


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (11): 711-720.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2019.11.003
• Lecture of science and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Wan-qing1,XU Mao-dong1,2,JIANG Jian-zhong1,CUI Zheng-gang1( )
)
Received:2019-10-03
Online:2019-11-22
Published:2019-11-26
Contact:
Zheng-gang CUI
E-mail:cuizhenggang@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Wan-qing,XU Mao-dong,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(V) Interactions between like-charged nanoparticles and ionic surfactants(i) Construction of novel emulsions using ultra-low concentration of nanoparticles/surfactants and their stabilization mechanism[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(11): 711-720.
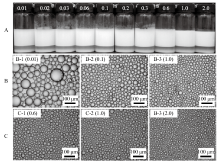
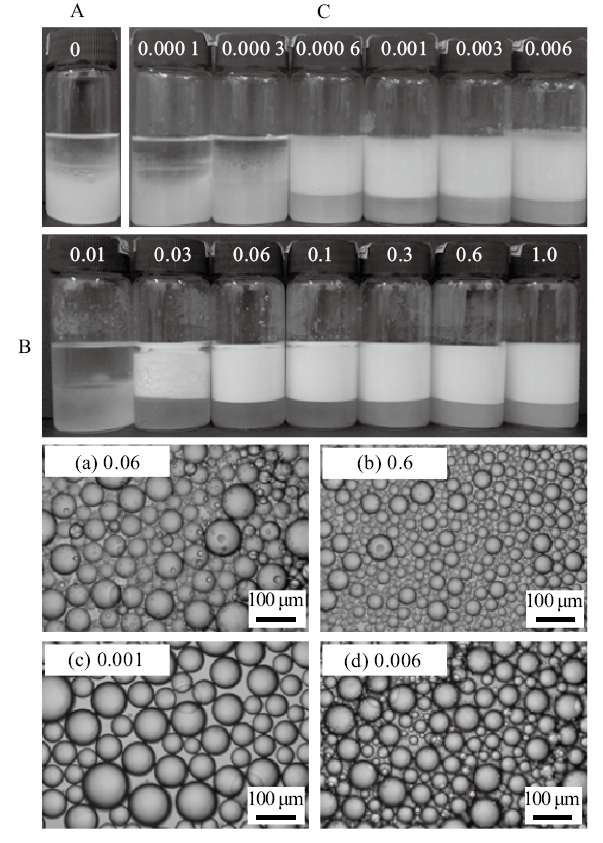
Fig. 3
Digital photographs(A)and selected micrographs(B)of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by mixtures of 0.5% nano-Al2O3 and CTAB of different concentrations, as well as selected micrographs(C)of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by CTAB alone at different concentrations, taken 24 h(B and C)and 1 month(A)after preparation. CTAB concentration(mmol/L)is given on each vessel and image"

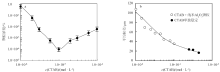
Fig. 5
Correlation between the nano-Al2O3 concentration and the CTAB concentration required for stabilizing n-decane-in-water emulsions(a)at 25 ℃, and average droplet diameter of emulsions co-stabilized by nano-Al2O3 and CTAB and stabilized by CTAB alone as a function of CTAB concentration(b); the average droplet diameter was measured from micrographs of the emulsions"
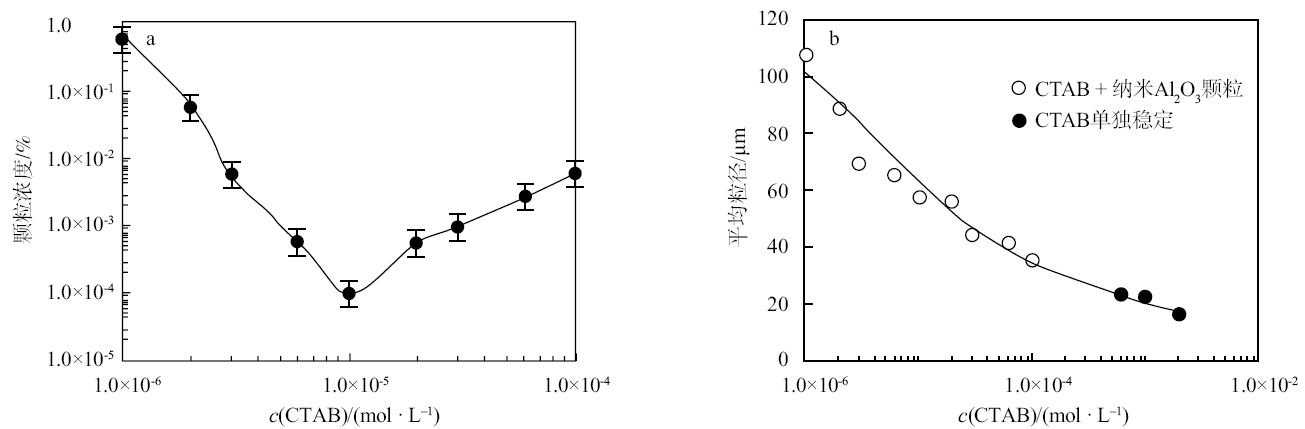
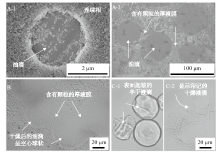
Fig. 6
SEM images(A)and optical micrographs(B)of dried n-hexane-in-water novel emulsion droplets co-stabilized by 0.5% nano-Al2O3 plus 0.1 mmol/L CTAB(A-1, B) or by 0.06% nano-Al2O3 plus 0.03 mmol/L CTAB(A-2), and optical micrographs(C) of n-hexane-in-water Pickering emulsion droplets half dried(C-1)and fully dried(C-2)co-stabilized by 0.5% nano-Al2O3 plus 0.1 mmol/L SDS"
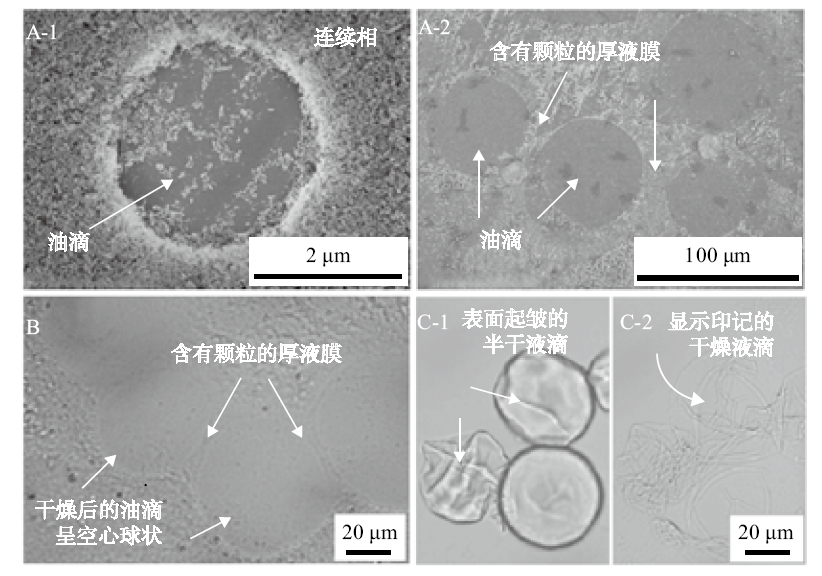
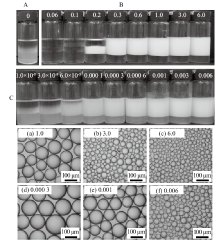
Fig. 7
Digital photographs of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by(A)0.5% nano-SiO2 alone,(B)SDS alone at different concentrations and(C) mixture of 0.5% nano-SiO2 and SDS at different concentrations, as well as micrographs of emulsions stabilized by SDS alone(a-c)and by nano-SiO2 in combination with SDS(d-f), taken 24 h after preparation. SDS concentration(mmol/L)is given on each vessel and image(cmc = 8 mmol/L)"
