Research and Technology, 2009, 15(2): 242-249.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0846.2009.00362.x pmid: 19622134 |
| [21] | Egawa M, Tagami H. Comparison of the depth profiles of water and water-binding substances in the stratum corneum determined in vivo by Raman spectroscopy between the cheek and volar forearm skin: effects of age, seasonal changes and artificial forced hydration[J]. British Journal of Dermatology, 2007, 158(2): 251-260. |
| [22] | Rawlings A V, Harding C R. Moisturization and skin barrier function[J]. Dermatologic Therapy, 2004, 17: 43-48. |
| [23] | Van Mierlo M M F, Caspers P J, Jansen M S, et al. Natural moisturizing factor as a biomarker for filaggrin mutation status in a multi-ethnic paediatric atopic dermatitis cohort[J]. Clinical and Experimental Allergy, 2021, 51(11): 1510. |
| [24] | Zhang L, Cambron T, Niu Y, et al. Mcr approach revealing protein, water, and lipid depth profile in atopic dermatitis patients’ stratum corneum via in vivo confocal Raman spectroscopy[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(4): 2784-2790. |
| [25] |
Rinnov M R, Halling A S, Gerner T, et al. Skin biomarkers predict development of atopic dermatitis in infancy[J]. Allergy, 2022, 78(3): 791-802.
doi: 10.1111/all.15518 pmid: 36112082 |
| [26] | Zolotas M, Schleusener J, Lademann J, et al. Atopic dermatitis: molecular alterations between lesional and non-lesional skin determined noninvasively by in vivo confocal Raman microspectroscopy[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(19): 14636. |
| [27] |
Koppes S A, Kemperman P, Van Tilburg I, et al. Determination of natural moisturizing factors in the skin: Raman microspectroscopy versus HPLC[J]. Biomarkers, 2017, 22(6): 502-507.
doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2016.1256428 pmid: 27805415 |
| [28] | Caspers P J, Lucassen G W, Wolthuis R, et al. In vivo Raman spectroscopy of human skin: determination of the composition of natural moisturizing factor[J]. Biomedical Applications of Raman Spectroscopy, 1999, 3608: 99-102. |
| [29] |
Richters R J H, Falcone D, Uzunbajakava N E, et al. Sensitive skin: assessment of the skin barrier using confocal Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 2017, 30(1): 1-12.
doi: 10.1159/000452152 pmid: 28122376 |
| [30] | Stamatas G N, Roux P F, Boireau-Adamezyk E, et al. Skin maturation from birth to 10 years of age: Structure, function, composition and microbiome[J]. Experimental Dermatology, 2023, 32(9): 1420-1429. |
| [31] | Jacobi U, Kaiser M, Toll R, et al. Porcine ear skin: an in vitro model for human skin[J]. Skin Research and Technology, 2006, 13(1): 19-24. |
| [32] |
Ashtikar M, Matthäus C, Schmitt M, et al. Non-invasive depth profile imaging of the stratum corneum using confocal Raman microscopy: First insights into the method[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2013, 50(5): 601-608.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.05.030 pmid: 23764946 |
| [33] | Hoppel M, Baurecht D, Holper E, et al. Validation of the combined ATR-FT IR/tape stripping technique for monitoring the distribution of surfactants in the stratum corneum[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2014, 472(1/2): 88-93. |
| [34] |
Egawa M, Hirao T, Takahash M. In vivo estimation of stratum corneum thickness from water concentration profiles obtained with Raman spectroscopy[J]. Acta Dermato-Venereologica, 2007, 87(1): 4-8.
