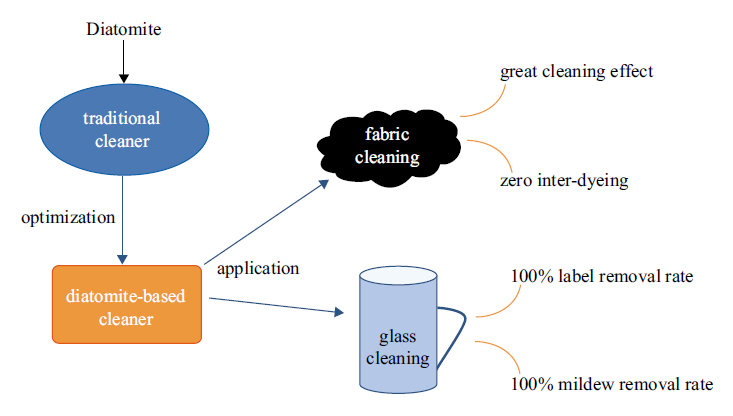
With the process of global economic integration and the development of people’s high-quality life, high-efficiency, energy-saving and multi-functional washing products are attracting more and more attention. Diatomite is a kind of biogenic siliceous sedimentary rock, mainly composed of the remains of ancient diatoms. It is loose, light, porous, water-absorbent, and strong in permeability, as well as has large specific surface area and chemically stable properties. In addition, the porous properties of diatomaceous earth can achieve functions such as humidity adjustment, dye adsorption and heavy metal ion removal. The paper introduced diatomite into traditional cleaning products, and through optimizing the types and proportions of surfactants and auxiliary materials, a new type of diatomaceous earth-based cleaning agent was prepared. Its cleaning effect and prevention of mutual dyeing, label and mildew removal and other multi-functional performance were explored. It shows that the auxiliary materials of diatomite-based cleaner need to be fine-tuned according to its different uses. Diatomite-based fabric cleaner consists of 5% diatomite, 15% AEO-9, 5% 6501, 5% AEO-7, 0.3% sodium silicate, 2% palmitic acid and 3% sodium citrate. Glass bottle cleaner comprises 5% diatomite, 15% AEO-9, 5% 6501, 5% AEO-7, 3.6% sodium silicate, 1.5% sodium sulfate, 1.8% sodium gluconate, and 7.5% sodium hydroxide. The prepared product has a good cleaning effect. In terms of fabric cleaning, the clean whiteness difference of the prepared cleaning agent on carbon black, protein and sebum stained cloth is 12.3, 3, 10.2, respectively, which are better than common cleaning products on the market, and the product can realize zero inter-dyeing of the cleaned fabric. In terms of glass cleaning, the clean whiteness difference of the prepared cleaning agent to carbon black, protein cloth is 11.26 and 4.19, respectively, which are better than common cleaning products on the market. When the temperature reaches 70 ℃, the adhesive layer on the back of the label can be effectively dissociated, and the effect is uniform. So that the label can be detached as a whole, thereby reducing secondary pollution. When the amount of cleaners is 2%, the mildew removal rate on the glass reaches 100%. The addition of diatomite improves the washing effect, dye removal and mildew removal. Diatomite can be used to formulate different cleaning agents.