


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (12): 774-782.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2019.12.002
• Lecture of science and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Wan-qing1,XU Mao-dong1,2,JIANG Jian-zhong1,CUI Zheng-gang1( )
)
Received:2019-11-21
Online:2019-12-22
Published:2019-12-24
Contact:
Zheng-gang CUI
E-mail:cuizhenggang@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Wan-qing,XU Mao-dong,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(VI)Interactions between like-charged nanoparticles and surfactants(ii)Stabilization mechanism and intelligentialization of the novel emulsions[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(12): 774-782.
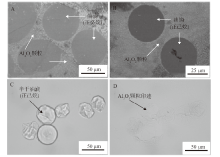
Fig. 5
SEM images(A, B)and optical micrographs(C, D)of dried(A, B and D)or half-dried(C)O/W emulsion droplets stabilized by alumina nanoparticles in combination with either DDMA-C(A, B)or SDS(C, D)taken 24 h after preparation.(A)0.01% alumina + 0.01 mmol/L DDMA-C, n-decane,(B)0.01% alumina + 0.01 mmol/L DDMA-C, n-hexane,(C, D)0.5% alumina + 0.1 mmol/L SDS, n-hexane"
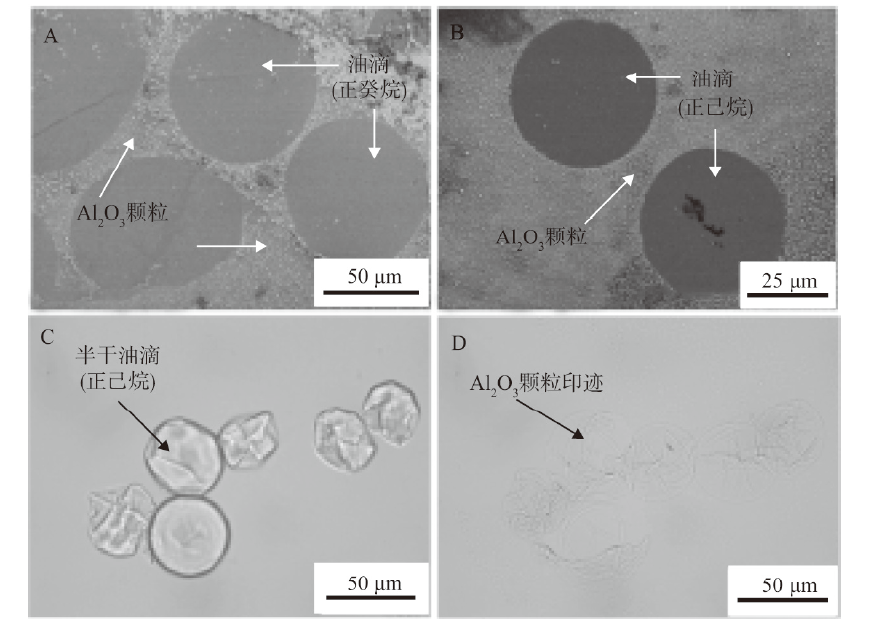
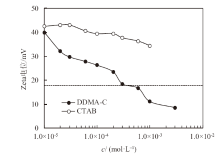
Fig. 6
Zeta potential of 0.1% alumina nanoparticles dispersed in aqueous cationic DDMA-C solution(●)as function of initial surfactant concentration and the comparison with that dispersed in aqueous CTAB solution(○). The dashed line shows the critical Zeta potential which separates stable(above the line)and unstable(below the line)emulsions"
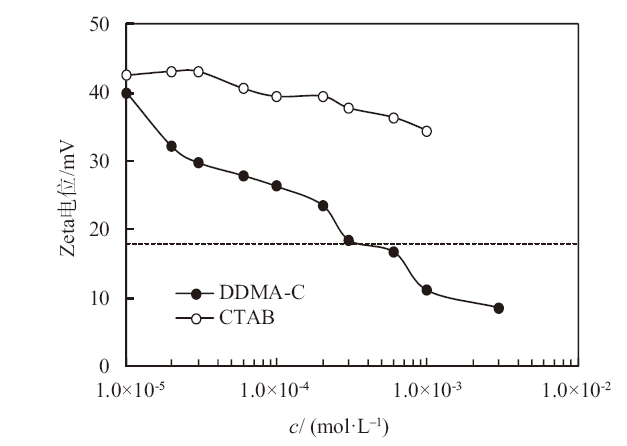
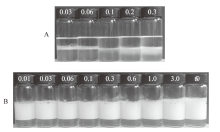
Fig. 7
Digital photographs of gasoline-in-water emulsions stabilized by 0.1% negatively charged silica nanoparticles in combination with SDBS at different concentration using either(A)tap water or(B)DI water as aqueous phase, respectively, taken 24 h after preparation. SDBS concentration in mmol/L for(A)and in μmol/L for(B)is shown on each vessel"
Tab. 1
Zeta potential of 0.1% nano-silica dispersed in DI water containing different concentration of NaCl and corresponding droplet size and stability(24 h after preparation)of the diesel oil-in-water emulsions at 25 ℃"
