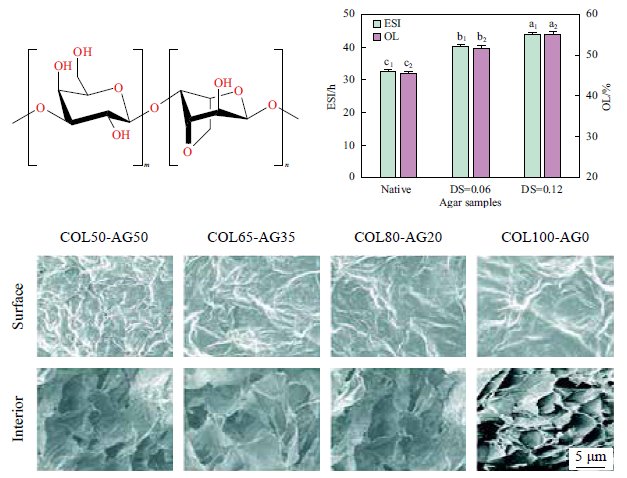
Agar is a kind of seaweed polysaccharide extracted from marine red algae, and it is also one of the most widely used algal gels in the world. Agar consists of neutral agarose and charged agaropectin, in which agarose is based on a disaccharide backbone of 1,3-linked -β-D-galactopyranose and 1, 4-linked 3, 6 anhydro-ɑ-L-galactopyranose repeating units, while agaropectin possesses molecular structure similar to that of agarose, with some sulfate groups, methoxyl groups and pyruvate groups linked to the galactopyranose in varying degrees. Due to its excellent properties such as gelling, non-toxicity, stability, thickening, transparence, suspending, shaping, as well as the more and better functions that could be obtained by the degradation, oxidization, carboxyalkylation, hydroxyalkylation and hydrophobization of the active groups including hydroxy groups and glycosidic bonds in the agar molecules, agar and its derivatives have been extensively used in food, biology, medicine, cosmetics, agriculture and other fields. Herein, the name, source and molecular structure of agar, the physical properties, conventional and improved production methods, and typical modification technology of agar, as well as the current research and application status of agar and its derivatives were introduced. The current problems, research trend and development prospect of agar and its modified products were also pointed out.