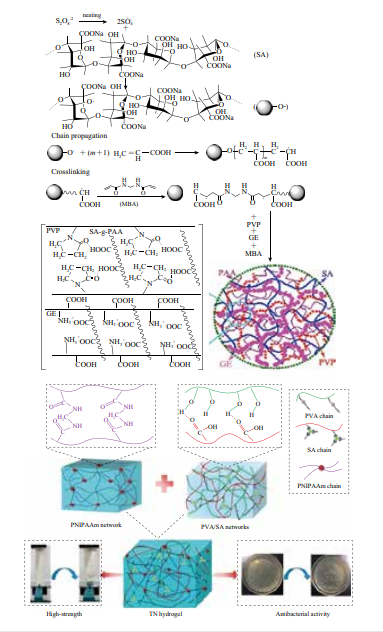
Sodium alginate is a kind of typical, widely used, pH-sensitive functional marine polysaccharide, which is extracted from the abundant seaweed in ocean. Sodium alginate is composed of β-D-mannuronic acid (M) and α-L-gulonic acid (G) linked by 1 → 4 glycosidic bonds and can be chemically modified due to the presence of reactive hydroxyl group, carboxyl group and glucosidic bond in the molecular structure, via oxidation, reductive amination, sulfation, copolymerization of hydroxyl group, esterification, Ugi reaction, amidation of carboxyl group, and degradation of glucosidic bond. For possessing many excellent properties including non-toxic, water-soluble, biocompatible, biodegradable, film-forming, gelling, thickening, anti-allergy, flocculation, chelation, plant growth promotion and flame retardant, sodium alginate and its derivatives, composites and blends have been extensively studied and applied in food, medicine, cosmetics, textile printing and dyeing, water treatment, agriculture, functional materials and other industrial fields. Herein, the name, source, structure, physical and chemical properties and conventional production methods of sodium alginate, and the current application status of sodium alginate and sodium alginate-based materials were introduced. The research trend and development prospect of this valuable natural marine biomass material were also pointed out.