


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (10): 633-642.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2019.10.002
• Lecture of science and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Wan-qing,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang( )
)
Received:2019-09-05
Online:2019-10-22
Published:2019-10-24
Contact:
Zheng-gang CUI
E-mail:cuizhenggang@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Wan-qing,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and theconstruction of smart systems(IV)Interactions between nanoparticles and nonionic surfactantsConstruction of temperature-responsive Pickering emulsionsvia hydrogen bonding[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(10): 633-642.
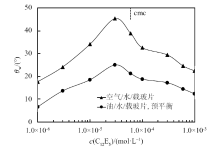
Fig. 2
The contact angles of drops of aqueous C12E5 solution on a quartz slide in air and the contact angles of aqueous solution of C12E5 coexisting with toluene on a quartz slide(measured by captured oil droplet method)as a function of the initial surfactant concentration in water at 25 ℃. Toluene was pre-equilibrated with an equal volume of aqueous C12E5 solution for 24 h at 25 ℃"
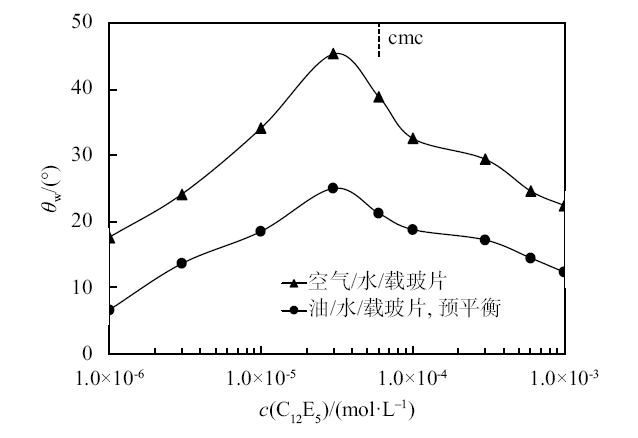
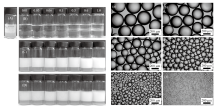
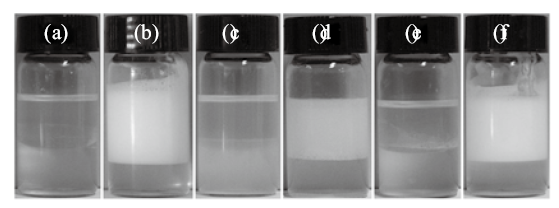
Fig. 3
Left: Photographs of vessels containing toluene-water(7 mL/7 mL)emulsions stabilized by(A)0.5% silica nanoparticles alone,(B)C12E5 alone at different concentrations and(C, D)0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with C12E5 at different concentrationstaken 24 h(A-C)and 1 week(D)after preparation. C12E5 concentration(B-D)in mmol/L is shown on top of the graph.Right: Optical micrographs of toluene-in-water emulsion droplets stabilized by 0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination withdifferent concentrations of C12E5(a-e)and dodecane-in-water emulsion droplets stabilized by C12E5 alone(f)taken 24 hafter preparation. C12E5 concentration(a-f, mmol/L)in water: 0.06, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1.0, and 3.0. Temperature =(22±2) ℃"
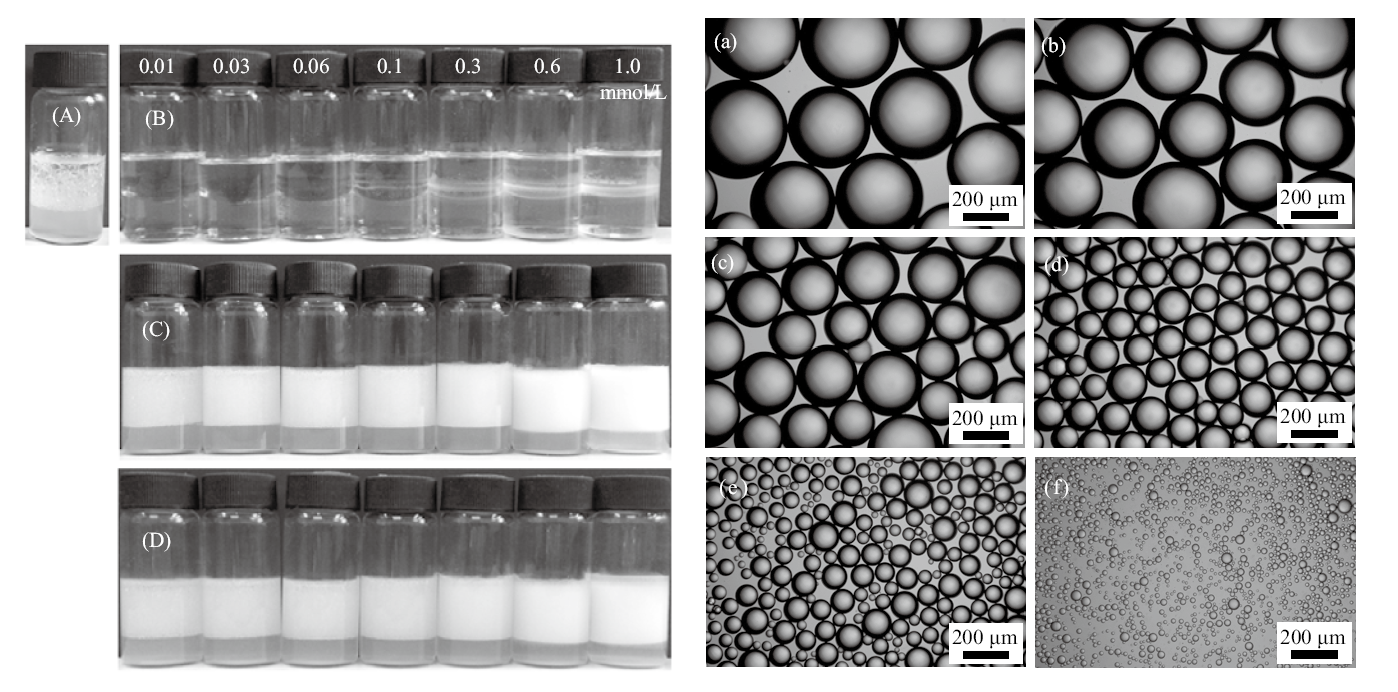
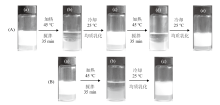
Fig. 4
Photographs of(A)a toluene-in-water emulsion and(B)a dodecane-in-water emulsion stabilized by 0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.3 mmol/L C12E5 following heating under stirring to 45 ℃ and cooling to 25 ℃ followed by re-homogenization for a number of cycles, taken 24 h after preparation.(a)Initial emulsions at 25 ℃,(b)demulsified for the first time,(c)re-emulsified,(d)demulsified for the fifth time, and(e)emulsified for the sixth time"
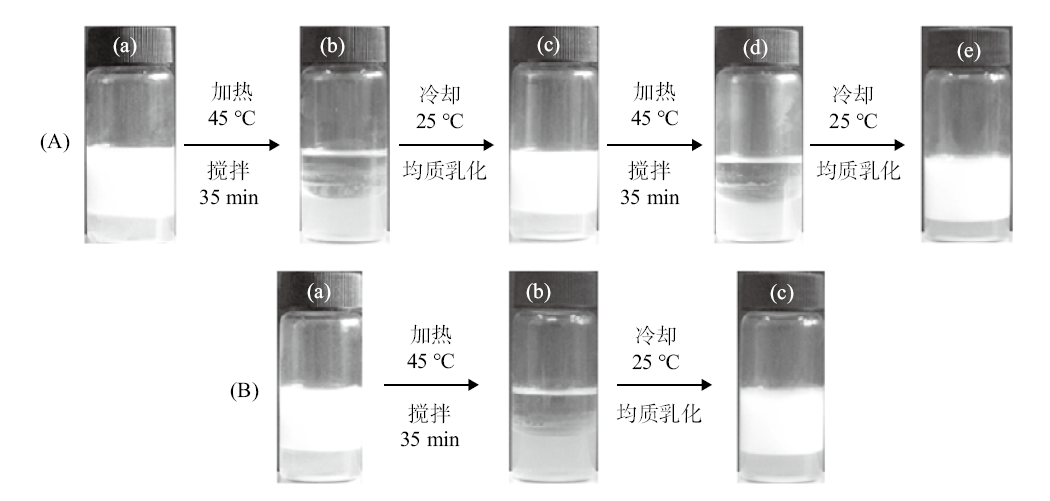
Fig. 6