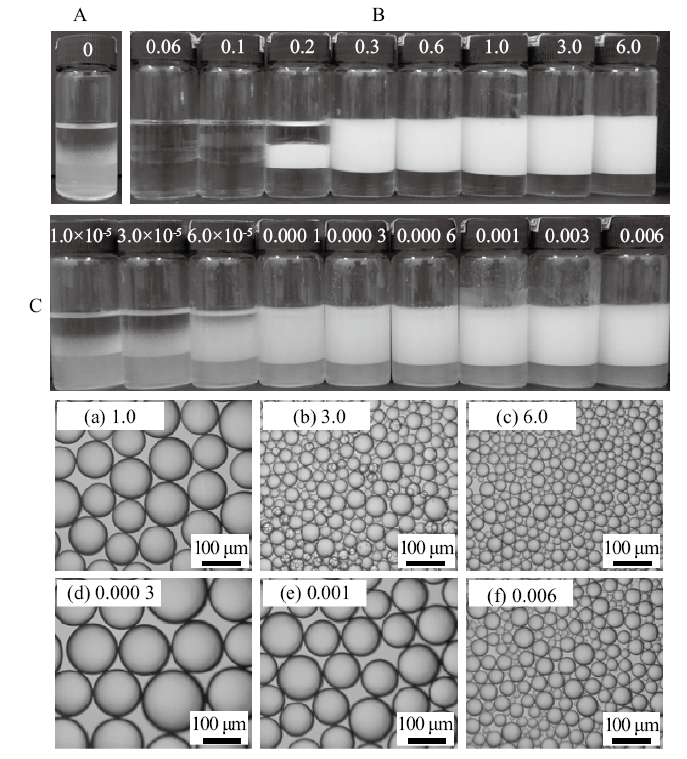

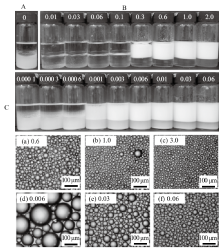
Fig. 8
Digital photographs of toluene-in-water emulsions stabilized by(A)0.5% nano-Al2O3 alone,(B)CTAB alone at different concentrations and(C)mixtures of 0.5% nano-Al2O3 and CTAB at different concentrations, as well as micrographs of emulsions stabilized by CTAB alone(a-c)and by nano-Al2O3 in combination with CTAB(d-f), taken 24 h after preparation. CTAB concentration(mmol/L)is given on each vessel and image(cmc=0.9 mmol/L)"
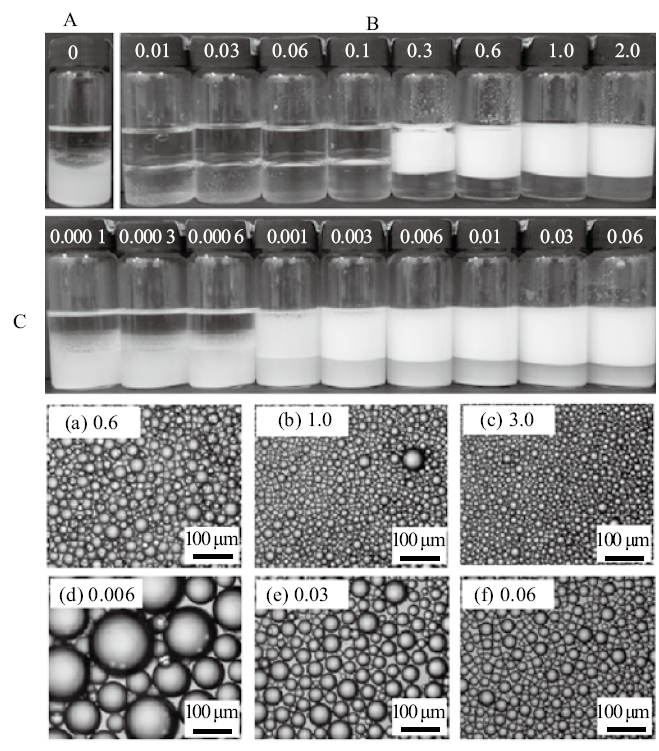
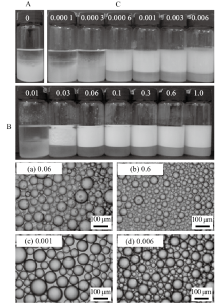
Fig. 9
Digital photographs of tricaprylin-in-water emulsions stabilized by(A)0.5% nano-Al2O3 alone,(B)CTAB alone at different concentrations and(C)mixtures of 0.5% nano-Al2O3 and CTAB at different concentrations, as well as micrographs of emulsions stabilized by CTAB alone(a, b)and by nano-Al2O3 in combination with CTAB(c, d), taken 24 h after preparation. CTAB concentration(mmol/L)is given on each vessel and image(cmc=0.9 mmol/L)"
| [1] | Saji T, Hoshino K, Aoyagui S . Reversible formation and disruption of micelles by control of the redox state of the head group[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1985,107:6865-6868. |
| [2] | Dexter A F, Malcolm A S, Middelberg A P J . Reversible active switching of the mechanical properties of a peptide film at a fluid-fluid interface[J]. Nature Mater., 2006,5:502-506. |
| [3] | Eastoe J, Sánchez-Dominguez M, Wyatta P , et al. A photo-responsive organogel[J]. Chem. Commun., 2004, 2608-2609. |
| [4] | Li L, Rosenthal M, Zhang H , et al. Light-switchable vesicles from liquid-crystalline homopolymer-surfactant complexes[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012,51:11616-11619. |
| [5] | Liu Y X, Jessop P G, Cunningham M , et al. Switchable surfactants[J]. Science, 2006,313:958-960. |
| [6] | Jiang J, Zhu Y, Cui Z , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a switchable surfactant[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013,52:12373-12376. |
| [7] | Liang C, Liu Q X, Xu Z H . Surfactant-free switchable emulsions using CO2-responsive particles[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014,6:6898-6904. |
| [8] | Tang J, Quinlan P J, Tam K C . Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: Recent advances and potential applications[J]. Soft Matter, 2015,11:3512-3529. |