| c(NaCl)/(mol·L-1) | Zeta电位/mV | 油滴直径/mm | 乳状液稳定性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -27.11 | 20~ 80 | 稳定 |
| 0.01 | -20.84 | 25~ 70 | 稳定 |
| 0.02 | -17.08 | 45~300 | 不稳定 |
| 0.03 | -14.68 | 180~380 | 不稳定 |
| 0.06 | -12.65 | 420~650 | 不稳定 |
| 0.10 | -8.83 | 600~780 | 不稳定 |
| 0.30 | -5.44 | - | 不稳定 |
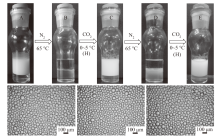
Fig. 9
Appearance(A-E)and micrographs(a, c and e)of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by 0.01% alumina nanoparticles in combination with 0.2 mmol/L DDMA-C upon alternately bubbling N2(30 mL/min at 65 ℃ for 50 min, B and D)and CO2(40 mL/min at 0-5 ℃ for 150 min)followed by homogenization(H)(C and E)"

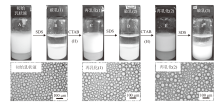
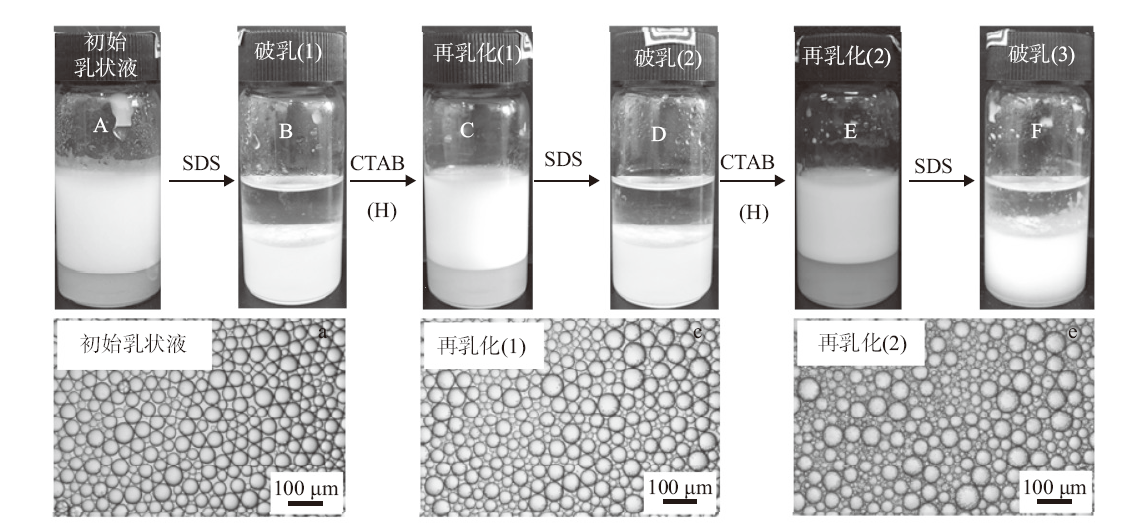
Fig. 11
Appearance(A)and micrographs(a, c and e) of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by 0.5% alumina nanoparticles plus 0.3 mmol/L CTAB, subsequent switching off(B, D and F)via addition of 0.3 mmol/L SDS and switching on(C and E)via addition of 0.3 mmol/L CTAB and homogenization(H)at 25 ℃, taken 24 h after operation"
| [1] |
Jiang J Z, Zhu Y, Cui Z G , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ by a switchable surfactant[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013,52:12373-12376.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201305947 pmid: 24123666 |
| [2] |
Pera-Titus M, Leclercq L, Clacens J M , et al. Pickering interfacial catalysis for biphasic systems: From emulsion design to green reactions[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015,54:2006-2021.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201402069 pmid: 25644631 |
| [3] |
Fernandes D A, Fernandes D D, Li Y , et al. Synjournal of stable multifunctional perfluorocarbon nanoemulsions for cancer therapy and imaging[J]. Langmuir, 2016,32:10870-10880.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01867 pmid: 27564412 |
| [4] |
Tang J, Quinlan P J, Tam K C . Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: Recent advances and potential applications[J]. Soft Matter, 2015,11:3512-3529.
doi: 10.1039/c5sm00247h pmid: 25864383 |
| [5] |
