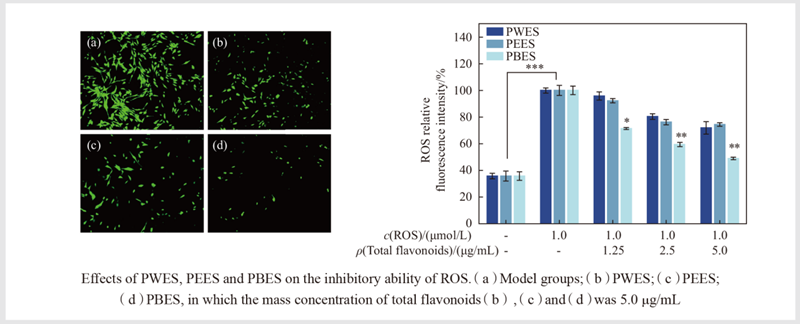
Using an aqueous 1,4-butanediol solution as the solvent combined with ultrasonic-assisted extraction, total flavonoids from Platycladus orientalis leaves were extracted. The extraction process was optimized using response surface methodology with the yield of total flavonoids, quercitrin, and myricitrin as the evaluation indicators. The optimized extraction conditions are as follows: 40 wt% 1,4-butanediol, extraction temperature of 60 ℃, extraction time of 60 min, and solid-to-liquid ratio of 1∶10(g∶mL). Under these optimized conditions, the yield of total flavonoids is 50.74 mg/g, while the yields of quercitrin and myricitrin are 3.65 mg/g and 2.10 mg/g, respectively. Compared with water and ethanol extraction, the stability of the extract is significantly improved. Furthermore, the efficacy of the 1,4-butanediol-extracted Platycladus orientalis leaf extract on human dermal papilla cells (HDPCs) was evaluated in comparison with the extracts obtained using traditional solvents (water and ethanol). Cell viability, changes in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the cell culture supernatant, as well as the inhibitory effects on intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the inflammatory factor IL-6 were measured. The results indicate that, compared with the extracts obtained using water or ethanol, the 1,4-butanediol extract more effectively promotes the proliferation of HDPCs and enhances VEGF secretion. It also demonstrates significantly stronger inhibition of ROS and IL-6, suggesting its potential efficacy in promoting hair growth, as well as in scalp antioxidant and anti-inflammatory applications.