


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (9): 561-571.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2019.09.002
• Lecture of science and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Wan-qing,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang( )
)
Received:2019-08-25
Online:2019-09-22
Published:2019-09-19
Contact:
Zheng-gang CUI
E-mail:cuizhenggang@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Wan-qing,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(III)Interactions between oppositely charged nanoparticles and ionic surfactants(ii)Construction of stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions and Pickering foams by using ordinary commercial surfactants[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(9): 561-571.
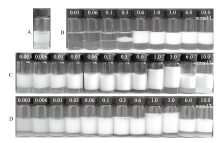
Fig. 1
Photographs of some dodecane-in-water emulsions stabilized by(A)0.5% silica particles alone,(B)CTAB alone at different concentrations and(C, D)mixtures of 0.5% silica nanoparticles and CTAB at different concentrations(mmol/L)as shown on top of the vessels, taken 24 h(A, B, C), and 6 months(D)after preparation"
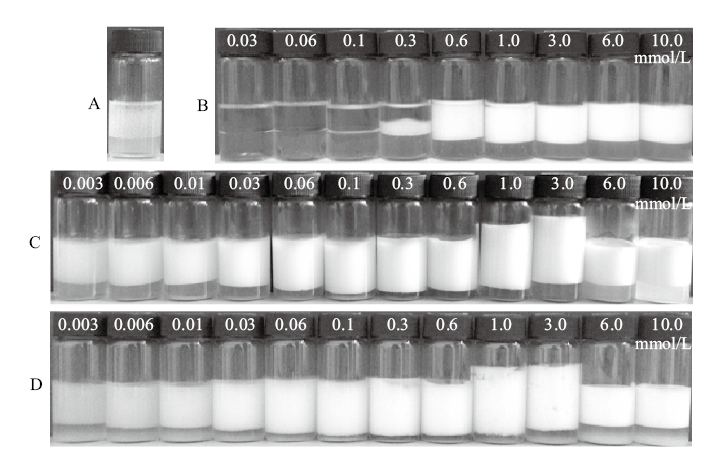
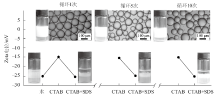
Fig. 2
Photographs and micrographs of the dodecane-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized by 0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.01 mmol/L CTAB, following switching off(by adding 0.01 mmol/L SDS)and switching on(by adding 0.01 mmol/L CTABfollowed by homogenization)cycles taken 24 h after emulsification and demulsification, and change of the Zeta potential(black points, 25 ℃)of the silica nanoparticles in corresponding systems. The CTAB-SDS ion pair concentrations in the systems are 0.01 mmol/L(cycle 1), 0.05 mmol/L(cycle 5)and 0.1 mmol/L(cycle 10), respectively"
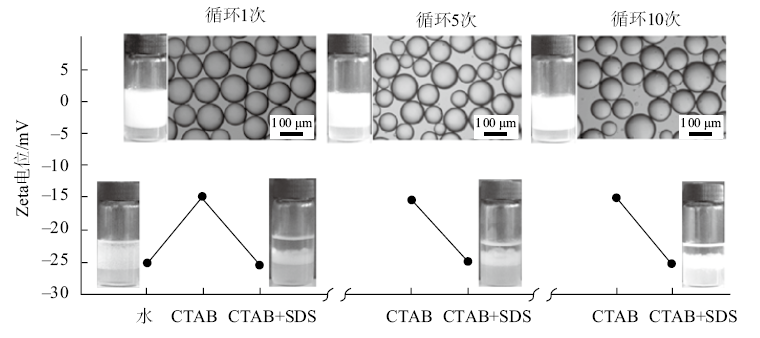
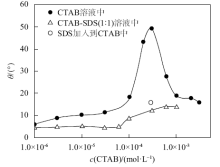
Fig. 4
Contact angles of the aqueous solution of CTAB and the equimolar mixture of CTAB-SDS on hydrophilic glass slides in air at 25 ℃ as a function of initial CTAB concentration. The unfilled circle was measured by adding a drop of SDS solution into a drop of CTAB solution already on a slide both at a concentration of 0.3 mmol/L"
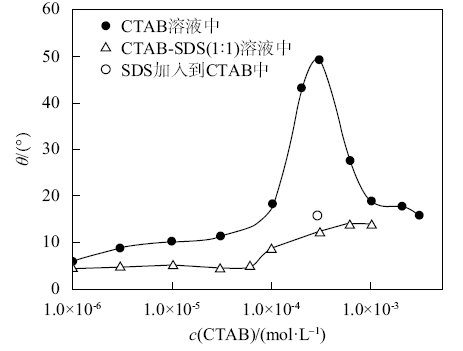
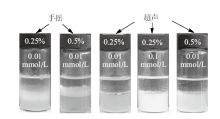
Fig. 5
Photographs of dodecane-in-water emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles + CTAB which were demulsified by adding an equimolar amount of SDS followed by either shaking or sonication for 5 min, taken 2 h after operation. The concentrations of particle(%)and CTAB(mmol/L)are shown on the vessels"
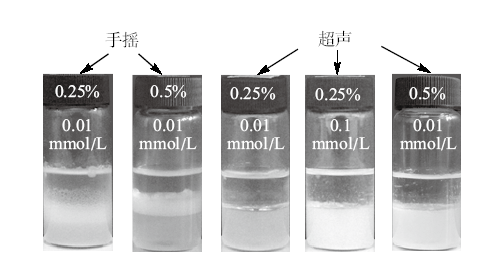
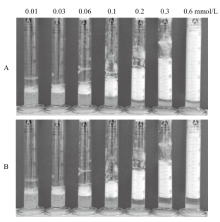
Fig. 7
Digital photographs of aqueous foams stabilized by 0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with CTAB at different concentrations as shown on top of the figure, taken immediately(A)and 30 min(B)after shaking 10 mL concentration of dispersion in cylindrical graduated flasks. CTAB(mmol/L)are shown on top of the figure"
