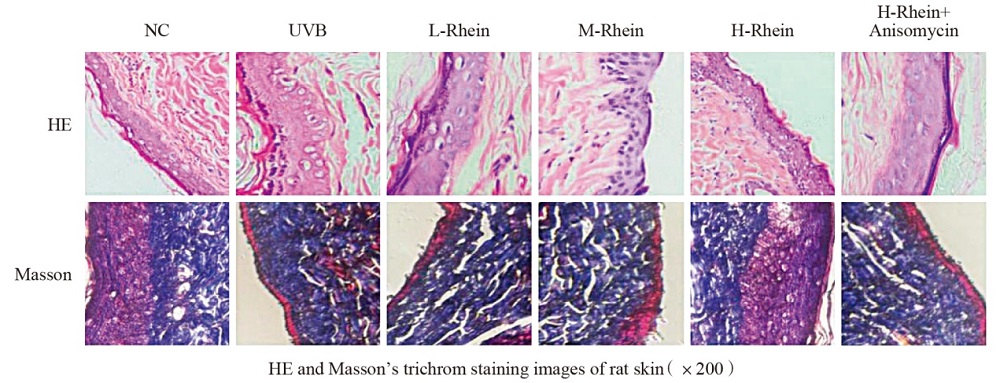
The study aimed to reveal the effect and mechanism of rhein on skin photoaging injury induced by ultraviolet B (UVB). Rats were divided into 6 groups: normal control group (NC), UVB group, low dose Rhein group (L-Rhein), medium dose Rhein group (M-Rhein), high dose Rhein group (H-Rhein) and high dose Rhein+p38 MAPK agonist Anisomycin group (H-Rhein+Anisomycin). Rats in the NC group were shaved without irradiation, while the other groups were irradiated with UVB. In this study, the administration route of rhein was oral administration. Rats were treated for 8 weeks. After treatment, the body weight, water content of epidermis and the levels of oxidative stress indexes (SOD, CAT, GSH-Px and MDA) in skin tissue were measured, and the skin tissue was stained with HE staining and Masson trichrome staining, and the volume fraction of collagen (CVF) was calculated. The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, MMP-1, MMP-3 and Collagen Ⅰ mRNA in skin tissue were detected by RT-qPCR. The protein levels of p-p38 MAPK and p38 MAPK in skin tissue were detected by Western blotting. The results show that compared with UVB group, the phosphorylation level of p38 MAPK in L-Rhein group, M-Rhein group and H-Rhein group decreases, the water content of epidermis increases, the skin injury is alleviated, CVF increases, the relative expression of MMP-1 and MMP-3 mRNA decreases, the relative expression of Collagen Ⅰ mRNA increases, the level of SOD, CAT and GSH-Px increassd, the level of MDA decreases, and the relative expression of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA decreases in the skin (P<0.05). Anisomycin attenuates the skin protective effect of rhein (P<0.05). This study shows that rhein attenuates UVB-induced skin photoaging injury by inhibiting p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Therefore, Rhein may be a candidate natural drug for the prevention and treatment of skin photoaging.