


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2026, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 28-40.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-2806.2026.01.004
• Basic research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Haiyong Tang1,2,Yueqing Huo1,2,Enze Li3,Shengti Cao1,2,Chunxin Gao1,2,Chuangxin Ji1,2,Xiaochen Liu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-02-11
Revised:2025-12-23
Online:2026-01-22
Published:2026-02-05
Contact:
E-mail: CLC Number:
Haiyong Tang, Yueqing Huo, Enze Li, Shengti Cao, Chunxin Gao, Chuangxin Ji, Xiaochen Liu. Excellent temperature/salt resistant foam by alcohol ether sulfates(AEnS)for gas well deliquification[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2026, 56(1): 28-40.
Tab.1
Diffusion coefficient of AEnS"
| AEnS | ρ (NaCl)/(g/L) | kt → 0 /(mN/(m·s1/2)) | Dt → 0 | kt → ∞ /(mN/(m·s-1/2)) | Dt → ∞ | Dt → ∞ /Dt → 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE2S | 0 | -28.04 | 2.42×10-12 | 3.62 | 2.88×10-14 | 1.19×10-2 |
| 100 | -17.70 | 9.64×10-13 | 24.63 | 6.24×10-16 | 6.47×10-4 | |
| 200 | -26.66 | 2.19×10-12 | 21.36 | 8.30×10-16 | 3.79×10-4 | |
| AE5S | 0 | -21.44 | 1.41×10-12 | 2.78 | 4.88×10-14 | 3.45×10-2 |
| 100 | -59.57 | 1.09×10-11 | 3.86 | 2.54×10-14 | 2.3×10-3 | |
| 200 | -28.08 | 2.43×10-12 | 18.85 | 1.07×10-15 | 4.40×10-4 | |
| AE7S | 0 | -19.40 | 1.16×10-12 | 2.47 | 6.19×10-14 | 5.35×10-2 |
| 100 | -49.53 | 7.55×10-12 | 3.40 | 3.28×10-14 | 4.34×10-3 | |
| 200 | -47.26 | 6.87×10-12 | 12.83 | 2.30×10-15 | 3.35×10-4 |
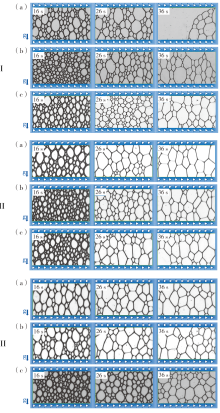
Fig.6
Liquid film photos of AEnS at different NaCl mass concentrations:Ⅰ- (a) AE2S in the absence of NaCl,Ⅰ- (b) AE5S in the absence of NaCl,Ⅰ- (c) AE7S in the absence of NaCl,Ⅱ- (a) AE2S at 100 g/L NaCl,Ⅱ- (b) AE5S at 100 g/L NaCl,Ⅱ- (c) AE7S at 100 g/L,Ⅲ- (a) AE2S at 200 g/L NaCl,Ⅲ- (b) AE5S at 200 g/L NaCl,Ⅲ- (c) AE7S at 200 g/L NaCl"

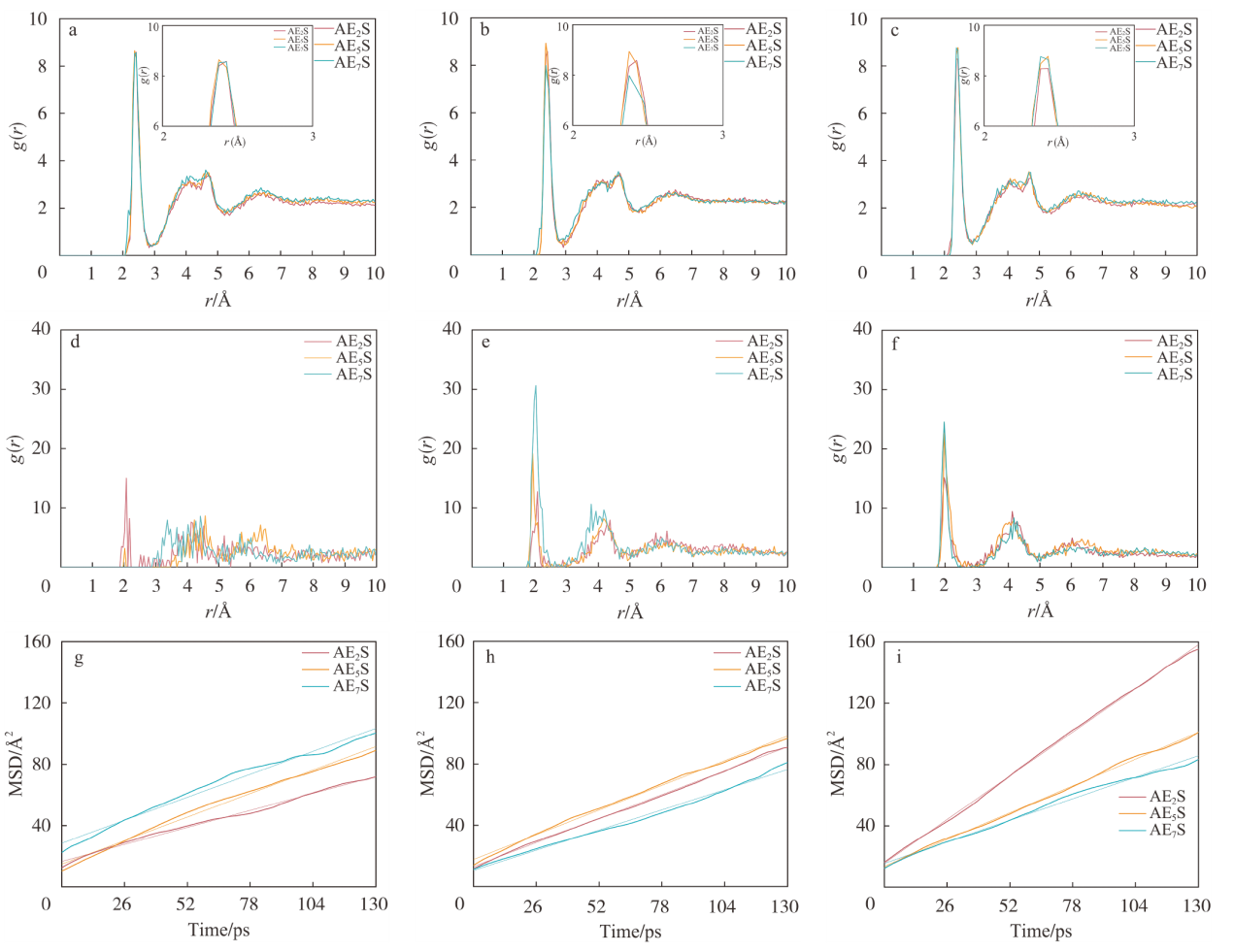
Fig.11
RDF curves between water and AEnS hydrophilic head group in water phases with zero (a), 30 (b) and 60 (c) NaCl molecules. RDF curves between AEnS hydrophilic head group and Na+ ions in water phases with zero (d), 30 (e) and 60 (f) NaCl molecules. MSD curves of the AEnS in water phases with zero (g), 30 (h) and 60 (i) NaCl molecules"
Tab.5
The position of the first and second characteristic peaks and the number of binding water in the first hydration layer from RDF curves between water and AEnS hydrophilic head group in water phases with different NaCl molecules (N(NaCl))"
| N(NaCl) | AEnS | Position of the first characteristic peak/? | Number of binding water in the first hydration layer | Position of the second characteristic peak/? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | AE2S | 2.435 | 0.839 5 | 3.975 |
| AE5S | 2.375 | 0.856 2 | 4.125 | |
| AE7S | 2.425 | 0.847 8 | 4.025 | |
| 30 | AE2S | 2.425 | 0.838 2 | 3.975 |
| AE5S | 2.375 | 0.821 1 | 4.125 | |
| AE7S | 2.375 | 0.776 3 | 4.125 | |
| 60 | AE2S | 2.425 | 0.819 4 | 4.025 |
| AE5S | 2.425 | 0.802 9 | 4.225 | |
| AE7S | 2.375 | 0.802 4 | 4.075 |
| [1] | Lea J F, Rowlan L. Gas well deliquification[M]. Gulf Professional Publishing, 2019. |
| [2] |
Li Xiaoke, Xiong Ying, Chen Dajun, et al. Utilization of nanoparticle-stabilized foam for gas well deliquification[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2015, 482: 378-385.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.05.053 |
| [3] |
Xiong Chunming, Cao Guangqiang, Zhang Jianjun, et al. Nanoparticle foaming agents for major gas fields in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(5): 1022-1030.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)60259-4 |
| [4] |
Yang Jiang, Jovancicevic V, Ramachandran S. Foam for gas well deliquification[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 309(1-3): 177-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.10.011 |
| [5] |
Xiao Xiao, Qi Jinwan, Zhou Jingjie, et al. Enhanced salt thickening effect of the aqueous solution of peaked-distribution alcohol ether sulfates(AES)[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 636: 128146.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.128146 |
| [6] |
Mu Jianhai, Li Ganzuo, Xiao Hongdi, et al. Formation of wormlike micelles in anionic surfactant AES aqueous solutions[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46: 1360-1363.
