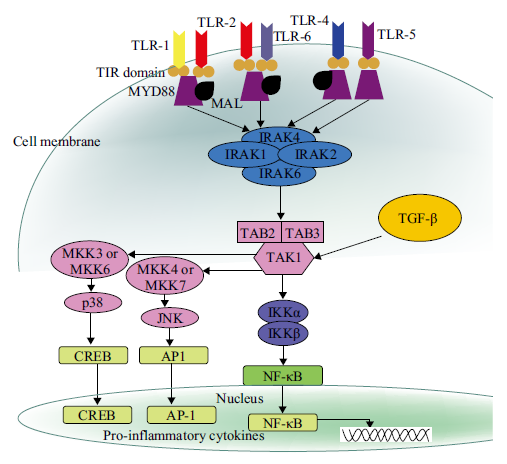
The recent literature has been reviewed from the signal transduction and related factors of oral ulcers to provide theoretical reference for the research and treatment thereof. The pathogenic mechanism of oral ulcers is complex, involving immune abnormalities, trauma, excessive fatigue, hormone changes, vitamin deficiency, genetic factors, etc. Common manifestations include oral candidiasis, recurrent aphthous ulcers, or cancer patients with radiation or drug treatment, which have resulted in mucosal ulcers that greatly affect the life quality of patients. The pathogenic mechanism of oral ulcers involves many inducing factors and signal pathways. The composition and content of factors, such as external signal factors, immune factors of the body, receptor molecules on the cell surface, and intracellular signal transmission, as well as the changes in their related signal pathways, have played different roles in the development and healing process of oral ulcers. In this review, NF-κB and TNF-α have been discussed a lot. This review combines recent reports in the literature, from the aspects of TGF-β, Smad7, FOXO1, TNF-α, IL-17, NO and ROS, JNK, targeted therapy drugs, immune checkpoint inhibitors, etc. Thus the current research progress of related factors and signal pathways in causes and repair mechanisms of oral ulcers has been reviewed. IL-6, IL-8, COX-2, TLRs, Dectine-1, p38 MAPK, etc. are interspersed in relevant introductions. By analyzing the possible connections between them, it is found that a balance between inflammation and tissue repair is needed to promote oral ulcer healing. For example, ROS/NO aggravates inflammation through PGE2, but it promotes cell proliferation and migration through JNK/TGF-β pathway for repair. TNF-α promotes the production of various inflammatory factors by T cells, and yet it promotes the synthesis of collagen and MMPs through the JNK/c-Jun pathway to help tissue repair. Smad7 and IL-17 are involved in inhibiting inflammation and promoting cell secretion of antibacterial substances. Targeted therapies or immune checkpoint inhibitors that act on a single target mostly cause oral inflammation in patients to varying degrees. Therefore, balancing the immune system may be the future direction of research for oral ulcer drugs.