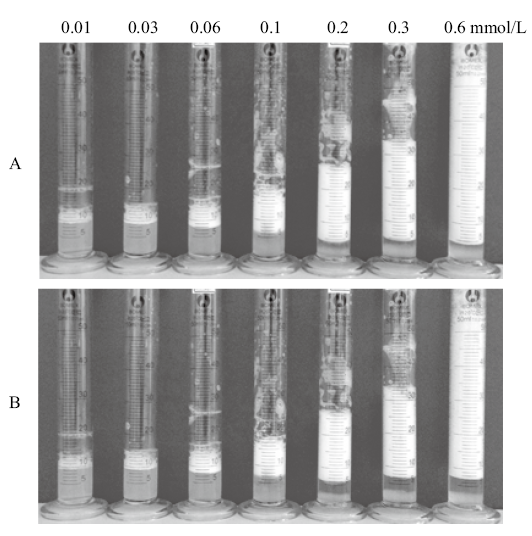
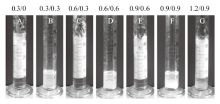
Fig. 8
Photographs of cycles between foaming and defoaming of a dispersion(10 mL)of 0.3 mmol/L CTAB aqueous solution containing 0.5% silica nanoparticles(foaming)by adding equal moles of SDS(0.1 g solution of 30 mmol/L, defoaming), and another amount of free CTAB(0.1 g solution of 30 mmol/L)(foaming again)alternately. The photographs were taken 10 min after shaking, and the total CTAB/SDS concentrations(mmol/L)are shown on top of the figure"
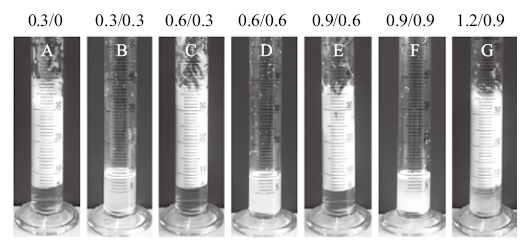
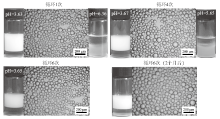
Fig. 11
Photographs and micrographs of the n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5% silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.06 mmol/L DAP following pH alternation cycling, taken 24 h(cycle 1-6)and 2 months(cycle 6 only)after homogenization(for stable emulsions)and 20 min after adding dropwise NaOH solution with agitation(for unstable emulsions)"
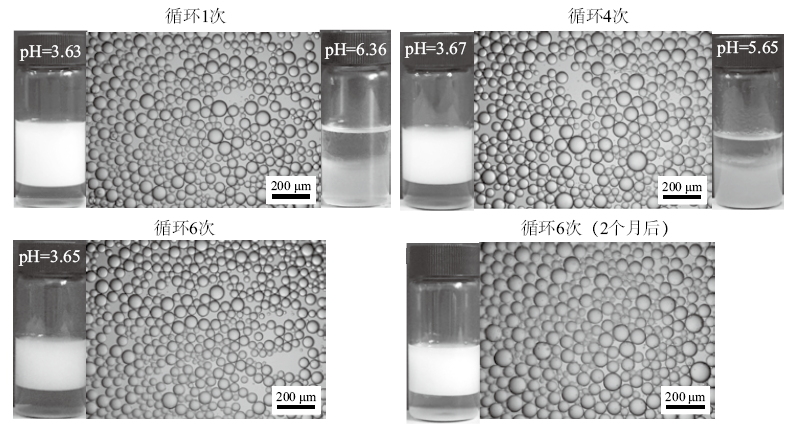

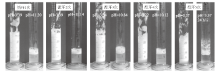
Fig. 14
Photographs showing cycles between foaming and defoaming of a 10 mL dispersion of 0.5% silica nanoparticles in aqueous C12B solution(0.6 mmol/L)at room temperature(20-25 ℃), taken immediately after shaking(foaming)and gentle mixing (defoaming)following adding dropwise HCl and NaOH aqueous solutions, respectively"
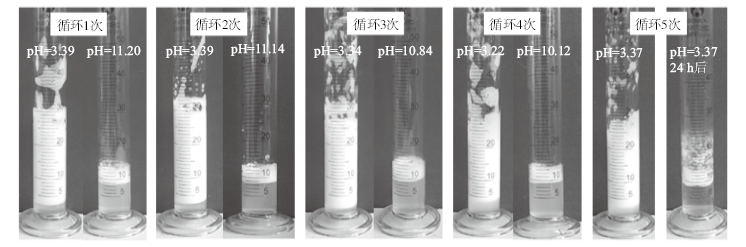
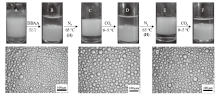
Fig. 15
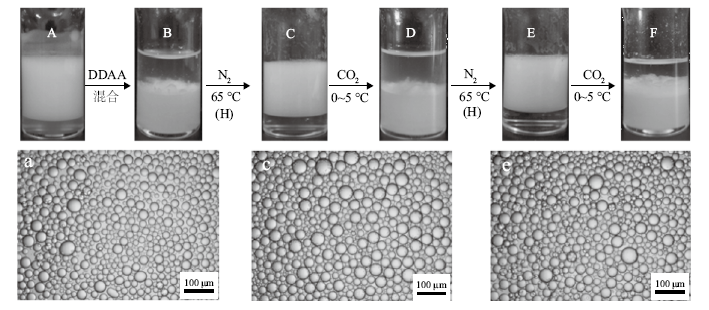
Digital photographs of n-decane-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized by 0.5% alumina nanoparticles in combination with 0.3 mmol/L SDS(A), and then 0.3 mmol/L DDAA was added, which was transformed between demulsified state(B, D and F)and emulsified state(C and E)by alternately switching on(bubbling with CO2 at a flow rate of 160 mL/min at 0-5 ℃ for 80 min)and switching off(bubbling with N2 at a flow rate of 160 mL/min at 65 ℃ for 80 min)the CO2/N2 switchable surfactant followed by homogenization(H). Micrographs of the corresponding stable emulsions are also given(a, c and e)"
| [1] | Lin Q, Xu M D, Cui Z G , et al. Structure and stabilization mechanism of diesel oil-in-water emulsions stabilized solely by either positively or negatively charged nanoparticles[J]. Colloids Surfaces A, 2019,573:30-39. |
| [2] | Liu Y X, Jessop P G, Cunningham M , et al. Switchable surfactants[J]. Science, 2006,313:958-960. |
| [3] | Jiang J Z, Zhu Y, Cui Z G , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ by a switchable surfactant[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013,52:12373-12376. |
| [4] | Tang J, Quinlan P J, Tam K C . Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: Recent advances and potential applications[J]. Soft Matter, 2015,11(18) : 3512-3529. |
| [5] | Yu S J, Zhang D Y, Jiang J Z , et al. Biphasic biocatalysis using a CO2-switchable Pickering emulsion[J]. Green Chem., 2019,21:4062-4068. |