| [9] | Zhu Y, Jiang J Z, Liu K H , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31:3301-3307. |
| [10] | Zhu Y, Pei X, Jiang J , et al. Responsive aqueous foams stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31:12937-12943. |
| [11] | Xu M D, Zhang W Q, Pei X M , et al. CO2/N2 triggered switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by alumina nanoparticles in combination with a conventional anionic surfactant[J]. RSC Advances, 2017,7:29742-29751. |
| [12] | Liu K H, Jiang J Z, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with a conventional zwitterionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2017,33:2296-2305. |
| [13] | Despert G, Oberdisse J . Formation of micelle-decorated colloidal silica by adsorption of nonionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2003,19:7604-7610. |
| [14] | Notley S M . Adsorption of nonionic surfactants with ethylene oxide headgroup chemistry at the titania-water interface[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012,116:6059-6064. |
| [15] | Zhu Y, Fu T, Liu K H , et al. Thermo-responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with alkyl polyoxyethylene ether nonionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2017: 5724-5733. |
| [16] | Arab D, Kantzas A, Bryant S L . Nanoparticle stabilized oil in water emulsions: a critical review[J]. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng., 2018,163:217-242. |
| [17] | Aveyard R, Binks B, Fletcher P D I , et al. Contact angles in relation to the effects of solids on film and foam stability[J]. J. Disper. Sci. Technol., 1994,15(3):251-271. |
| [18] | Sun Q, Li Z, Wang J , et al. Aqueous foam stabilized by partially hydrophobic nanoparticles in the presence of surfactant[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A, 2015,471:54-64. |
| [19] | Xu M D, Jiang J Z, Pei X M , et al. Novel oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by ionic surfactant and similarly charged nanoparticles at very low concentrations[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018,130:7864-7868. |
| [20] | Xu M D, Xu L F, Lin Q , et al. Switchable oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by like-charged surfactant and particles at very low concentration[J]. Langmuir, 2019,35:4058-4067. |
| [21] | Khosravani S, Alaei M, Rashidi A M , et al. O/W emulsions stabilized with γ-alumina nanostructures for chemical enhanced oil recovery[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2013,48(6) : 2186-2190. |