pmid: 17225007 |
| [35] | Böhling A, Bielfeldt S, Himmelmann A, et al. Comparison of the stratum corneum thickness measured in vivo with confocal Raman spectroscopy and confocal reflectance microscopy[J]. Skin Research and Technology, 2013, 20(1): 50-57. |
| [36] | Tfayli A, Piot O, Pitre F, et al. Follow-up of drug permeation through excised human skin with confocal Raman microspectroscopy[J]. European Biophysics Journal, 2007, 36(8): 1049-1058. |
| [37] |
Kourbaj G, Gaiser A, Bielfeldt S, et al. Assessment of penetration and permeation of caffeine by confocal Raman spectroscopy in vivo and ex vivo by tape stripping[J]. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2022, 45(1): 14-28.
doi: 10.1111/ics.12820 pmid: 36350131 |
| [38] | Krombholz R, Liu Y, Lunter D J. In-line and off-line monitoring of skin penetration profiles using confocal Raman spectroscopy[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13(1): 67. |
| [39] |
Mélot M, Pudney P D A, Williamson A-M, et al. Studying the effectiveness of penetration enhancers to deliver retinol through the stratum cornum by in vivo confocal Raman spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2009, 138(1): 32-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.04.023 pmid: 19401210 |
| [40] | Mateus R, Moore D J, Hadgraft J, et al. Percutaneous absorption of salicylic acid-in vitro and in vivo studies[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2014, 475(1/2): 471-474. |
| [41] | Iliopoulos F, Tang C F, Li Z, et al. Confocal Raman spectroscopy for assessing bioequivalence of topical formulations[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2023, 15(4): 1075. |
| [42] | Mohammed D, Matts P J, Hadgraft J, et al. In vitro-in vivo correlation in skin permeation[J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 31(2): 394-400. |
| [43] | Kichou H, Munnier E, Dancik Y, et al. Estimating the analytical performance of Raman spectroscopy for quantification of active ingredients in human stratum corneum[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(9): 2843. |
| [44] |
Caspers P J, Williams A C, Carter E A, et al. Monitoring the penetration enhancer dimethyl sulfoxide in human stratum corneum in vivo by confocal Raman spectroscopy[J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2002, 19(10): 1577-1580.
pmid: 12425479 |
| [45] | Caspers P J, Nico C, Bakker Schut T C, et al. Method to quantify the in vivo skin penetration of topically applied materials based on confocal Raman spectroscopy[J]. Translational Biophotonics, 2019, 1(1/2). |
| [46] | He Y, Wu W, Li J, et al. In vivo Raman spectroscopy study on the stimulation mechanism of surfactant[J]. Skin Research and Technology, 2020, 26(6): 898-904. |
| [47] | Iliopoulos F, Caspers P J, Puppels G J, et al. Franz cell diffusion testing and quantitative confocal Raman spectroscopy: in vitro-in vivo correlation[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2020, 12(9): 887. |
| [48] |
Singer S, Karrer S, Berneburg M. Modern sun protection[J]. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 2019, 46: 24-28.
doi: S1471-4892(18)30124-3 pmid: 30731327 |
| [49] | Supe S, Takudage P. Methods for evaluating penetration of drug into the skin: a review[J]. Skin Res Technol, 2020, 27(3): 299-308. |
| [50] | Wang M, Tan J, Qi Z, et al. A combined study of skin penetration by confocal Raman spectroscopy and human metabolism: a case of benzophenone-3 in sunscreen[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2023, 340: 122368. |
| [51] | Tippavajhala V K, De Oliveira Mendes T, Martin A A. In vivo human skin penetration study of sunscreens by confocal Raman spectroscopy[J]. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2017, 19(2): 753-760. |
| [52] |
Benson H a E. Assessment and clinical implications of absorption of sunscreens across skin[J]. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 2000, 1(4): 217-224.
pmid: 11702366 |
| [53] |
Dai T, Pikkula B M, Wang L V, et al. Comparison of human skin opto-thermal response to near-infrared and visible laser irradiations: a theoretical investigation[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2004, 49(21): 4861-4877.
pmid: 15584524 |
| [54] |
Ramírez-Elías M G, Alda J, González F J. Noise and artifact characterization of in vivo Raman spectroscopy skin measurements[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2012, 66(6): 650-655.