Time required for complete demulsification of a toluene-in-water emulsion stabilized by(a)0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.3 mmol/L C12E5 after warming to different temperatures with gentle stirring(100 r/min)and(b)0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with C12E5 at different concentrations after warming to 45 ℃ with gentle stirring(100 r/min)"
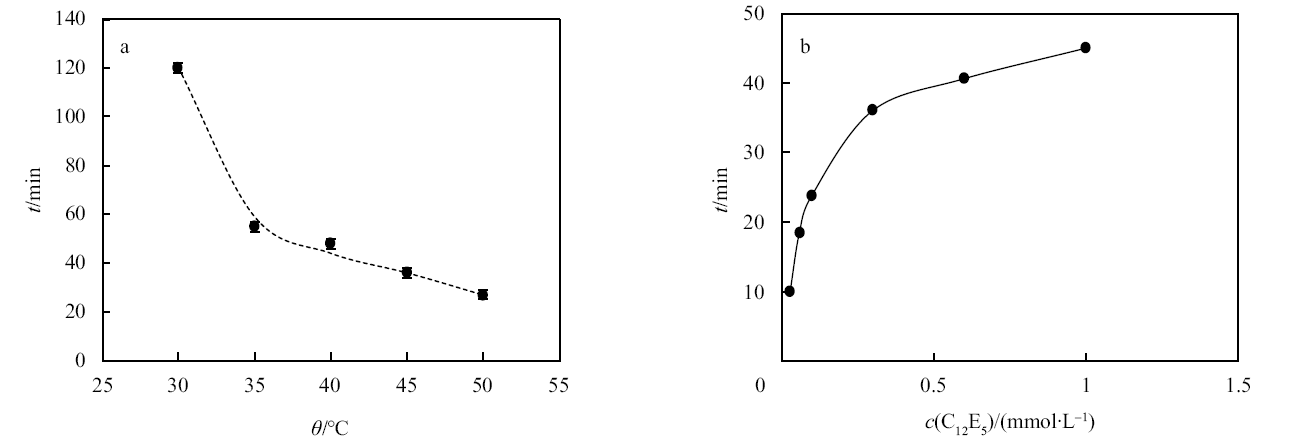
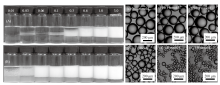
Fig. 7
Photographs of toluene-in-water emulsions stabilized by(A)C12E10 alone and(B)0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with C12E10 at different concentrations, taken 1 week after preparation at room temperature(22±2) ℃; micrographs of the emulsions stabilized by silica +C12E10(a-d)and by C12E10 alone(e)taken 24 h after preparation, as well as the emulsion(b)taken 4 h after being placed in a water bath at 45 ℃ with gentle stirring (100 r/min)(b′). The C12E10 concentration(mmol/L)is shown on the top of the graph and micrographs"

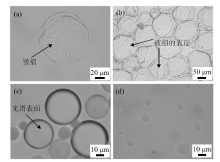
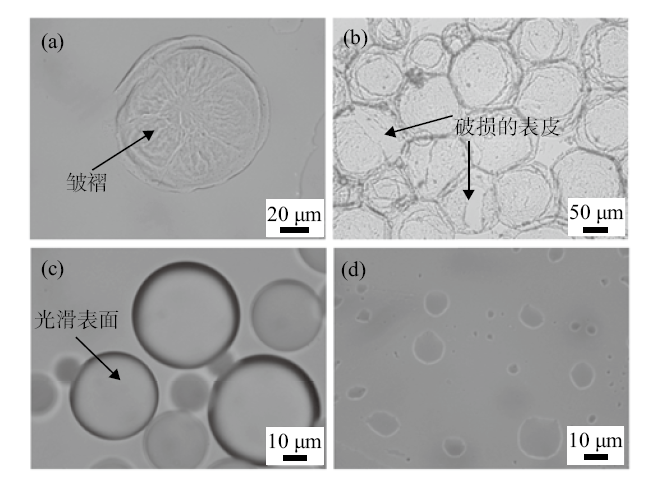
Fig. 9
Micrographs of toluene-in-water emulsion droplets during drying process at room temperature(22±2) ℃.(a)A Pickering droplet stabilized by 0.5% silica + 0.3 mmol/LC12E5, partially dried with wrinkled surface;(b)Pickering droplets stabilized by 0.5% silica + 0.3 mmol/L C12E10, fully dried displaying broken solid films;(c and d)emulsion droplets stabilized by 1 mmol/L C12E10 alone, fresh oil droplets with smooth surfaces and nearly fully dried exhibiting no surface shell, respectively"
Tab. 1
Percentage of silica nanoparticles adsorbed at oil/water interfaces in toluene-in-water emulsions stabilized by 0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.3 mmol/L C12E5 at two temperatures, obtained by measuring the concentration of particles(Cp)remaining in the aqueous phase after emulsification"
| θ/℃ | V(分出水相)/mL | m(水相中颗粒)/g | Cp/% | 吸附百分数/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 4.998 | 0.015 | 0.308 | 37.4±1.4 |
| 25 | 5.002 | 0.016 | 0.318 | |
| 45 | 5.012 | 0.023 | 0.453 | 11.0±2.2 |
| 45 | 5.005 | 0.022 | 0.438 |

Fig. 11
Photographs of liquid paraffin-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized by 0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with C12E9 of different concentrations without(a)and with(b)CO2 treatment, taken 24 h(a)and 15 days(b)after preparation. The concentrations(mmol/L)of C12E9 from left to right are 0.001, 0.005, 0.008, 0.01, 0.05, 0.08, and 0.1, respectively"


Fig. 12
Digital photographs of the liquid paraffin-in-water Pickering emulsion stabilized by 0.5% silica nanoparticles and 0.05 mmol/L C12E9 during switching process.(a)Homogenization of liquid paraffin and aqueous dispersion(1∶1 volume ratio)at 25 ℃, 24 h later;(b)bubbling CO2 at 25 ℃ for 30 min, followed by homogenization, 15 d later;(c)bubbling N2 at 65 ℃ for 50 min;(d)homogenization at 25 ℃, 1 h later;(e)24 h later;(f)bubbling CO2 at 25 ℃ for 30 min, followed by homogenization, 15 d later"