doi: 10.1007/BF03183389 |
| [7] |
Li Hua, Zhu Weiyao, Song Zhiyong. 2-D pore-scale oil recovery mechanisms of the anionic and nonionic surfactants[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 655: 130245.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130245 |
| [8] |
Li Chunling, Zhang Tiantian, Ji Xianjing, et al. Effect of Ca2+/Mg2+ on the stability of the foam system stabilized by an anionic surfactant: A molecular dynamics study[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 489: 423-432.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.11.012 |
| [9] |
Wu Gang, Yuan Congtai, Ji Xianjing, et al. Effects of head type on the stability of gemini surfactant foam by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2017, 682: 122-127.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2017.06.017 |
| [10] |
Wu Gang, Zhu Qianqian, Yuan Congtai, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of the influence of polyacrylamide on the stability of sodium dodecyl sulfate foam[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 166: 313-319.
doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2017.03.011 |
| [11] |
Sun Huai, Ren Pengyu, Fried J R. The COMPASS force field: parameterization and validation for phosphazenes[J]. Computational and Theoretical Polymer Science, 1998, 8(1-2): 229-246.
doi: 10.1016/S1089-3156(98)00042-7 |
| [12] |
Martyna G J, Tuckerman M E, Tobias D J, et al. Explicit reversible integrators for extended systems dynamics[J]. Molecular Physics, 1996, 87(5): 1117-1157.
doi: 10.1080/00268979600100761 |
| [13] | Darden T, York D, Pedersen L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log (N)method for Ewald sums in large systems[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1993, 98(12): 10089-10092. |
| [14] |
Ewald P P. Die Berechnung optischer und elektrostatischer Gitterpotentiale[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1921, 369(3): 253-287.
doi: 10.1002/andp.v369:3 |
| [15] |
Karasawa N, Goddard III William A. Force fields, structures, and properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)crystals[J]. Macromolecules, 2002, 25(26): 7268-7281.
doi: 10.1021/ma00052a031 |
| [16] |
Liu Xiaochen, Zhao Yongxiang, Li Qiuxiao, et al. Adsorption behavior of fatty alcohol ether sulfonate at different interfaces[J]. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 2017, 20: 401-409.
doi: 10.1007/s11743-016-1918-4 |
| [17] |
Pu Wanfen, Du Daijun, Tang Yanli, et al. Synthesis of an alkyl polyoxyethylene ether sulfonate surfactant and its application in surfactant flooding[J]. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 2018, 21(5): 687-697.
doi: 10.1002/jsde.2018.21.issue-5 |
| [18] |
Fainerman V B, Makievski A V, Miller R. The analysis of dynamic surface tension of sodium alkyl sulphate solutions, based on asymptotic equations of adsorption kinetic theory[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1994, 87(1): 61-75.
doi: 10.1016/0927-7757(94)02747-1 |
| [19] |
Rillaerts E, Joos P. Rate of demicellization from the dynamic surface tensions of micellar solutions[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1982, 86(17): 3471-3478.
