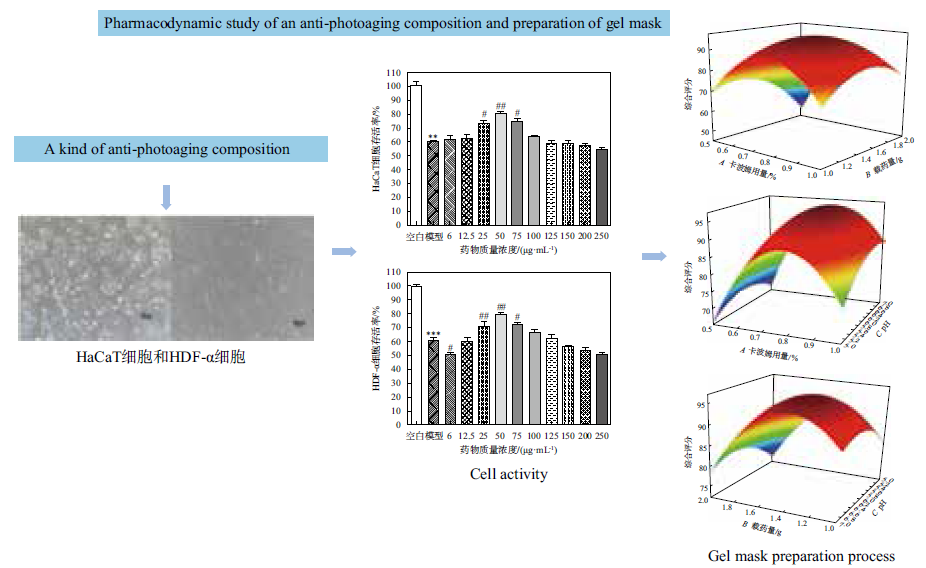
Ginsenosides, velvet antler peptides, sodium hyaluronate and cod collagen are used to make a composition to explore its anti-aging effect and prepare a gel mask. Through ultraviolet (UVB) induced human immortalized keratinocytes (HaCaT) and human dermal fibroblasts (HDF-α) to establish a light injury model, MTT method was used to determine the effects of different concentrations of compositions on cell viability, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to determine the contents of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) in the cell supernatant. The composition was prepared into a gel mask, and the carbomer dosage, drug loading, and pH value were used as the inspection factors, and the comprehensive score of the gel mask was used as the evaluation index. The response surface method was used to screen the optimal process parameters to obtain the best preparation process for the gel mask. The test results show that compared with the blank group, the cell viability of the model group is significantly reduced (P<0.01). Compared with the model group, when the mass concentration of the composition reaches 50 μg/mL, the survival rate of HaCaT cells is 89.47%±1.81%, SOD content is (39.56±0.29) ng/mL, GSH-Px content is (41.62±0.40) ng/mL, MMP-9 content is (5.46±0.21) ng/mL. While the survival rate of HDF-α cells is 81.04%±4.09%, SOD content is (38.76±0.29) ng/mL, the content of GSH-Px is (44.28±0.05) ng/mL, and the content of MMP-9 is (4.91±0.13) ng/mL. Therefore, 50 μg/mL composition can significantly increase the activity of HaCaT cells and HDF-α cells, promote the secretion level of SOD and GSH-Px, reduce the secretion level of MMP-9, and it has a certain protective effect on HaCaT cells and HDF-α cells against light injury. Through the experimental optimization of the response surface method, the optimal process parameters of the gel mask are as follows: the dosage of carbomer is 0.6%, the drug loading is 1.3 g, and the pH=6. The gel mask prepared according to the optimal process parameters has a smooth appearance, uniformity and fineness, moderate viscosity, and good spreadability, which provides basic research for the further development of the product.