| [1] | Jiang J Z, Zhu Y, Cui Z G , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ by a switchable surfactant[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013,52:12373-12376. |
| [2] | Tang J, Quinlan P J, Tam K C . Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: Recent advances and potential applications[J]. Soft Matter, 2015,11(18):3512-3529. |
| [3] | Fameau A L, Carl A, Saint-Jalmes A , et al. Responsive aqueous foams[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2015,16:66-75. |
| [4] | Liang M Q, Yin H Y, Feng Y J . Smart aqueous foams: State of the art[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2016,32(11):2652-2662. |
| [5] | Harman C L G, Patel M A, Guldin S , et al. Recent developments in Pickering emulsons for biomedical applications[J]. Curent Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science, 2019,39:173-189. |
| [6] | Saji T, Hoshino K, Aoyagui S . Reversible formation and disruption of micelles by control of the redox state of the head group[J]. J Am. Chem. Soc., 1985,107(24):6865-6868. |
| [7] | Liu Y, Jessop P G, Cunningham M , et al. Switchable surfactants[J]. Science, 2006,313(5789):958-960. |
| [8] | Yang Y, Fang Z, Chen X , et al. An overview of Pickering emulsions: solid-particle materials, classification, morphology, and applications[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017,8:287. |
| [9] | Wu J, Ma G H . Recent studies of Pickering emulsions: Particles make the difference[J]. Small, 2016,12(34):4633-4648. |
| [10] | Zhu Y, Jiang J Z, Liu K H , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31(11):3301-3307. |
| [11] | Zhu Y, Pei X, Jiang J , et al. Responsive aqueous foams stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31(47):12937-12943. |
| [12] | Xu M D, Zhang W Q, Pei X M , et al. CO2/N2 triggered switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by alumina nanoparticles in combination with a conventional anionic surfactant[J]. RSC Advances, 2017,7:29742-29751. |
| [13] | Liu K H, Lin Q, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with N-dodecyl-β-aminopropionate[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2017,38:85-93. |
| [14] | Liu K H, Jiang J Z, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with a conventional zwitterionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2017,33(9):2296-2305. |
| [15] | Lin Q, Liu K H, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering foams stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with trace amount of dodecyl dimethyl carboxyl betaine[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A, 2018,544:44-52. |
