


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 605-613.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-2806.2024.05.015
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiaqi Zhang1,2,Fan Wu1,2,Yuqing Han1,2,Qi Liu3,Junjie Wang4,Yao Pan1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-19
Revised:2024-05-08
Online:2024-05-22
Published:2024-05-21
Contact:
*E-mail: CLC Number:
Jiaqi Zhang, Fan Wu, Yuqing Han, Qi Liu, Junjie Wang, Yao Pan. Multi-photon imaging technology and its application in cosmetic evaluation[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(5): 605-613.
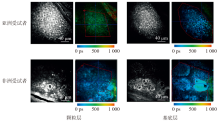
Fig. 3
Fluorescence intensity map after 740 nm excitation and corresponding fast (τ1) lifetime color maps obtained upon excitation wavelength at 800 nm[29] (The color of the image represents the fluorescence lifetime of the region, the weaker the fluorescence lifetime, the bluer the color, and the stronger the fluorescence lifetime, the greener the color. The red boxes indicate the regions of being studied in which the normalized fluorescence intensities are calculated and show that fluorescence intensities decrease linearly with increasing skin color lightness)"
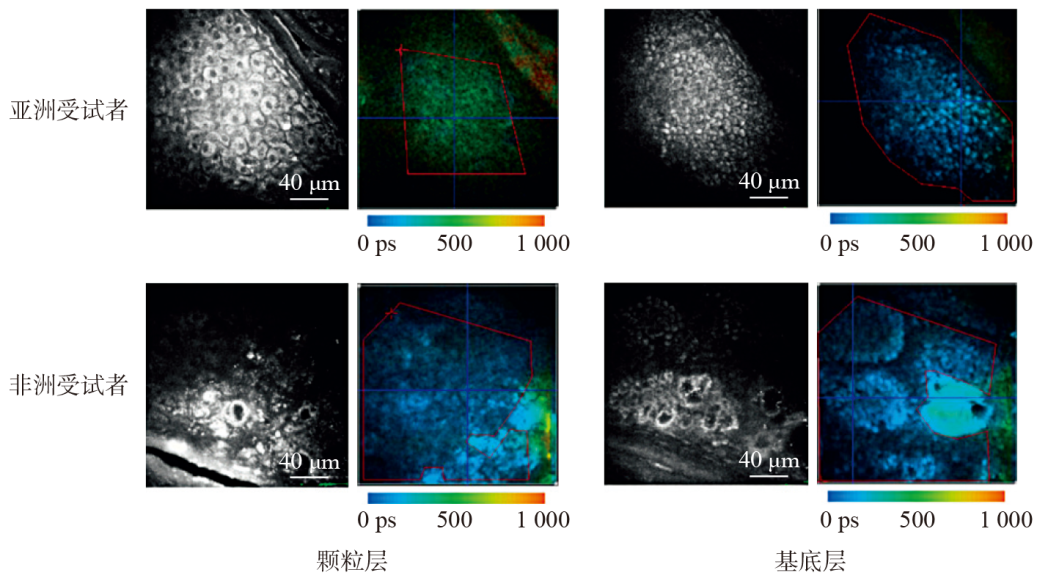
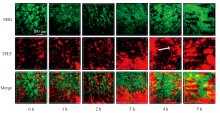
Fig. 4
2D SHG and TPEF imaging of in vivo absorption of recombinant human collagen (R-hc) labeled with infrared fluorescence probes[33] (Green represents the SHG signal emitted by endogenous collagen in histological structures of the skin, while red represents the TPEF signal emitted by R-hc labeled with infrared fluorescence probes, and white arrow represents reticular structure. Merge image reveals intrinsic collagen and exogenous R-hc are mutually linked to reticular structures in the dermis)"
