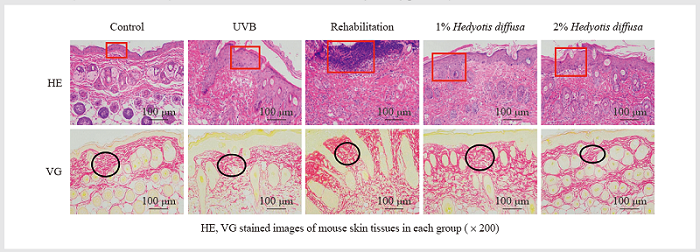
研究白花蛇舌草提取液对紫外线B(UVB)诱导的日光性皮炎小鼠的抗氧化和抗炎作用。使用KM小鼠进行UVB照射7天,同时外涂质量分数1%和2%的白花蛇舌草提取液进行治疗。对小鼠皮肤组织进行苏木精-伊红染色(HE)染色、苦味酸-酸性品红法(VG)染色观察小鼠皮肤状态。通过生化和免疫组化检测皮肤组织中氧化应激指标NOS、NO、T-SOD以及炎症指标TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β水平,通过qRT-PCR和Western blotting检测皮肤组织中Nrf2、Keap1、HO-1、NQO1、GCLC、NF-κB、HMGB1、p65的mRNA或蛋白表达水平。结果表明,与UVB组对比,白花蛇舌草提取液1%组和2%组小鼠皮肤损伤程度有所改善,胶原纤维排列整齐,胶原密度升高,NOS、NO水平降低、T-SOD水平提高,TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β表达水平降低,皮肤组织中Nrf2、Keap1、HO-1、NQO1、GCLC的mRNA表达水平升高,NF-κB、HMGB1 mRNA表达水平降低,皮肤组织中Nrf2、Keap1、HO-1、NQO1、GCLC、p65的蛋白相对表达量升高,HMGB1的蛋白表达水平降低。可见,白花蛇舌草提取液可以改善UVB介导的小鼠日光性皮炎,其抗氧化抗炎机制可能与Nrf2和NF-κB信号通路有关。
The paper aimed to study the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Hedyotis diffusa extract on mice with ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced solar dermatitis. KM mice were subjected to UVB irradiation for 7 days, which were also treated with topical application of 1% and 2% Hedyotis diffusa extract. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, and picric acid-acidic magenta method (VG) staining were performed to observe the state of mouse skin. The levels of oxidative stress indicators NOS, NO, T-SOD, and inflammation indicators TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β were detected by biochemistry and immunohistochemistry, and the mRNA or protein levels of Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, NF-κB, HMGB1 and p65 were detected by qRT-PCR and western blotting in skin tissues. Compared with the UVB group, the degree of skin damage in mice in the 1% and 2% Hedyotis diffusa extract groups is improved, with collagen fibers aligned, collagen density increased, NOS and NO levels decreased, T-SOD levels increased, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β expression levels decreased, mRNA expression levels of Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1, NQO1, and GCLC in skin tissue increased, NF-κB, HMGB1 mRNA expression levels decreased, the relative protein expression levels of Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, and p65 in skin tissues increased, and the protein expression level of HMGB1 decreased. It can be seen that Hedyotis diffusa extract can ameliorate UVB-mediated solar dermatitis in mice, and its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanism may be related to Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathway.