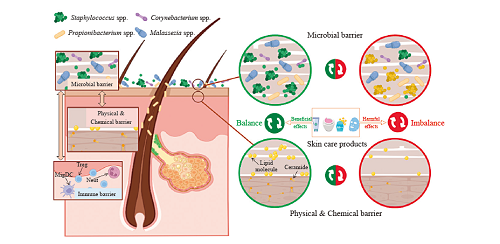
The skin microecosystem is comprised of the components including: the microbiome, encompassing bacteria, fungi, archaea, viruses, protozoa, and other microorganisms; host cells, including epithelial cells, immune cells, and various glands; chemical constituents, such as sebum, sweat, skin care products, environmental molecules, and their metabolic products; and the physical microenvironment, which includes factors such as oxygen, ultraviolet light, and temperature. The microbiome serves as the central component of the skin microecosystem, playing a crucial role in the maintenance of skin homeostasis through its mediation of the interactions among the physical barrier, chemical barrier, and immune barrier. Understanding the skin microecosystem, and how to maintain its delicate balance is an essential way to gain insight into the mechanisms responsible for healthy skin. The daily use of skin care products has become a modern living habit, and its impacts on skin microecosystem cannot be ignored. Therefore, this article aims to summarize the various factors that may affect the skin microecosystem in skin care products, and systematically analyze the common effects, harmful effects, beneficial effects and uncertainty effects. Based on this premise, the following development directions are proposed: further elucidation of the skin microecology mechanism with multi-omics technology, the creation of in vitro skin microecology models, the establishment of evaluation systems and regulations for assessing the effects of skincare products on skin microecology, and the exploration of beneficial skin bacteria and substitutes for potentially harmful ingredients.