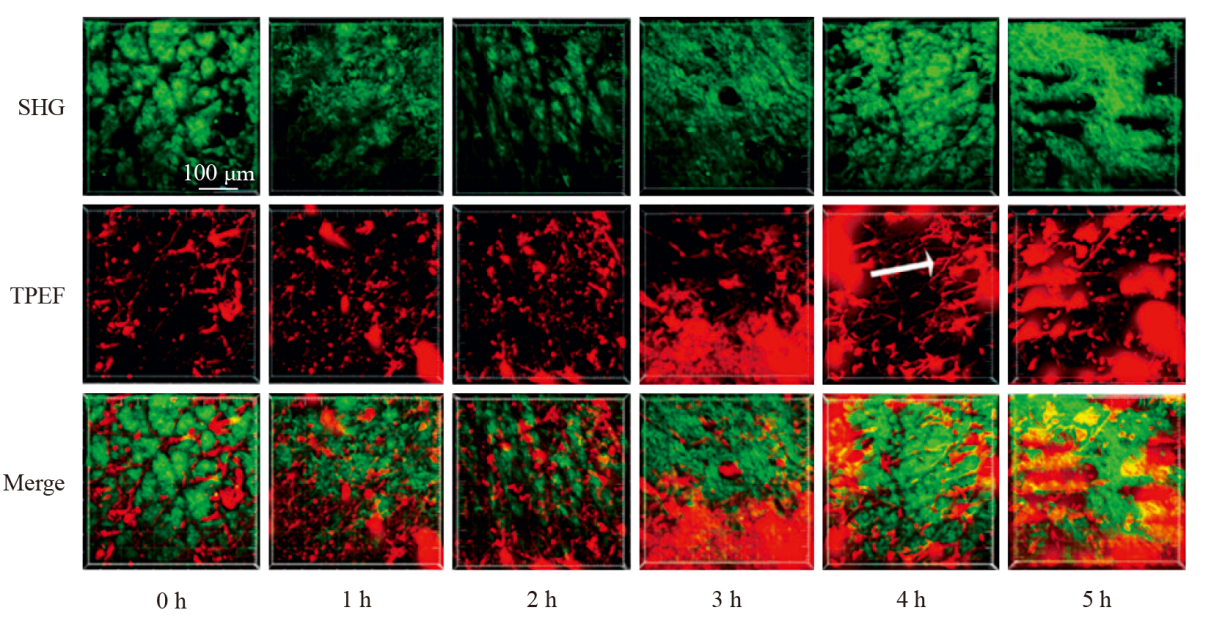
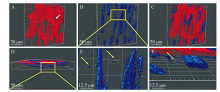
Fig. 5
Reconstruction of 3D surface visual Imaris rendering images of recombinant human collagen (R-hc) labeled with external fluorescent probes during in vivo absorption process: (A) SHG imaging of endogenous collagen in dermis (Red), arrow represents cavities in the hair follicle structure; (B) Exogenous R-hc TPEF imaging (Blue); (C, D)Aggregation sites of endogenous collagen and exogenous R-hc imaging overlay (C: Cross-section, D: Sagittal plane); (E, F) Partial enlarged view(Exogenous R-hc is concentrated in the hair follicle and a small amount spreads from the hair follicle to the dermis, with a depth of up to 150 μm), arrow represents R-hc diffuses from hair follicles to the dermis [34]"

Tab. 1
Application of multi-photon imaging technology in cosmetic evaluation"
| 评估内容 | 皮肤层次 | 自发荧光团 | 检测信号 | 多光子技术成像结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 紧致抗皱 | 角质层 | 富含角蛋白的角质细胞和细胞间质 | 检测到强烈的TPEF信号 | 随着紫外线照射的增强,表皮皮肤层NAD(P)H的荧光寿命增加[ |
| 颗粒层 | 胞质内含有少量线粒体、黑素颗粒的扁平细胞 | 检测到较弱的TPEF信号 | ||
| 棘层 | 胞质内含有许多线粒体、少量黑素颗粒的多角形细胞 | 检测到较强的TPEF信号 | ||
| 基底层 | 胞质内含有许多线粒体、黑素复合体的柱状细胞 | 检测到较强的TPEF信号 | ||
| 真皮浅层 | 胶原纤维、弹性纤维 | 胶原纤维能产生SHG信号、弹性纤维能产生TPEF信号 | 随着年龄的增加,SAAID自体荧光衰老指数=(a-b)/(a+b)(真皮中SHG的像素为a,真皮浅层处自发荧光的像素为b) 降低[ | |
| 祛斑美白 | 角质层 | 细胞间隙中的黑色素颗粒 | 检测黑色素的荧光寿命信号 | 与对照组相比,视黄醇处理区域受试者表皮中的黑色素含量明显下降[ |
| 颗粒层 | 排列密集的扁平细胞 | 检测黑色素的荧光寿命信号 | 与日光暴露区域相比,受试者非日光暴露区域皮肤的黑色素含量显著降低,并随着色素沉着现象的加重(黑色素浓度增加)差距变小[ | |
| 基底层 | 含有大量黑色素细胞 | 检测黑色素的荧光寿命信号 | 与日光暴露区域相比,受试者非日光暴露区域皮肤的黑色素含量无明显差异[ | |
| 透皮吸收 | 角质层 | ZnO纳米颗粒 | ZnO纳米颗粒的自发荧光寿命信号 | ZnO纳米颗粒的荧光寿命信号只出现在了角质层最上层的沟槽,在活的表皮细胞中没有检测出荧光寿命信号[ |