| [22] | Xu M D . Study on the fluid-fluid dispersion systems stabilized by Al2O3 nanoparticles in combination with surfactants and their stimuli-responsive properties[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2019. |
| [23] | Yang F, Liu S, Xu J , et al. Pickering emulsions stabilized solely by layered double hydroxides particles: The effect of salt on emulsion formation and stability[J]. J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2006,302(1):159-169. |
| [24] | Binks B P, Rodrigues J A . Enhanced stabilization of emulsions due to surfactant-induced nanoparticle flocculation[J]. Langmuir, 2007,23:7436-7439. |
| [25] | Becher P . Encyclopedia of Emulsion Technology[M]. Vol 1, Basic Theory. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1983. |
| [26] | Rosen M J, Kunjappu J T . Surfactants and interfacial phenomena[M]. 4 th edition. Hoboken, Wiley , 2012. |
| [27] | Ma H, Luo M X, Dai L L . Influences of surfactant and nanoparticles assembly on effective interfacial tensions[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2008,10:2207-2213. |
| [28] | Haffner B, Khidas Y, Pitois O . Flow and jamming of granular suspensions in foams[J]. Soft Matter, 2014,10:3277-3283. |
| [29] | Khidas Y, Haffner B, Pitois O . Capture-induced transition in foamy suspensions[J]. Soft Matter, 2014,10:4137-4141. |
| [30] | Rouyer F, Haffner B, Louvet N , et al. Foam clogging[J]. Soft Matter, 2014,10:6990-6998. |
| [1] | Zhao Yilu,Cheng Hongxiao,Xu Lina,Wang Xiaodong,Zhao Changxi,Li Xindan,Ren Hong. Optimization and emulsification mechanism of emulsified viscosity reducer with high temperature resistance for heavy oil in Henan Oilfield [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(7): 724-730. |
| [2] | Xu Dekun,Fang Yinjun,Liu Xuefeng. Synergistic effect of N, N-dimethyl-9-decenamide and sodium dodecyl sulfate [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(9): 825-831. |
| [3] | ZHOU Hu-wu,HUO Yong-li,FANG Li,MA Shi-jing,HAN Ping,LIN Li,DU Zhi-yun. Studies on the synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of Ectoin and Madecassoside [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 535-538. |
| [4] | Sun Qing,Fang Yinjun,Liu Xuefeng. Detection of dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide based on aggregation-induced emission phenomenon [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(12): 1163-1170. |
