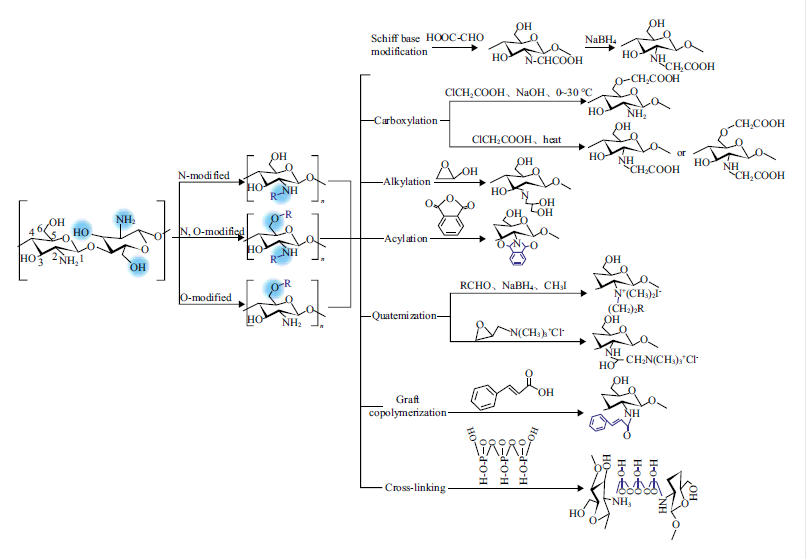
Chitin is the second most abundant naturally occurring biological material after cellulose, as well as the unique alkaline polysaccharide in nature. Chitin, and its deacetylated derivative, chitosan, i.e., a linear copolymer of β-(1→4)-linked 2- acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranose and 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranose, offer an excellent set of characteristics as functional materials: biocompatibility, biodegradability to harmless products, high bioavailability, nontoxicity, physiological inertness, antibacterial properties, heavy metal ions chelation, gel forming properties and hydrophilicity, and remarkable affinity to protein and tissue. Due to the presence of amino, hydroxyl, acetyl amino groups and glycosidic bonds in the molecules of chitin and chitosan, many special functional derivatives can be produced by schiff base modification, carboxylation, alkylation, acylation, quaternization, graft copolymerization, cross-linking, and degradation. Owing to these unique characteristics and excellent functions, chitin, chitosan and their derivatives have been widely used in various industrial fields, such as pharmaceutical industry, environmental protection, textile printing and dyeing, paper making, food, tissue engineering, enzyme immobilization, and daily-use chemical industries. Herein, the name, structure and origin of chitin and chitosan, as well as the conventional production methods, physical and chemical properties and current application status of chitin, chitosan and their derivatives, were introduced.