| 真皮浅层 | 重组人源胶原蛋白(R-hc) | 被红外荧光探针标记的R-hc产生的荧光信号可以与内源性胶原纤维的SHG信号相区分 | 被红外荧光探针标记的R-hc使得皮下的荧光信号随着时间的增加而增强,通过三维重建可视化了R-hc,其通过毛囊和皮脂腺渗透表皮到达真皮层并形成网状结构的实时动态过程[ |
| [1] | Giovannacci I, Meleti M, Garbarino F, et al. Correlation between autofluorescence intensity and histopathological features in non-melanoma skin cancer: An ex vivo study[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13 (16) : 3974. |
| [2] | Borile G, Sandrin D, Filippi A, et al. Label-free multiphoton microscopy: Much more than fancy images[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22 (5) : 2657. |
| [3] | Shi Yujie, Zhang Guangjie, Lu Zhengyuan, et al. Advances in multiphoton microscopy technologies[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 3 (11) : 296-307. |
| [4] | Göppert-Mayer M. Über Elementarakte mit zwei Quantensprüngen[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1931, 9: 273-294. |
| [5] |
Denk W, Strickler J, Webb W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy[J]. Science, 1990, 248: 73-76.
doi: 10.1126/science.2321027 pmid: 2321027 |
| [6] |
Masters B R, So P T, Gratton E. Multiphoton excitation fluorescence microscopy and spectroscopy of in vivo human skin[J]. Biophysical Journal, 1997, 72 (6) : 2405-2412.
pmid: 9168018 |
| [7] | Li Shaoqiang, Geng Junxian, Li Yanping, et al. New advances in biomedical applications of multiphoton imaging technology[J]. About Acta Physica Sinica, 2020, 22 (69). |
| [8] |
Stachowiak D, Boguslawsk J, Gluszek A, et al. Frequency-doubled femtosecond Er-doped fiber laser for two-photon excited fluorescence imaging[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2020, 11 (8) : 4431.
doi: 10.1364/BOE.396878 pmid: 32923054 |
| [9] | Ke W, Horton N G, Charan K, et al. Advanced fiber soliton sources for nonlinear deep tissue imaging in biophotonics[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2014, 20 (2). |
| [10] | Parodi V, Jacchetti E, Osellame R, et al. Nonlinear optical microscopy: From fundamentals to applications in live bioimaging[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8 (9). |
| [11] | Chi H H, Lee J C, Chen C C, et al. An index combining lost and remaining nerve fibers correlates with pain hypersensitivity in mice[J]. Cells, 2020, 9 (11) : 2414. |
| [12] | Stutzmann G E, Parker I. Dynamic multiphoton imaging: A live view from cells to systems[J]. Physiology (Bethesda, Md.), 2005, 20: 15-21. |
| [13] | Seidenari S, Arginelli F, Bassoli S, et al. Multiphoton laser microscopy and fluorescence lifetime imaging for the evaluation of the skin[J]. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2012. |
| [14] | Liang Xiaoxuan, Vogel Alfred, Zhang Zhenxi. Photodamage of biotissue in multiphoton imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50 (3). |
| [15] | Dong Yinmao, Meng Hong, Ma Laiji. Skin epigenetic physiology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2018. |
| [16] | Liu Chao, Jiang Zhao, Wang Xin, et al. Continuous optical zoom microscope with extended depth of field and 3D reconstruction[J]. PhotoniX, 2022, 3 (1) : 1-18. |
| [17] | Li Chengtong, Zhao Hua, Wang Min. Efficacy evaluation of cosmetics (Ⅸ): Application of image analysis method in the evaluation of cosmetic efficacy[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2018, 10 (48) : 551-557. |
| [18] | Pham D L, Miller C R, Myers M S, et al. Development and characterization of phasor-based analysis for FLIM to evaluate the metabolic and epigenetic impact of HER2 inhibition on squamous cell carcinoma cultures[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2021, 26 (10). |
| [19] | Lin S J, Wu R J, Tan H Y, et al. Evaluating cutaneous photoaging by use of multiphoton fluorescence and secondharmonic generation microscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30 (17) : 2275-2277. |
| [20] |
Koehler M J, König K, Elsner P, et al. In vivo assessment of human skin aging by multiphoton laser scanning tomography[J]. Optics Letters, 2006, 31 (19) : 2879.
pmid: 16969409 |
| [21] | Puschmann S, Rahn C D, Wenck H, et al. Approach to quantify human dermal skin aging using multiphoton laser scanning microscopy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2012, 17 (3). |
| [22] | Ung T P L, Lim S, Solinas X, et al. Simultaneous NAD(P)H and FAD fluorescence lifetime microscopy of long UVA-induced metabolic stress in reconstructed human skin[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11 (1). |
| [23] | Li Shaoqiang, Geng Junxian, Li Yanping, et al. New advances in biomedical applications of multiphoton imaging technology[J]. About Acta Physica Sinica, 2020, 22 (69). |
| [24] | Ying Yachen, Zhang Guangjie, Jia Huilin, et al. Multi-photon skin tissue imaging technology and its applications[J]. Chinese Optic, 2019, 1 (12) : 104-111. |
| [25] | Sanchez W Y, Obispo C, Ryan E, et al. Changes in the redox state and endogenous fluorescence of in vivo human skin due to intrinsic and photo-aging, measured by multiphoton tomography with fluorescence lifetime imaging[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2013, 18 (6). |
| [26] |
Koehler M J, Hahn S, Preller A, et al. Morphological skin ageing criteria by multiphoton laser scanning tomography: Non-invasive in vivo scoring of the dermal fibre network[J]. Experimental Dermatology, 2008, 17 (6) : 519-523.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2007.00669.x pmid: 18201192 |
| [27] |
Matts P J, Dykes P J, Mark S R. The distribution of melanin in skin determined in vivo[J]. British Journal of Dermatology, 2007, 156 (4) : 620-628.
