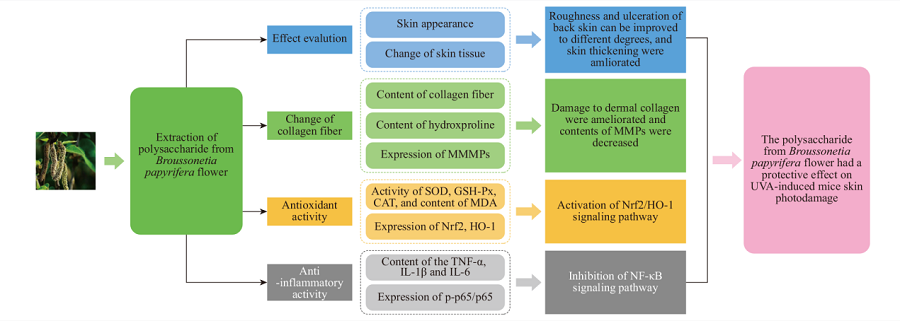
To investigate the protective effect of crude polysaccharide from Broussonetia papyrifera flower on skin photodamage, a total of 56 female Kunming mice were randomly divided into 7 groups: control group, model group, matrix gel group, vitamin A group, and crude polysaccharide low-dose, medium-dose and high-dose groups. The exposed back skin of the mice was irradiated by UVA to induce skin photodamage model, and the drugs were applied to the skin 1 hour before irradiation. After 8 weeks of continuous irradiation, the back skin was scored. The effects of crude polysaccharide from Broussonetia papyrifera flower on the back skin morphology, skin thickness and collagen fibers were investigated by hematoxylin-eosin and Masson staining. And the contents of skin hydroxyproline, SOD, GSH-Px, CAT, MDA, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, and the protein expressions of MMP-1/3, Nrf2, HO-1 and NF-κB pathway were also examined. Pre-treated skin with different dose of crude polysaccharide gel 1 hour before UVA irradiation can improve roughness and ulceration of the back skin to different degrees, ameliorate skin thickening, and dermal collagen damage. At the same time, the activities of SOD, GSH-Px and CAT in skin tissue are increased, and the content of MDA is decreased (P<0.05). The contents of pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, are decreased (P<0.05). The contents of MMP-1 and MMP-3 are decreased significantly (P<0.05), the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 protein are increased (P<0.01), and p-p65/p65 protein are decreased significantly (P<0.05) in the mouse back skin by pre-treatment with crude polysaccharide gel. The crude polysaccharide from Broussonetia papyrifera flower has a strong antioxidant activity in vitro, and a protective effect on UVA-induced mice skin photodamage in vivo. The mechanism may be related to the activation of Nrf2 and inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to the regulation of antioxidative enzyme SOD and improvement of inflammatory response.