Dexter A F, Malcolm A S, Middelberg A P J . Reversible active switching of the mechanical properties of a peptide film at a fluid-fluid interface[J]. Nature Mater, 2006,5:502-506.
doi: 10.1038/nmat1653 pmid: 16715085 |
| [6] |
Wang W, Lu W, Jiang L . Influence of pH on the aggregation morphology of a novel surfactant with single hydrocarbon chain and multi-amine headgroups[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008,112:1409-1413.
doi: 10.1021/jp075535u pmid: 18197654 |
| [7] |
Liu Y, Jessop P G, Cunningham M , et al. Switchable surfactants[J]. Science, 2006,313:958-960.
doi: 10.1126/science.1128142 pmid: 16917059 |
| [8] |
Zhou M, Wang G, Xu Y , et al. Synjournal and performance evaluation of CO2/N2 switchable tertiary amine gemini surfactant[J]. J. Surf. Deterg., 2017,20(25) : 1-7.
doi: 10.1007/s11743-016-1917-5 |
| [9] |
Lee H Y, Diehn K K, Sun K , et al. Reversible photorheological fluids based on spiropyran-doped reverse micelles[J]. J. Am. Chem. Society, 2011,133:8461-8463.
doi: 10.1021/ja202412z pmid: 21563769 |
| [10] |
Jiang J Z, Ma Y, Cui Z G , et al. Pickering emulsions responsive to CO2/N2 and light dual stimuli at ambient temperature[J]. Langmuir, 2016,32(34) : 8668-8675.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01475 pmid: 27477238 |
| [11] |
Saji T, Hoshino K, Aoyagui S . Reversible formation and disruption of micelles by control of the redox state of the head group[J]. J. Am. Chem. Society, 1985,107:6865-6868.
doi: 10.1021/ja00310a020 |
| [12] |
Ma N, Xu H, An L , et al. Radiation-sensitive diselenide block copolymer micellar aggregates: toward the combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy[J]. Langmuir, 2011,27(10) : 5874-5878.
doi: 10.1021/la2009682 pmid: 21488607 |
| [13] |
Brown P, Bushmelev A, Butts C P , et al. Magnetic control over liquid surface properties with responsive surfactants[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012,51:2414-2416.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201108010 pmid: 22266983 |
| [14] |
Wang B G, Lei L, Zheng C C , et al. pH and temperature-responsive wormlike micelles formed by single amine oxide surfactant[J]. J. Disper. Sci. Technol., 2018,39:539-547.
doi: 10.1080/01932691.2017.1334212 |
| [15] | Binks B P, Horozov T S. Colloid particles at liquid interfaces[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006. |
| [16] |
Paunov V N, Cayre O . Supraparticles and “Janus” particles fabricated by replication of particle monolayer at liquid surfaces using a gel trapping technique[J]. Adv. Mater., 2004,16:788-791.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 |
| [17] |
Aveyard R, Binks B P, Clint J H . Emulsions stabilized solely by solid colloid particles[J]. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, 100-102:503-546.
doi: 10.1016/S0001-8686(02)00069-6 |
| [18] |
Binks B P, Rodrigue J A, Frith W J . Synergistic interaction in emulsions stabilized by a mixture of silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2007,23:3626-3636.
doi: 10.1021/la0634600 pmid: 17316038 |
| [19] |
Binks B P, Rodrigues J A . Double inversion of emulsions by using nanoparticles and a di-chain surfactant[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007,46:5389-5392.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200700880 pmid: 17546717 |
| [20] |
Cui Z G, Shi K Z, Cui Y Z , et al. Double phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by a mixture of CaCO3 nanoparticles and sodium dodecyl sulphate[J]. Colloids Surf. A, 2008,329:67-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.06.049 |
| [21] |
Cui Z G, Yang L L, Cui Y Z , et al. Effects of surfactant structure on the phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by mixtures of silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2010,26:4717-4724.
doi: 10.1021/la903589e pmid: 19950938 |
| [22] |
Cui Z G, Cui C F, Zhu Y , et al. Multiple phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by in situ surface activation of CaCO3 nanoparticles via adsorption of fatty acids[J]. Langmuir, 2012,28:314-320.
doi: 10.1021/la204021v pmid: 22103933 |
| [23] |
Cui Z G, Cui Y Z, Cui C F , et al. Aqueous foams stabilized by in situ surface activation of calcium carbonate nanoparticles via adsorption of anionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2010,26:12567-12574.
doi: 10.1021/la1016559 pmid: 20608686 |
| [24] |
Zhu Y, Jiang J, Liu K , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31:3301-3307.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00295 pmid: 25736518 |
| [25] |
Zhu Y, Pei X, Jiang J , et al. Responsive aqueous foams stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31:12937-12943.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03681 pmid: 26542227 |
| [26] |
Xu M D, Zhang W Q, Pei X M , et al. CO2/N2 triggered switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by alumina nanoparticles in combination with a conventional anionic surfactant[J]. RSC Advances, 2017,7:29742-29751.
doi: 10.1039/C7RA03722H |
| [27] | Liu K H, Lin Q, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with N-dodecyl-β-aminopropionate[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2017,38:85-93. |
| [28] |
Liu K H, Jiang J Z, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with a conventional zwitterionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2017,33:2296-2305.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b04459 pmid: 28191963 |
| [29] |
Zhu Y, Fu T, Liu K , et al. Thermo-responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with alkyl polyoxyethylene Ether nonionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2017,33:5724-5733.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00273 pmid: 28510456 |
| [30] |
Xu M D, Jiang J Z, Pei X M , et al. Novel oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by ionic surfactant and similarly charged nanoparticles at very low concentrations[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018,130:7864-7868.
doi: 10.1002/ange.v130.26 |
| [31] |
Xu M D, Xu L F, Lin Q , et al. Switchable oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by like-charged surfactant and particles at very low concentration[J]. Langmuir, 2019,35:4058-4067.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b04159 pmid: 30807183 |
| [32] | Xu M D . Study on the fluid-fluid dispersion systems stabilized by Al2O3 nanoparticles in combination with surfactants and their stimuli-responsive properties[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2019. |
| [33] | Rosen M J, Kunjappu J T . Surfactants and interfacial phenomena[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. |
| [34] |
Tang Y L, Guan X H, Su T Z , et al. Fluoride adsorption onto activated alumina: Modeling the effects of pH and some competing ions[J]. Colloids Surf. A, 2009,337:33-38.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.11.027 |
| [35] |
Sharrad M O, Fan M . Adsorption of carbonate and bicarbonate on FeOOH[J]. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Sci., 2015,3:150-169.