pmid: 17493065 |
| [28] | Nielsenk P, Zhao L, Stamnes J J, et al. The importance of the depth distribution of melanin in skin for DNA protection and other photobiologicalprocesses[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 2006, 82 (3) : 194-198. |
| [29] | Dancik Y, Favre A, Loyc J, et al. Use of multiphoton tomography and fluorescence lifetime imaging to investigate skin pigmentation in vivo[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2013, 18 (2). |
| [30] | Su Ning, Liu Hongmei, Hu Nan, et al. In vivo exploring study of melanin content and distribution in human skin based on multiphoton tomography[J]. Flavour Fragrance Cosmetics, 2020, 1 (2) : 71-74. |
| [31] | Pena A M, Decenciere E, Brizion S, et al. In vivo melanin 3D quantification and z-epidermal distribution by multiphoton FLIM, phasor and Pseudo-FLIM analyses[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12 (1) : 1642. |
| [32] | Song Yanqing, Pan Yao, Zhao Hua. An overview of skin penetration test methods for cosmetics[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 12 (49) : 824-838. |
| [33] | Sun Yanan, Li Lishuang, Ma Shuhua, et al. In vivo visualization of collagen transdermal absorption by second-harmonic generation and two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10. |
| [34] | Sun Yanan, Zhao Jing, Li Chaohua, et al. Application of second harmonic generation and two-photon fluorescence in the distribution tracing of fluorescence labelled collagen[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2017, 26 (1) : 24-29. |
| [35] | Pflucker F, Wendel V, Hohenberg H, et al. The human stratum corneum layer: an effective barrier against dermal uptake of different forms of topically applied micronised titanium dioxide[J]. Skin Pharmacology and Applied Skin Physiology, 2001, 14: 92-97. |
| [36] |
Roberts M S, Roberts M J, Robertson T A, et al. In vitro and in vivo imaging of xenobiotic transport in human skin and in the rat liver[J]. Journal of Biophotonics, 2008, 1 (6) : 478-493.
doi: 10.1002/jbio.200810058 pmid: 19343674 |
| [37] | Wang Shaowei, Lei Ming. Near infrared-Ⅱ excited multiphoton fluorescence imaging[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59 (6). |
| [38] | Liu Zhaorui, Liu Jie. Applications of skin imaging techniques in cosmetic dermatology[J]. Dermatology Bulletin, 2018, 2 (35) : 202-209. |
| [39] |
Kucikas V, Werner M P, Schmitz-Rode T, et al. Two-photon endoscopy: State of the art and perspectives[J]. Molecular Imaging and Biology, 2021, 25 (1) : 3-17.
doi: 10.1007/s11307-021-01665-2 pmid: 34779969 |
| [1] | Deng Mengjie, Yi Guobin, Lv Ran, Liu Yafeng, Ye Dawei, Chen Jiazhi. Ferulic acid nanoethosomes: preparation, characterization, and performance of skin penetration in vitro [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(11): 1285-1292. |
| [2] | Huang Shaoyong,Zhou Lidan,Xun Wei,Shi Xuemei,Lu Yina. Study of the anti-aging efficacy of Prunus persica (peach) resin extract [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(2): 159-165. |
| [3] | Ran Xin,Wang Jilong,Liu Xiaoxia,He Hongjie,Wei Shuchang,Feng Xiaoli,Li Zhenzhen. Study on the effect of compound penetration enhancer on the permeability of Angelica’s water-soluble component ferulic acid in vitro [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(2): 134-139. |
| [4] | Fan Ting,Zhao Jianfeng,Chang Yejun,Ji Le. Effect of recombinant humanized type Ⅲ collagen on expression of skin functional related genes [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(12): 1326-1332. |
| [5] | CHEN Feng-feng,CAO Zhen-da,LIANG Rong. Study on the preparation and transdermal performance of EGCG flexible liposome [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(5): 390-395. |
| [6] | CAO Zhen-da,LIANG Rong. Study on the preparation and transdermal performance of epigallocatechin gallate liposome [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2020, 50(9): 609-614. |
| [7] | LIU Juan,YANG Li,PANG Jian-ping,ZHENG Hong-yan,JIA Xue-ting,SU Ning. Research on skin penetration of β-arbutin by confocal Raman spectroscopy [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(7): 452-455. |
| [8] | SONG Yan-qing,PAN Yao,ZHAO Hua. An overview of skin penetration test methods for cosmetics [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(12): 824-829. |
| [9] | QIAN Xin, LIANG Rong, YANG Cheng, CAO Guang-qun. Preparation and application of Pickering emulsion stabilized by modified waxy maize starch [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2018, 48(5): 255-259. |
| [10] | ZHAO Xiao-min,ZHAO Yun-shan,QU Xin. Study of a whitening and anti-wrinkle bio-functional ingredient based on epigenetics [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2016, 46(5): 274-278. |
| [11] | CAO Zhi, ZHANG Dao-jun. Inorganic sunscreening agents [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2014, 44(12): 700-705. |
|