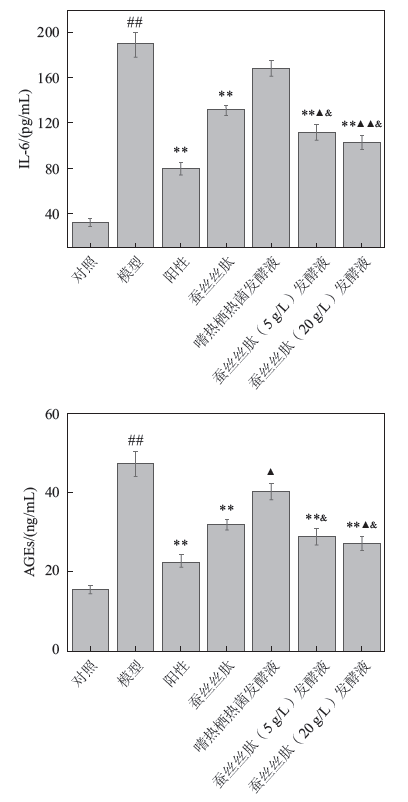
In order to study the synergistic effects of silk peptide fermented by thermophilus on skin anti- inflammatory, barrier moisturizing and anti-aging activities, silk peptides thermophilus fermentation was prepared referring to the method of microbial fermentation, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -induced keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) -induced fibroblasts (HDF cells) were used as research models. The inhibition rates of cell proliferation, the contents of interleukin 1β (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6), aquaporin 3 (AQP3), filaggrin (FLG), superoxide dismutase (SOD), advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs) and human collagen I alpha 1 (COL-1) were detected by colorimetric assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), et al. The results show that silk peptide fermentation can significantly reduce the expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and AGEs, and can significantly promote the expression of FLG, AQP3, SOD and COL-1. Especially the silk peptide fermentation can more significantly inhibit the expression of IL-6 and AGEs, and can more significantly promote the migration of HDF cells and SOD synthesis than the single silk peptide. And also the silk peptide fermentation can more significantly reduce the expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and AGEs, and can more significantly promote the expression of AQP3, HDF cell migration and SOD synthesis than the single fermentation of thermophilic bacteria. Compared with the single silk peptide and the fermentation of thermophilus, the silk peptide fermentation has obvious synergistic effects of anti-inflammatory, barrier moisturizing and anti-aging activities.