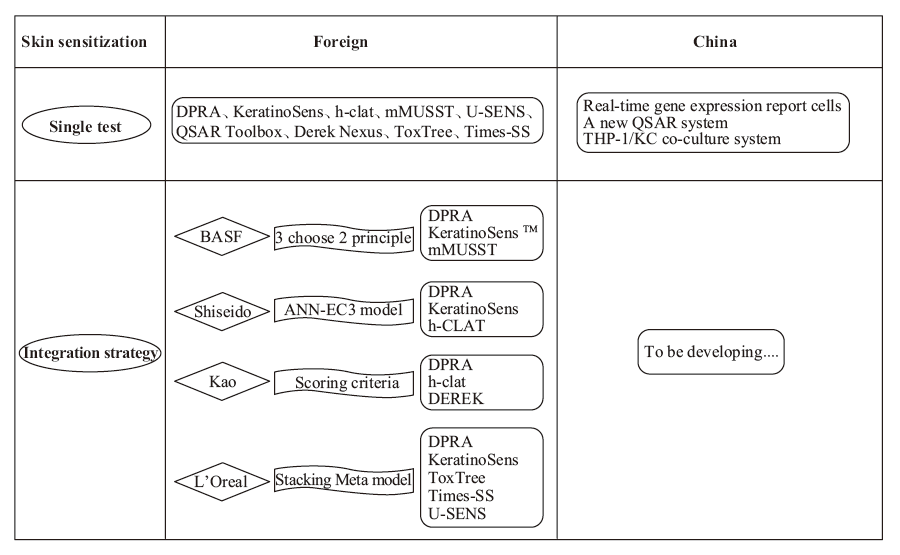
In recent years, the incidence of cosmetic skin diseases such as cosmetic contact dermatitis and cosmetic acne has been increasing significantly, and the increasingly severe safety issues of cosmetics have aroused widespread concern in the society. Therefore, the state has promulgated a series of laws and regulations to further regulate the safety of cosmetics, and the enterprises must also carry out sufficient safety evaluation and risk substance evaluation on cosmetics raw materials and finished products. Skin sensitization is one of the toxicological end points of cosmetic safety evaluation. Although traditional animal experiments can meet the requirements of skin sensitization testing, they do not comply with the 3R principle. The European Union has imposed a total ban on animal testing of cosmetic ingredients and on the sale of cosmetic ingredients and finished products tested on animals. Therefore, alternative methods have gradually replaced animal experiments as an important tool for cosmetic safety evaluation. At present, the alternative methods that have certified by OECD mainly include direct peptide reaction test, KeratinoSensTM test, human cell line activation test and so on. However, a single substitution test is usually insufficient to accurately determine the skin sensitization of a compound. Therefore, different single experimental results are often combined according to the AOP pathway into an integrated strategy to comprehensively determine the skin sensitization of compounds, so as to improve the prediction accuracy. At present, the existing integrated strategies are mainly developed by BASF, L ’Oreal, Shiseido and other industries, including the ‘2 out of 3’ principle, stacking Meta model, ANN-EC3 model, etc. Due to the late introduction of animal alternative methods in China, domestic cosmetic companies and institutions have not yet developed their own integrated models, but we are working hard to develop new skin sensitization alternative technologies, such as the construction of real-time gene expression reporter cells, the development of new QSAR computer system and the construction of THP-1/KC co-culture system. Good results have been achieved in these new technologies. This paper summarizes and expounds the integrated strategies and methods of skin sensitization test currently used by daily chemical related enterprises, and summarizes the development status of self-developed skin sensitization alternative methods in China.