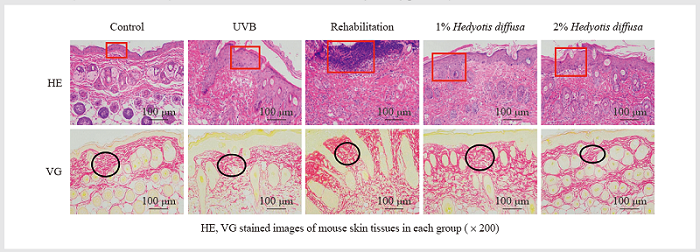
The paper aimed to study the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Hedyotis diffusa extract on mice with ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced solar dermatitis. KM mice were subjected to UVB irradiation for 7 days, which were also treated with topical application of 1% and 2% Hedyotis diffusa extract. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, and picric acid-acidic magenta method (VG) staining were performed to observe the state of mouse skin. The levels of oxidative stress indicators NOS, NO, T-SOD, and inflammation indicators TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β were detected by biochemistry and immunohistochemistry, and the mRNA or protein levels of Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, NF-κB, HMGB1 and p65 were detected by qRT-PCR and western blotting in skin tissues. Compared with the UVB group, the degree of skin damage in mice in the 1% and 2% Hedyotis diffusa extract groups is improved, with collagen fibers aligned, collagen density increased, NOS and NO levels decreased, T-SOD levels increased, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β expression levels decreased, mRNA expression levels of Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1, NQO1, and GCLC in skin tissue increased, NF-κB, HMGB1 mRNA expression levels decreased, the relative protein expression levels of Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, and p65 in skin tissues increased, and the protein expression level of HMGB1 decreased. It can be seen that Hedyotis diffusa extract can ameliorate UVB-mediated solar dermatitis in mice, and its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanism may be related to Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathway.