


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 457-467.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2022.05.001
• Basic research • Next Articles
Dong Leilei1,Huang Tianyi1,Duan Guolan1,Chen Hanjun1,Zhang Wanping2,3,Zhang Qianjie2,3,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-26
Revised:2022-04-24
Online:2022-05-22
Published:2022-05-24
Contact:
Qianjie Zhang
E-mail:zhangqj_sit@126.com
CLC Number:
Dong Leilei,Huang Tianyi,Duan Guolan,Chen Hanjun,Zhang Wanping,Zhang Qianjie. Effects of rheological modifiers on the rheological properties and stability of W/O emulsions[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(5): 457-467.
Tab. 2
Stability of W/O emulsions with different mass fractions of xanthan gum"
| 储存条件 | 稳定性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.05% | 0.10% | 0.15% | 0.20% | ||
| 室温 | 1天 | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ |
| 7天 | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| 低温 | 1次循环 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 2次循环 | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 3次循环 | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 高温 | 1天 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 3天 | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 7天 | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | |
Tab. 3
Stability of W/O emulsions with different mass fractions of sodium hyaluronate"
| 储存条件 | 稳定性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.05% | 0.10% | 0.15% | 0.20% | ||
| 室温 | 1天 | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ |
| 7天 | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| 低温 | 1次循环 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 2次循环 | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 3次循环 | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 高温 | 1天 | ++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ |
| 3天 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| 7天 | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
Tab. 5
Stability of W/O emulsions with different mass fractions of dimethyldistearyl ammonium lithium montmorillonite"
| 储存条件 | 稳定性 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.30% | 0.60% | 0.90% | ||
| 室温 | 1天 | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ |
| 7天 | ++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | |
| 低温 | 1次循环 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 2次循环 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| 3次循环 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| 高温 | 1天 | ++++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ |
| 3天 | +++ | +++++ | +++++ | +++++ | |
| 7天 | ++ | +++++ | ++++ | ++++ | |
Fig. 5
Viscosity change curves of W/O emulsions with different water-soluble polymers and oil-phase thickeners: (a) single water phase after adding xanthan gum; (b) W/O emulsions after adding xanthan gum; (c) single water phase after adding sodium hyaluronate; (d) W/Oemulsions after adding sodium hyaluronate; (e) W/O emulsions after adding glyceryl behenate; (f) W/O emulsions after adding dimethyldistearyl ammonium lithium montmorillonite"
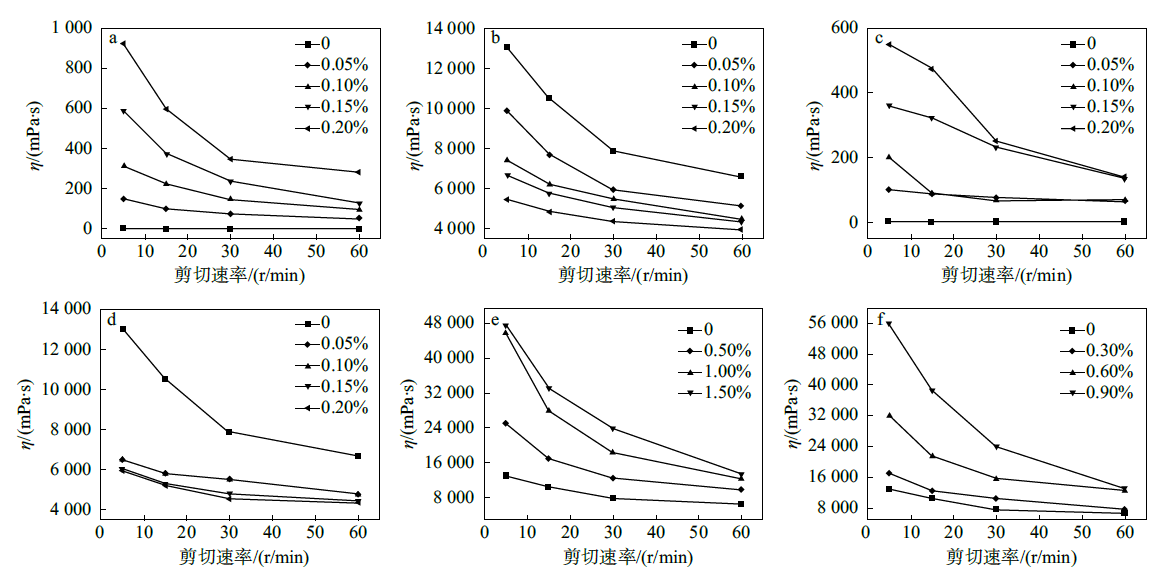
Fig. 6
Thixotropy of W/O emulsions with different water-soluble polymers (a) and oil-phase thickeners (b): A for blank W/O emulsions without rheological regulators; B for adding 0.15% xanthan gum into the W/O emulsions; C for adding 0.15% sodium hyaluronate into W/O emulsions; D for adding 1.00% glyceryl behenate into W/O emulsions; E for adding 0.60% dimethyldistearyl ammonium lithium montmorillonite into W/O emulsions"
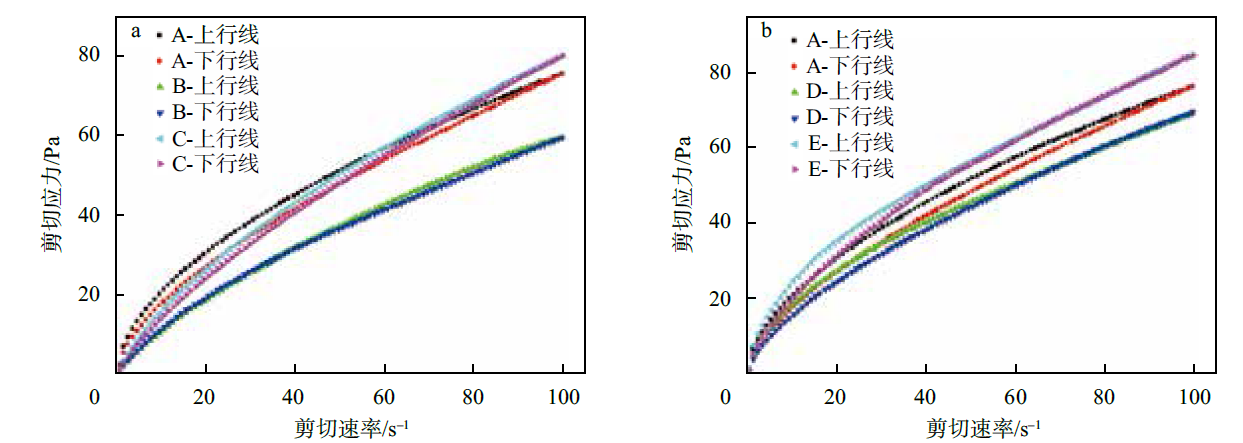
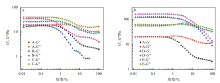
Fig. 7
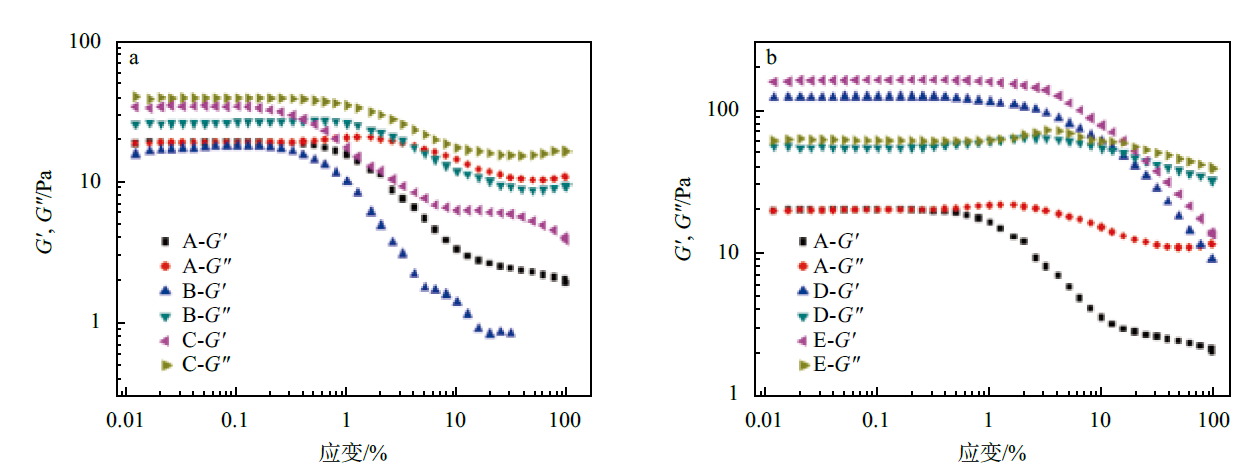
Elastic modulus (G') and viscous modulus (G'') of W/O emulsions with different water-soluble polymers (a) and oil-phase thickeners (b) at different strain: A for blank W/O emulsions without rheological regulators; B for adding 0.15% xanthan gum into W/O emulsions; C for adding 0.15% sodium hyaluronate into W/O emulsions; D for adding 1.00% glyceryl behenate into W/O emulsion; E for adding 0.60% dimethyldistearyl ammonium lithium montmorillonite into W/O emulsions"
| [1] |
Wang L, Gao J, An Z, et al. Polymer microsphere for water-soluble drug delivery via carbon dot-stabilizing W/O emulsion[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54 (4832): 5160-5175.
doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-03197-7 |
| [2] | Cao Y, Jin Y, Li J, et al. Effects of emulsion properties on demulsification of the phosphoric acid-tributyl phosphate (W/O) emulsion by hydrocyclone[J]. Separation Science & Technology, 2019, 55 (4): 1-11. |
| [3] | Gomes A, Costa A L R, Cunha R L. Impact of oil type and WPI/Tween 80 ratio at the oil-water interface: Adsorption, interfacial rheology and emulsion features[J]. Colloids & Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2018, 164: 272-280. |
| [4] |
Kumar N, Mandal A. Surfactant stabilized oil-in-water nanoemulsion: stability, interfacial tension, and rheology study for enhanced oil recovery application[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32 (6): 6452-6466.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b00043 |
| [5] |
Sasaki K, Kitajima M, Nishii K, et al. Novel W/O emulsion prepared in a water/isohexadecane/organoclay system and its application to skincare products[J]. Journal of Society of Cosmetic Chemists of Japan, 2013, 47 (1): 19-25.
doi: 10.5107/sccj.47.19 |
| [6] |
Zhang J. Movement of dispersed droplets of W/O emulsion in a uniform DC electrostatic field: Simulation on droplet coalescence[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2015, 23 (9): 1453-1459.
doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2015.07.007 |
| [7] | Liu Gangyong, Ge Hong, Zheng Gongming. Study on rheological property of W/O emollient lotion[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 120 (5): 98-101. |
| [8] |
Choi M H, Jeong S, Nam S I, et al. Rheology of decamethylceclopentasiloxane (cyclomethicone) W/O emulsion system[J]. Macromolecular Research, 2009, 17 (12): 943-949.
doi: 10.1007/BF03218640 |
| [9] |
Otsubo Y, Prud' homme R K. Rheology of oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Rheologica Acta, 1994, 33 (1): 29-37.
doi: 10.1007/BF00453461 |
| [10] | Zhang Qianjie, Duan Guolan, Zhang Wanping. Effects of the structure of emulsifiers and oils on the formation and stability of O/W/O multiple emulsions[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2020, 50 (11): 735-742. |
| [11] | Sumi T, Horikoshi S. Microwave selective heating for size effect of water droplet in W/O emulsion with sorbitan fatty acid monostearate surfactant[J]. Radiation Physics & Chemistry, 2015, 114: 31-37. |
| [12] | Su Lu, Zhang Jianghui, Dong Ming, et al. Research progress of xanthan gum and its modified products[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2020, 49 (24): 76-79. |
| [13] |
Weiss J, Herrmann N, Mcclements D J. Ostwald ripening of hydrocarbon emulsion droplets in surfactant solutions[J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15 (20): 6652-6657.
doi: 10.1021/la981739d |
| [14] |
Wei Yuanyuan, Zhang Hongbin, Ma Aiqin, et al. Rheological properties of hyaluronan thickened enteral nutritional preparations for dysphagia management[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40 (1): 50-55.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1975.tb03733.x |
| [15] |
Ribeiro H M, Morais J A, Eccleston G M. Structure and rheology of semisolid O/W creams containing cetyl alcohol/non-ionic surfactant mixed emulsifier and different polymers[J]. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2004, 26 (2): 47-59.
doi: 10.1111/j.0412-5463.2004.00190.x pmid: 18494913 |
| [16] |
Huang X B, Sun J S, Lv K H, et al. An alternative method to enhance W/O emulsion stability using modified dimer acid and its application in oil based drilling fluids[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8 (46): 26318-26324
doi: 10.1039/C8RA02293C |
| [17] | Kwon H I, In K S, Bum L S. Effects of HLB value on oil-in-water emulsions: Droplet size, rheological behavior, zeta-potential, and creaming index[J]. Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 67: 123-131. |
| [18] |
Pal R. Influence of interfacial rheology on the viscosity of concentrated emulsions[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 356 (1): 118-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.12.068 |
| [19] |
Chen Y, Liu X, Shi M. Effects of inertia on the rheology of a dilute emulsion of drops in shear[J]. Journal of Rheology, 49 (6): 1377-1394.
