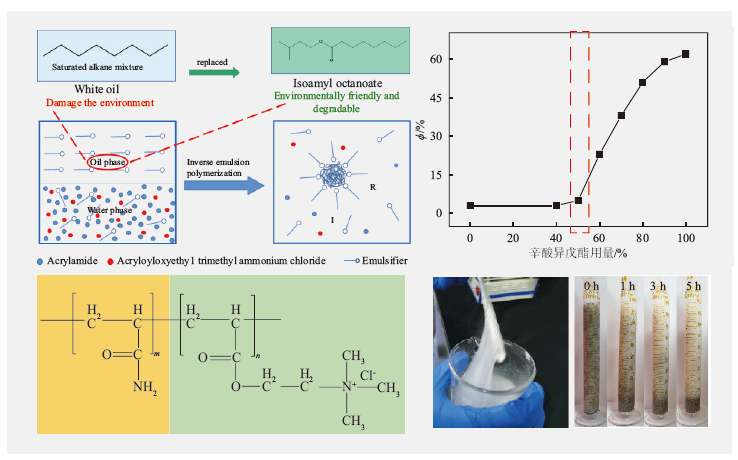
In the process of inverse emulsion polymerization, white oil, which is a mixture of saturated paraffins, is usually used as the oil phase, but white oil will pollute the environment during the process of use. In this work,W/O-type poly(acrylamide-acryloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) (P(AM-DAC)) was synthesized by inverse emulsion polymerization. A biodegradable compound, isoamyl octanoate, was used to replace part of the white oil as mixed oil phase, and acrylamide (AM) and acryloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DAC) were monomers. The structure of P(AM-DAC) was characterized by 1H NMR, FT-IR and SEM. The effects of the dosages of emulsifier and isoamyl octanoate on the stability, viscosity and interfacial tension of the pre-emulsion were studied, and the effects of initiator dosage and reaction temperature on the viscosity of aqueous P(AM-DAC) solution were investigated. The results showed that, when the dosage of emulsifier was 10%, the dosage of isoamyl octanoate was 50%, the initiator dosage was 0.8%, and the reaction temperature was 38 ℃, the viscosity of aqueous P(AM-DAC) solution reached the maximum value of 129 mPa·s. The properties of P(AM-DAC) were compared with that of poly(acrylamide-acryloxyethyl trimethylammonium chloride) synthesized by using white oil as oil phase (P(AM-DAC)-W). The viscosity-average molecular weights of P(AM-DAC) and P(AM-DAC)-W were 5.019×106 and 5.045×106, respectively. The viscosities of 1% aqueous solutions were 129 and 132 mPa·s, respectively. When the mass concentration of Na+ was3 000 mg/L, the viscosities of 1% aqueous solutions were 65 and 67 mPa·s, respectively. After continuous shear at 90 ℃ and 170 s-1 for 45 min, the viscosities of 1% aqueous solutions were 36.9 and 43.1 mPa·s, respectively. The settling velocities of ceramsite in 1% aqueous solutions were 0.049 and 0.053 mm/s, respectively. The surface tension of the gel-breaking fluids was 27.8 and 28.9 mN/m, respectively. The residue contents were 1.63 and 1.76 mg/L, respectively. Therefore, partial substitution of white oil by isoamyl octanoate in the preparation of the thickening agent for fracturing fluid is feasible, without any negative influence on the thickening performance, salt resistance, temperature resistance, shear resistance, sand carrying, gel breaking and residue content.