| [16] | Zhu Y, Fu T, Liu K , et al. Thermo-responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with alkyl polyoxyethylene ether nonionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2017,33(23):5724-5733. |
| [17] | Zhang Y M, Guo S, Ren X F , et al. CO2 and redox dual responsive Pickering emulsion[J]. Langmuir, 2017,33(45):12973-12981. |
| [18] | Midmore B R . Effect of aqueous phase composition on the properties of a silica-stabilized W/O emulsion[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 1999,213(2):352-359. |
| [19] | Lagaly G, Reese M, Abend S . Smectites as colloidal stabilizers of emulsions: I. Preparation and properties of emulsions with smectites and nonionic surfactants[J]. Applied Clay Science, 1999,14(1-3):83-103. |
| [20] | Midmore B R . Synergy between silica and polyoxyethylene surfactants in the formation of O/W emulsions[J]. Colloids & Surfaces A, 1998,145(1-3):133-143. |
| [21] | Shinoda K, Friberg S . Emulsion and solubilization[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1986. |
| [22] | Rosen M J, Kunjappu J T . Surfactants and interfacial phenomena[M]. 4 th edition. Hoboken, Wiley , 2012. |
| [23] | Becher P . Encyclopedia of emulsion technology[M]. Vol 1, Basic Theory. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1983. |
| [24] | Despert G, Oberdisse J . Formation of micelle-decorated colloidal silica by adsorption of nonionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2003,19(18):7604-7610. |
| [25] | Notley S M . Adsorption of nonionic surfactants with ethylene oxide headgroup chemistry at the titania-water interface[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2012,116(20):6059-6064. |
| [26] | Sing S K, Notley S M . Adsorption of nonionic surfactants CnEm at the silica-water and cellulose-water interface[J]. J. phys. Chem. B, 2010,114:14977-14982. |
| [27] | Jian G Q, Puerto M G, Wehowsky A , et al. Static adsorption of an ethoxylated nonionic surfactant on carbonate minerals[J]. Langmuir, 2016,32:10244-10252. |
| [28] | Zhang L, Zhang G, Ge J , et al. CO2/N2 responsive Pickering emulsion stabilized by silica nanoparticles and a common nonionic surfactant[J]. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., 2018,186(2):12012. |
| [1] | Pei Liu, Ting Pan, Xiaomei Pei, Binglei Song, Jianzhong Jiang, Zhenggang Cui, Bernard P. Binks. Dual-responsive oil-in-water emulsions co-stabilized by a nonionic-anionic Bola surfactant and silica nanoparticles [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | Ding Zhengqing, Wu Yingyi, Wang Weiyun, Huang Xujuan, Cai Zhaosheng. Study on Pickering emulsion stabilized by hydroxyethyl cellulose/nanocellulose and its rheological properties [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(3): 245-252. |