doi: 10.1366/11-06495 pmid: 22732535 |
| [55] |
Schleusener J, Carrer V, Patzelt A, et al. Confocal Raman imaging of skin sections containing hair follicles using classical least squares regression and multivariate curve resolution-alternating least squares[J]. Quantum Electronics, 2019, 49(1): 6-12.
doi: 10.1070/QEL16901 |
| [56] |
Wang H, Zhao J, Lee A M D, et al. Improving skin Raman spectral quality by fluorescence photobleaching[J]. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 2012, 9(4): 299-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2012.02.001 pmid: 23200009 |
| [1] | 赵化冰, 李颖甜, 王熙函, 黄正梅, 路福平. 皮肤微生态与微生态护肤品[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2025, 55(3): 390-398. |
| [2] | 李生鹏, 李静, 梁超, 赵冉, 张晓洁, 孙丽丽. 丝素蛋白对皮肤光损伤的保护作用[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2024, 54(9): 1117-1124. |
| [3] | 刘兆亿, 陈鑫宇, 王艳, 李雪, 郭若曦, 张晗. 氧化苦参碱对小鼠皮肤屏障功能障碍的修复作用研究[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2024, 54(7): 777-783. |
| [4] | 何一凡, 吴文海, 苏牧楠, 蒋晓龙, 刘宇红. 拉曼光谱研究表面活性剂对皮肤刺激和皮肤防护的体内分子机制[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2024, 54(4): 401-409. |
| [5] | 李惠玲, 周春霞, 章漳. 细梗蔷薇愈伤组织提取物在人真皮成纤维细胞及3D表皮模型上的护肤功效探究[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2023, 53(3): 300-307. |
| [6] | 邓梦洁, 易国斌, 吕冉, 柳亚锋, 叶大威, 陈佳志. 阿魏酸纳米醇质体的制备、表征及体外经皮吸收研究[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2023, 53(11): 1285-1292. |
| [7] | 柏玮,韩春乐,王淼,杜焕青,董凤伟,葛啸虎. 牛奶外泌体对皮肤屏障的影响研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2022, 52(9): 981-989. |
| [8] | 赵云珊,江月明,鲁文嘉,贾明明,瞿欣. 广藿香叶提取物的皮肤舒缓和修护功效研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2022, 52(8): 833-836. |
| [9] | 樊雨梅,帖航,赵海晴,苏宁,廖峰. 驴油提升皮肤屏障功能及潜在作用机制研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2022, 52(6): 626-631. |
| [10] | 帖航,吕瑜峰,张阳,徐亮,闫妍. 表皮葡萄球菌发酵提取物对人体皮肤屏障的影响[J]. 日用化学工业, 2022, 52(4): 383-389. |
| [11] | 刘娟,贾雪婷,杨丽,苏宁,张思华,朱建宇,郑洪艳. 应用共聚焦拉曼光谱法对烟酰胺在人体皮肤角质层渗透性的研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2021, 51(2): 104-108. |
| [12] | 车飙,王静,邓明高,韩萍,陈惠雄,杜志云. 柚皮苷对紫外线诱导小鼠皮肤屏障损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2020, 50(8): 560-565. |
| [13] | 刘娟,杨丽,庞建平,郑洪艳,贾雪婷,苏宁. 共聚焦拉曼光谱法在β-熊果苷经皮渗透性研究中的应用[J]. 日用化学工业, 2019, 49(7): 452-455. |
| [14] | 李潇, 张晓娥, 卢永波, 金岩. 化妆品功效评价(Ⅷ)—— 3D皮肤模型在化妆品功效评价中的应用[J]. 日用化学工业, 2018, 48(9): 489-494. |
| [15] | 卢伊娜, 杨雅迪, 谢智勇, 田军. 墨藻胶对皮肤水合及屏障功能的促进作用研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2017, 47(12): 709-712. |
|