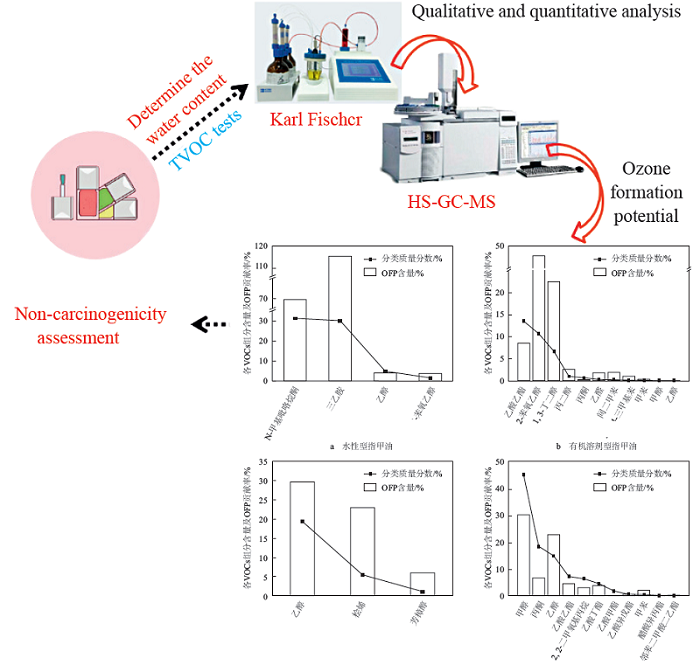
VOCs emission control is one of the main means to control ozone concentration at present. In recent years, the use of nail cosmetics has been increasing year by year. Since it contains more volatile solvents, it is necessary to study the emission inventory of VOCs released. This study collected 25 representative nail polish samples with a large amount of use through market research, and established a detection method for the total VOCs and VOCs emission list in different types of nail cosmetics. Firstly, a certain amount of samples were placed in an oven (105 ℃) to determine the total volatile content of the product, the Karl Fischer method was used to determine the water content, and headspace-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(HS-GC-MS) was used for qualitative and quantitative detection of VOCs. The average VOCs content of water-based nail polish, organic solvent-based nail polish, nutritional oil and nail remover are 0.314 5, 0.366 9, 0.049 6, 0.904 2 g/g, respectively. The main VOCs categories in the four types of nail cosmetics are amines (N-methylpyrrolidone, triethylamine), esters (ethyl acetate), terpenes ((±)-limonene) and alcohols (2-phenoxyethanol, methanol, ethanol). Organic solvent-based nail polishes contain a small amount of BTEX: toluene, m-xylene, and 1, 2, 4-trimethylbenzene, and the nail remover contains 18.39% acetone. According to the VOCs emission list and content in the different types nail polish, its contribution to ozone generation is calculated. The amount of O3 generated per unit mass of nail polish is 0.000 061 2~1.15 g/g, of which the O3 per unit mass of organic solvent-based nail polish has the largest contribution rate. Among the VOCs released by various types of nail cosmetics, OFP contributes the most to amines, BTEX, and alcohols. Among them, BTEX has high reactivity and contributes greatly to O3. Based on respiratory exposure, the non-carcinogenic hazard quotient (HQ) of VOCs in nail cosmetics to human health is calculated in the range of 6.66×10-6-8.64×10-4, and the hazard index (HI)<1. The health risk assessment results show that there is no non-carcinogenic risk to adult women. This study provides basic data for the control of the VOCs emission of nail cosmetic products.