| [6] | Zhu Y, Jiang J Z, Liu K H , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31(11) : 3301-3307. |
| [7] | Zhu Y, Pei X, Jiang J , et al. Responsive aqueous foams stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2015,31(47) : 12937-12943. |
| [8] | Xu M D, Zhang W Q, Pei X M , et al. CO2/N2 triggered switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by alumina nanoparticles in combination with a conventional anionic surfactant[J]. RSC Advances, 2017,7:29742-29751. |
| [9] | Liu K H, Lin Q, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with N-dodecyl-β-aminopropionate[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2017,38:85-93. |
| [10] | Liu K H, Jiang J Z, Cui Z G , et al. pH-Responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with a conventional zwitterionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2017,33(9) : 2296-2305. |
| [11] | Lin Q, Liu K H, Cui Z G , et al. pH-responsive Pickering foams stabilized by silica nanoparticles in combination with trace amount of dodecyl dimethyl carboxyl betaine[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A, 2018,544:44-52. |
| [12] | Tomlinson E, Davis S S, Mukhayer G I. Ionic interaction and phase stability, in Solution Chemistry of Surfactants[M]. Volume 1,ed. by Mittal K L, New York:, Plenum Press, 1979. |
| [13] | Cui Z G, Canselier J P . Interfacial and micellar properties of some anionic/cationic binary surfactant systems. 1. Surface properties and prediction of surface tension[J]. Colloid Polym. Sci., 2000,278:22-29. |
| [14] | Cui Z G, Canselier J P . Interfacial and aggregation properties of some anionic/cationic binary surfactant systems. II. Mixed micelle formation and surface tension reduction effectiveness[J]. Colloid Polym. Sci., 2001,279:259-267. |
| [15] | Kume G, Gallotti M, Nunes G . Review on anionic/cationic surfactant mixtures[J]. Journal of Surfactants & Detergents, 2008,11(1) : 1-11. |
| [16] | Tah B, Pal P, Mahato M , et al. Aggregation behavior of SDS/CTAB cataninic surfactant mixture in aqueous solution and at the air/water interface[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2011,115:8493-8499. |
| [17] | Cui Z G, Yang L L, Cui Y Z , et al. Effects of surfactant structure on the phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by mixtures of silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactants[J]. Langmuir, 2010,26(7) : 4717-4724. |
| [18] | Zhu Y . Controllable and switchable/stimuli-responsive surface active inorganic nanoparticles[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015. |
| [19] | Cui Z G, Shi K Z, Cui Y Z , et al. Double phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by a mixture of CaCO3, nanoparticles and sodium dodecyl sulphate[J]. Colloids & Surfaces A, 2008,329:67-74. |
| [20] | Cui Z G, Cui Y Z, Cui C F , et al. Aqueous foams stabilized by in situ surface activation of calcium carbonate nanoparticles via adsorption of anionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2010,26:12567-12574. |