doi: 10.1021/j100214a040 |
| [20] |
Yang Weiguang, Cao Yupeng, Ju Hongbin, et al. Amide Gemini surfactants linked by rigid spacer group 1,4-dibromo-2-butene: Surface properties, aggregate and application properties[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 326: 115339.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115339 |
| [21] |
Binks B P, Meunier J, Abillon O, et al. Measurement of film rigidity and interfacial tensions in several ionic surfactant-oil-water microemulsion systems[J]. Langmuir, 1989, 5(2): 415-421.
doi: 10.1021/la00086a022 |
| [22] |
Han Weiwei, Fan Jiabao, Qiang Taotao, et al. A novel salt and condensate-resistant foam co-stabilized by mixtures of surfactants and citric acid for gas well deliquification[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 385: 122426.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2023.122426 |
| [23] |
Han Weiwei, Fan Jiabao, Lv Hongmiao, et al. Excellent foaming properties of anionic-zwitterionic-Gemini cationic compound surfactants for gas well deliquification: Experimental and computational investigations[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 653: 129944.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129944 |
| [24] | Han Weiwei, Lv Hongmiao, Kar T, et al. Experimental studies and computational exploration on an exceptionally salt/condensate resistant gas well foaming mixture compromising amino-betaine-ammonium surfactants and dodecanol[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 397. |
| [25] | Mitchell B J. Viscosity of foam[M]. The University of Oklahoma, 1970. |
| [26] |
Smith D L. Comparison of salt thickening of conventional and peaked alcohol ether sulfates[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 1991, 68: 629-633.
doi: 10.1007/BF02660167 |
| [27] |
Mu Jianhai, Li Ganzuo, Jia Xiaolei, et al. Rheological properties and microstructures of anionic micellar solutions in the presence of different inorganic salts[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002, 106(44): 11685-11693.
doi: 10.1021/jp014096a |
| [28] |
Yaacob I I, Bose A. An investigation of microstructures in cationic/anionic surfactant suspensions by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1996, 178(2): 638-647.
doi: 10.1006/jcis.1996.0161 |
| [29] |
Zhao Qiang, Qian Jinwen, Gui Zhangliang, et al. Interfacial self-assembly of cellulose-based polyelectrolyte complexes: pattern formation of fractal “trees”[J]. Soft Matter, 2010, 6(6): 1129-1137.
doi: 10.1039/b918529a |
| [30] |
Kalur G C, Raghavan S R. Anionic wormlike micellar fluids that display cloud points: rheology and phase behavior[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(18): 8599-8604.
doi: 10.1021/jp044102d |
| [31] |
Arleth L, Bergström M, Pedersen J S. Small-angle neutron scattering study of the growth behavior, flexibility, and intermicellar interactions of wormlike SDS micelles in NaBr aqueous solutions[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(14): 5343-5353.
doi: 10.1021/la015693r |
| [32] |
Yang Jiang. Viscoelastic wormlike micelles and their applications[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2002, 7(5-6): 276-281.
doi: 10.1016/S1359-0294(02)00071-7 |
| [33] |
Mu Jianhai, Li Ganzuo. The formation of wormlike micelles in anionic surfactant aqueous solutions in the presence of bivalent counterion[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2001, 345(1-2): 100-104.
doi: 10.1016/S0009-2614(01)00799-0 |
| [34] |
Mu Jianhai, Li Ganzuo. Rheology of viscoelastic anionic micellar solutions in the presence of a multivalent counterions[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2001, 279: 872-878.
doi: 10.1007/s003960100508 |
| [35] |
Darvas M, Gilányi T, Jedlovszky P. Adsorption of poly(ethylene oxide)at the free water surface. A computer simulation study[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2010, 114(34): 10995-11001.
doi: 10.1021/jp1034272 |
| [36] |
Ahmadi H, Hosseini E, Cha-Umpong W, et al. Incorporation of natural lithium-ion trappers into graphene oxide nanosheets[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2021, 6(10): 2000665.
doi: 10.1002/admt.v6.10 |
| [1] | Zhisheng Zhang, Chanliang Shen, Jianxun Li, Yanqiang Liu, Weiwei Han, Sanbao Dong. Preparation and performance of betaine/AOS/Gemini ternary surfactant foam for gas well deliquification [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 239-249. |
|
||