doi: 10.1021/es4020597 pmid: 23885755 |
| [36] |
Lin Q, Xu M D, Cui Z G , et al. Structure and stabilization mechanism of diesel oil-in-water emulsions stabilized solely by either positively or negatively charged nanoparticles[J]. Colloids Surf. A, 2019,573:30-39.
doi: 10.1007/s00249-019-01415-x pmid: 31865397 |
| [37] | Schuster D. Encyclopedia of emulsion technology[M]. Vol. 4, New York: CRC Press, 1996. |
| [38] | Tomlinson E, Davis S S, Mukhayer G I. Ionic interaction and phase stability, in solution chemistry of surfactants[M]. Vol. 1, ed. by Mittal K L, New York: Plenum Press, 1979. |
| [1] | Zhang Xin, Zhang Guanghua, Sun Qi, Li Hui, Tang Mingxuan, Guo Zehua. Study on the synthesis and performance of a responsive surfactant of tertiary amine type [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(11): 1250-1256. |
| [2] | Zhao Yilu,Cheng Hongxiao,Xu Lina,Wang Xiaodong,Zhao Changxi,Li Xindan,Ren Hong. Optimization and emulsification mechanism of emulsified viscosity reducer with high temperature resistance for heavy oil in Henan Oilfield [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(7): 724-730. |
| [3] | Xu Dekun,Fang Yinjun,Liu Xuefeng. Synergistic effect of N, N-dimethyl-9-decenamide and sodium dodecyl sulfate [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(9): 825-831. |
| [4] | ZHOU Hu-wu,HUO Yong-li,FANG Li,MA Shi-jing,HAN Ping,LIN Li,DU Zhi-yun. Studies on the synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of Ectoin and Madecassoside [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 535-538. |
| [5] | GONG Cheng-yi,YU Hao,WANG Qi-qi,SUN Ji-yong,SONG Ai-xin. Progress on stimulus-responsive Pickering emulsions and their applications [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 554-563. |
| [6] | Li Huan,Fang Yinjun,Liu Xuefeng. Synthesis and properties of pH-switchable surfactants based on dynamic imine bond [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(11): 1039-1044. |
| [7] | ZHANG Wan-qing,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(III)Interactions between oppositely charged nanoparticles and ionic surfactants(ii)Construction of stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions and Pickering foams by using ordinary commercial surfactants [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(9): 561-571. |
| [8] | JIANG Jian-zhong,YU Shi-jie,CUI Zheng-gang. The interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(I)——Switchable or stimuli-responsive surfactants and smart surfactant systems [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(7): 426-434. |
| [9] | Yang YU,Li-qiang ZHENG,Ji-chao SUN. Self-assembly of surfactants controlled by weak interactions(Ⅲ) Responsive surfactants [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(3): 141-149. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wan-qing,XU Mao-dong,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(V) Interactions between like-charged nanoparticles and ionic surfactants(i) Construction of novel emulsions using ultra-low concentration of nanoparticles/surfactants and their stabilization mechanism [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(11): 711-720. |
| [11] | REN Dong-yin, SHANG Zhi-xin, WANG Qi-bao. Study on the modification of chitosan and its CO2/N2-switchable emulsification [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2018, 48(5): 260-265. |
| [12] | QIN Fei, LIU Xue-feng. Dual stimuli-responsive properties of ammonium 11-benzylselanyl undecanoate [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2018, 48(3): 123-128. |
| [13] | ZHANG Peng, MEI Ping, LAI Lu. Synthesis and performance of CO2 switchable amine surfactants [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2017, 47(7): 369-373. |
| [14] | LI Gang-sen,ZHAO Lin-xiu,WANG Pei-yi,SU Hao,ZHAI Jia-bin,JIANG Dong-fang. Study on surface activity of N,N'-p-xylylene-bis- (dodecyldimethylammonium chloride)/AEO9 blend systems [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2016, 46(7): 392-396. |
| [15] | HUANG Man,LI Can-qi,LIU Xue-feng. CO2/N2-switchable microemulsion as well as its oil dirt washing and separation performance [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2016, 46(6): 328-333. |
|