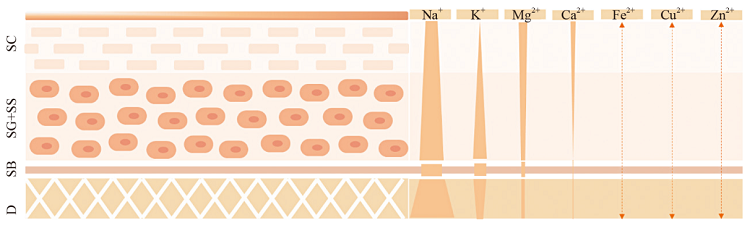
Skin tissues are rich in metal ions. Due to the complexity of skin structure, these ions exist in both free and bound forms. Metal ions have been involved in many biological processes, such as maintaining barrier homeostasis, stimulating wound healing, and balancing redox state. Given their unique characteristics of multi-targets and multi-pathways, metal ions are widely used in skincare applications, exhibiting the functions of promoting skin repairing, soothing, wrinkle reduction, tightening, whitening, etc. Herein, the biological effects and cosmetic applications of metal ions, including calcium, magnesium, potassium, zinc, strontium and copper, were systematically reviewed. The concentration and distribution of common metal ions in skin were summarized. The dermatologic effects and mechanisms were also concluded. Calcium, magnesium and potassium ions were relatively abundant in skin, and they could play important roles in stimulating wound healing, maintaining integrity of skin barrier, and strengthening the barrier. For those ions with trace amount, such as zinc, strontium, copper, iron and manganese, they could exert specific skin functions including inflammation inhibition, reduction of skin sensitivity, or modulation of redox system. In addition, the metal ion-related active ingredients in cosmetic raw materials were summarized and their skin functions were reviewed. Finally, the current limits and challenges for the use of metal ions in skin care products were proposed. This review could shed new light on the design of functional formulas and novel active components.