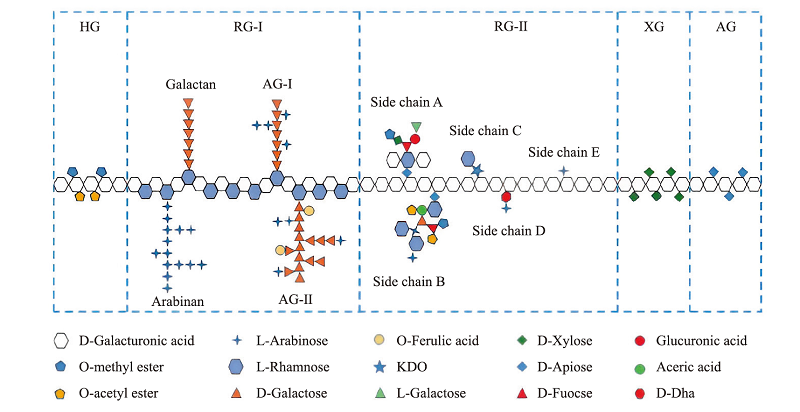
Pectin is a kind of natural hydrophilic colloid with complicated composition and structure, which has been abundantly found in the cells of higher plants. Pectin has good water solubility, stability, gelling ability and emulsifying ability, as well as safety and non-toxicity, good biocompatibility, biodegradability, and many excellent biological activities such as lowering cholesterol, anti-tumor, anti-oxidation, and lowering blood sugar. Moreover, both its physicochemical properties and functional performance can be further improved by physical, chemical and enzymatic treatments and compound modification upon the active functional groups, such as hydroxyl groups, carboxyl groups and glycosidic bonds. Therefore, pectin has been widely used in many fields, including food industry and pharmaceutical industry. Furthermore, great application potential has emerged in daily-use chemical industry, functional materials, and biodegradable biological materials. In this review, the source, chemical structure, main physicochemical properties and functional characteristics of pectin were briefly introduced. The extraction methods, separation and purification technologies, and modification methods for pectin were also systematically presented. In addition, the situation of application as well as the current problems for pectin and its modified products were summarized. Finally, some of the directions of future research and development of pectin were pointed out.