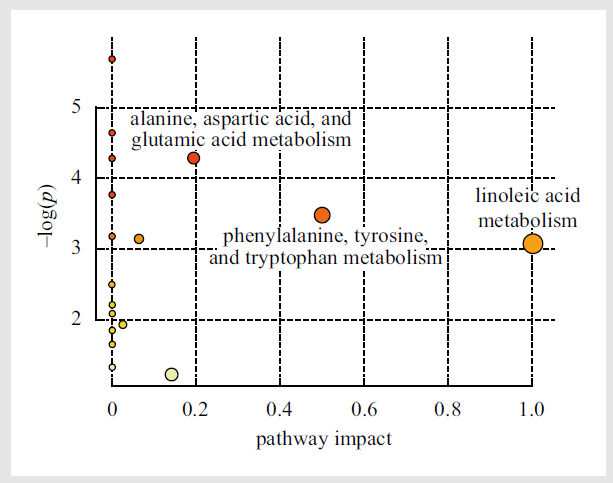
The aim of the study was to explore the anti-aging effect and physiological mechanism of Camellia seed oil and Camellia emollient oil on the skin of D-galactose-induced aging mice. The skin tissues of mice in normal group, model group, Camellia seed oil group, Camellia emollient oil group and vitamin E group (positive control) were analyzed by gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOF/MS). After obtaining the data, the multidimensional statistical method was used to analyze the data and to mine the biological information. The data were analyzed by the mathematical model of principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal projections to latent structures discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), and the differential metabolites were determined by the indices of variable importance in the projection (VIP) andp value. The differential metabolites which were filtered out were substituted into the MetaboAnalyst platform, and the important metabolic pathways involved were screened by indices of pathway impact and p value. The analysis of differential metabolites shows that the differential metabolites between normal group and model group are propionic acid, linoleic acid, aminomalonic acid, aspartic acid, tyrosine, succinic acid, stearic acid, alanine and proline; the differential metabolite between model group andCamellia seed oil group is palmitic acid; the differential metabolites between model group and Camelliaemollient oil group are propionic acid, succinic acid, aminomalonic acid, stearic acid, fumaric acid, proline, linoleic acid and alanine; the differential metabolites between model group and vitamin E group are propionic acid, succinic acid, aminomalonic acid, stearic acid, linoleic acid, aspartic acid, proline and phosphoric acid. Camellia seed oil and Camellia emollient oil can regulate the metabolism disorder of the skin of D-galactose-induced aging mice. From the perspective of the number of differential metabolites, Camellia emollient oil is better than Camelliaseed oil, close to vitamin E in the anti-aging effect of skin. Metabolic pathway analysis indicates three major metabolic pathways: alanine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid metabolism, phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan metabolism, and linoleic acid metabolism. Through further analysis, it is speculated that the effect of Camellia emollient oil andCamellia seed oil may be related to the regulation of oxidative stress. This research result may provide a reference for further study revealing the anti-aging mechanism of Camellia oil.