doi: 10.1122/1.2048748 |
| [20] | Wei Lixin, Bi Hangming, Dong Hang, et al. Influence of microstructure on rheology of W/O waxy crude oil emulsion[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2020, 49 (12): 2637-2645. |
| [21] | Fan Yue, Chen Qiang, Jin Hao, et al. Application research of rheological properties in emulsifying process conditions[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2018, 48 (10): 577-581. |
| [22] | Jiang Tong, Zhang Chen, Zhang Zhiwei, et al. Study on the relationship between rheological properties and the thickness of O/W creams[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2020, 50 (4): 227-232. |
| [23] |
Freitas G B, Duncke A C, Barbato C N, et al. Influence of wax chemical structure on W/O emulsion rheology and stability[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 558 (5): 45-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.08.008 |
| [1] | Xinyu Peng, Haiyan Liang, Zixian Wen, Meiting Li, Xin Li, Xiaofeng Qiu. Impact of rheology modifiers on Bag-on-valve spray products [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 181-187. |
| [2] | Xiaohong Pan, Ziqi Gao, Zhen Chen, Shuai Yin, Haiping Huang, Bin Hu. Discussion on the current situation of research and management on the stability of cosmetic products in China [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 201-208. |
| [3] | Yaru Wang, Tingyuan Mo, Hongxia Lai, Yue Zhou, Jiaying Xie, Jianhua Tan. Analysis of the causes of skin irritation of niacinamide cosmetics based on patch test and stability test [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 51-56. |
| [4] | Wang Huazheng, Zhang Liang, Kang Xin, Kang Wanli, Li Zhe, Yang Hongbin. Effect of CO2 on physical properties of produced oil and water in Changqing and emulsion stabilization mechanism [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(6): 617-624. |
| [5] | Zhen Enlong, Zhang Wen, Qian Zhen, Du Ruotong, Wang Yang. Construction and plugging performance evaluation of emulsified thermosetting resin system [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(6): 649-657. |
| [6] | Ding Zhengqing, Wu Yingyi, Wang Weiyun, Huang Xujuan, Cai Zhaosheng. Study on Pickering emulsion stabilized by hydroxyethyl cellulose/nanocellulose and its rheological properties [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(3): 245-252. |
| [7] | Yang Chao, Tong Zhiming, Wang Zhansheng, Chen Wu. Study on the influence mechanisms of polymers and solid particles on the stability of crude oil emulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(10): 1156-1165. |
| [8] | Guo Fang. Influence of emulsifiers and thickener on formation of low-viscosity liquid crystal emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(1): 16-23. |
| [9] | Yan Yongli,Cai Yuxiu,Dou Longlong,Cao Yuxia. Research progress in the dynamics of liquid drainage from complex foam system [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(9): 1011-1015. |
| [10] | Liang Yihuan,Du Jing. “Jelly” phenomenon rheology study and improvement in shampoo system [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(9): 920-929. |
| [11] | Mai Jingzhang,Li Lin,He Jinqing,Li Zeyong. Study on the synthesis and application of thickening-fixing hybrid rheology modifier [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(9): 960-968. |
| [12] | Xu Jie,Zhu Yuan,Xu Xiangliang,Bao Hongjie. Study on multidimensional evaluation method of foam performance of daily chemicals [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(5): 506-513. |
| [13] | Guo Hua,Xu Jin,He Yunping,Xu Hujun. Effects of potassium cocoyl hydrolyzed oat protein on the performance of the amino acid facial cleanser [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(12): 1307-1313. |
| [14] | Tang Wenjun,Wang Changyun,Xu Guiyun,Niu Qianxue,Fan Jinshi. Common cosmetic preparation technologies(Ⅵ) Preparation sharing properties of both solids and liquids: Semisolid [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(12): 1278-1285. |
| [15] | Zhang Hucheng,Yang Guowei,Yang Jun,Fan Haitao,Luo Shuai,Liu Linying. Preparation of cordycepin nanoemulsion and its repair mechanism on the photoaged skin [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(10): 1072-1080. |
|