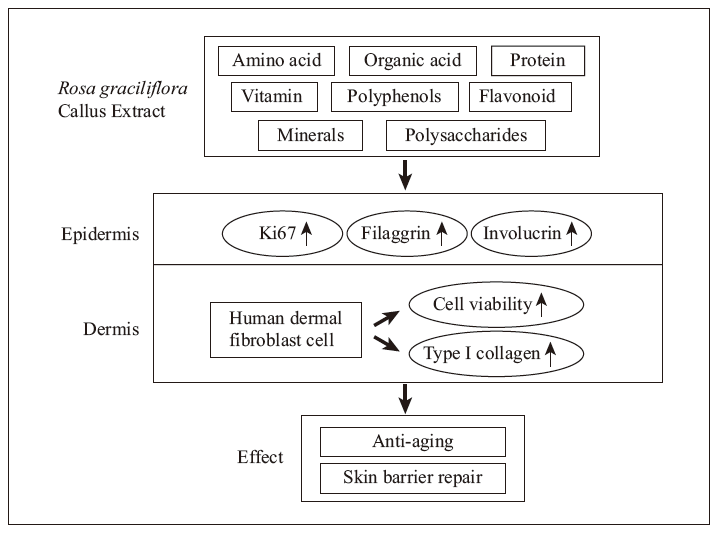
The Rosa graciliflora callus was induced from seedling leaves by plant tissue culture, and the Rosa graciliflora callus extract (RCE) was obtained by ultrasonic extraction and lyophilization. To investigate the active component of RCE and its skin care efficacy in vitro, the contents of amino acids, vitamins and organic acids were detected by LC-MS, and the effect of RCE on skin was evaluated by normal human dermal fibroblast (HDF) cells and 3D epidermal model. Cells viabilities and the content of collagen I (Col-I) were detected in HDF cells to evaluate the skin anti-aging function and the immunohistochemical staining (Ki67) and immunofluorescence staining (Filaggrin and Involucrin) were detected in 3D epidermal model to evaluate the skin barrier function of RCE. The results show that 4.27%±0.23% RCE powder can be obtained by ultrasonic extraction and lyophilization. In addition, LC-MS results show that RCE contained 3.88% amino acids, 0.003 5% vitamins, and 1.04% organic acids, and other experimental results show that RCE also contained 6.20% minerals, 43.80% sugar, 10.00% protein, 1.37% polyphenols, 14.6% ash and 21.90% water. Furthermore, cells assay results show that RCE can significantly promote HDF cells viability and type I collagen content. Compared with the blank control, 0.01% and 0.05% RCE can increase type I collagen content by 83% and 79%, respectively (P<0.01), with the effect similar to the positive control vitamin C. Moreover, in the reconstructed 3D epidermal model assay, compared with the results of the model group, 0.01% RCE can significantly up-regulate the expression of Ki67, Filaggrin and Involucrin, the relative positive rates of Ki67, Filaggrin and Involucrin are increased by 308%, 853% and 349%, respectively, and the fluorescence intensities of Filaggrin and Involucrin are increased by 824% and 159%, respectively. The results indicate that RCE has the potential effect of anti-aging and improving skin barrier function and is expected to be used as a green raw material in cosmetics.