| [5] | LI Yun-qing,WANG Li-yan,TANG Li,LIU Jia-qing,DU Yu-ying,WU Ding-cheng. Bactericidal activity of pyridine-containing heterocyclic ammonium chloride cationic surfactants [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2020, 50(5): 314-318. |
| [6] | KANG Wan-li,LI Xin-xin,ZHAO Yi-lu,WANG Peng-xiang,HOU Xiao-yu,YANG Hong-bin. Construction of N-erucamido-N, N-dimethylamine and benzoic acid fracturing fluid system [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(9): 555-560. |
| [7] | ZHANG Wan-qing,XU Mao-dong,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(VI)Interactions between like-charged nanoparticles and surfactants(ii)Stabilization mechanism and intelligentialization of the novel emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(12): 774-782. |
| [8] | YAO Mei-huan, WEI Xi-lian. Phase diagram and rheological behaviors of 14-3(OH)-14(2Cl)/Brij-30 blend aqueous solution [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2017, 47(2): 61-66. |
| [9] | MIAO Zong-cheng,REN Jian-wei,JI Jing,ZHAO Yang,CHEN Yan-mei. A diester type cationic surfactant based on waste oil from trench sewer and its degradation behavior [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2016, 46(9): 507-510. |
| [10] | LI Gang-sen,ZHAO Lin-xiu,WANG Pei-yi,SU Hao,ZHAI Jia-bin,JIANG Dong-fang. Study on surface activity of N,N'-p-xylylene-bis- (dodecyldimethylammonium chloride)/AEO9 blend systems [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2016, 46(7): 392-396. |
| [11] | CHEN Xiao-xiao,GUO Yan,HAN Chuan-hong,ZHANG Jun-hong,ZHOU Shi-yan,WEI Xi-lian. Effect of addition of salt on solution of Gemini cationic surfactant [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2016, 46(10): 549-554. |
| [12] | HOU Cong, WU Xiao-mei, LAI Lu, CHENG Li, MEI Ping. Studies on the oil/water interfacial properties of anionic/cationic blended Gemini surfactant systems [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2015, 45(12): 697-701. |
| [13] | CHEN Hong, ZHU Bao-wei, ZHANG Dan, ZHAO Wei. Application of anionic-nonionic Gemini surfactants in neutral deinking of waste paper [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2015, 45(12): 702-705. |
| [14] | XIAO Zi-bing, XING Hang, XIAO Jin-xin. Synthesis and performance of a cationic fluorinated surfactant [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2015, 45(11): 611-615. |
| [15] | MA Li-na, YANG Qing-li, WANG Feng-shou, ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Gao-fei. Performance of the blend system of alkyl polyglucoside and octyl imidazoline [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2015, 45(10): 561-563. |
|