| [3] | Ting Pan, Junhui Wu, Xiaomei Pei, Zhenggang Cui. Temperature and pH responsive behavior of wormlike micelles formed by novel pseudo-gemini surfactant [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(12): 1361-1368. |
| [4] | Chen Ningru, Zhang Ruoqi, Han Xu, Shang Yazhuo. New emulsion system and its application in cosmetics (III)Pickering emulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(11): 1257-1265. |
| [5] | Shen Jiajun,Huan Jingjing,Wang Bijia,Sui Xiaofeng. Properties of oleogel-in-water Pickering emulsion stabilized by nano-chitin [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(8): 844-850. |
| [6] | Zhang Qianjie,Shen Xingliang,Sheng Taotao,Zhang Wanping,Xu Jianying. The interaction of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide-pearl powder and its stabilization of the double phase inversion in emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(5): 468-475. |
| [7] | Xie Xin,Wang Weihao,Liu Huanyu,Sun Mengmeng,Li Qinyuan,Jia Lufan,Meng Tao. Study on the Pickering emulsion stabilized by Alg@TiO2 microspheres for sunscreen formulation [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(3): 229-236. |
| [8] | Chen Yunbo,Li Xinyi,Mao Zhiping,Xu Hong,Sui Xiaofeng. Fabrication of phase change microcapsules via nano-chitin stabilized Pickering emulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(12): 1286-1292. |
| [9] | Li Yingxue,Sun Yongqiang,Zhou Jingjie,Sun Jinyuan,Liang Huibin,Liu Yuqi. Synthesis and performance study of C12-14 secondary alcohol ethoxylates [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(11): 1155-1161. |
| [10] | Huan Jingjing,Wang Bijia,Mao Zhiping,Sui Xiaofeng. Rapid preparation of nano-chitin for stabilizing Pickering emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(10): 1081-1087. |
| [11] | Shen Yongqiang,Sun Yajuan,Yang Cheng,Wang Jing. Study on the preparation and emulsifying properties of peach seed protein isolate nanoparticles [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(9): 809-816. |
| [12] | Yu Hui,Zhu Yongfeng,Hui Aiping,Yang Fangfang,Wang Aiqin. Advances in the application of attapulgite in Pickering emulsion preparation [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(7): 670-678. |
| [13] | GONG Cheng-yi,YU Hao,WANG Qi-qi,SUN Ji-yong,SONG Ai-xin. Progress on stimulus-responsive Pickering emulsions and their applications [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 554-563. |
| [14] | FANG Zhen-xing,WANG Xi-ying,WU Jing,ZENG Ying,PAN Hong,XIE Zhen-hua. Preparation of Pickering emulsion from volcano mud and its pH stability [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 506-512. |
| [15] | HE Yi-jing,XU Hu-jun. Preparation of Pickering emulsion stabilized by lauroyl lysine [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(5): 413-420. |
|