| [21] | Fang Y, Xia Y M . Amphiphilic surfactants (I) : Review of amphiphilic surfactants[J]. China Surfactants Detergents and Cosmetics, 2000 ( 3) : 53-55. |
| [22] | Xu H J, Liu X M, Cao H X , et al. Synjournal and properties of N-alkyl-β-aminopropionate[J]. Detergent and Cosmetics, 1999: 47-49. |
| [1] | Pei Liu, Ting Pan, Xiaomei Pei, Binglei Song, Jianzhong Jiang, Zhenggang Cui, Bernard P. Binks. Dual-responsive oil-in-water emulsions co-stabilized by a nonionic-anionic Bola surfactant and silica nanoparticles [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | Ting Pan, Junhui Wu, Xiaomei Pei, Zhenggang Cui. Temperature and pH responsive behavior of wormlike micelles formed by novel pseudo-gemini surfactant [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(12): 1361-1368. |
| [3] | GONG Cheng-yi,YU Hao,WANG Qi-qi,SUN Ji-yong,SONG Ai-xin. Progress on stimulus-responsive Pickering emulsions and their applications [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 554-563. |
| [4] | Mu Meng,Zhang Xing,Jiang Yan,Li Jianbing,Lu Pingping,Zhang Yongmin. pH-responsive vesicles based on dynamic covalent bond [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(11): 1060-1066. |
| [5] | CUI Xiu,FANG Bo,XU Hai-tao. Rheological properties of pH-responsive viscoelastic micellar system of oleylamidopropyl dimethyl amine/potassium hydrogen phthalate [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2020, 50(7): 433-438. |
| [6] | CHEN Zhao,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(II)Interaction of the nanoparticle with an oppositely charged ionic surfactant(i) Construction of switchable Pickering emulsions and Pickering foams via switch transference [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(8): 492-502. |
| [7] | JIANG Jian-zhong,YU Shi-jie,CUI Zheng-gang. The interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(I)——Switchable or stimuli-responsive surfactants and smart surfactant systems [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(7): 426-434. |
| [8] | Yang YU,Li-qiang ZHENG,Ji-chao SUN. Self-assembly of surfactants controlled by weak interactions(Ⅲ) Responsive surfactants [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(3): 141-149. |
| [9] | ZHANG Wan-qing,XU Mao-dong,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(VI)Interactions between like-charged nanoparticles and surfactants(ii)Stabilization mechanism and intelligentialization of the novel emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(12): 774-782. |
| [10] | SUN Xiao-feng,LI Hong-guang. Carbon quantum dot-doped worm-like micelles [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2018, 48(9): 483-488. |
| [11] | QIN Fei, LIU Xue-feng. Dual stimuli-responsive properties of ammonium 11-benzylselanyl undecanoate [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2018, 48(3): 123-128. |
| [12] | ZHANG Meng, QI Li-yun, LONG Yu, WANG Ji-yuan, QI Song-zhu, HUANG Yuan-lin, FANG Xue-jin. Study on rheological behaviors of pH-responsive wormlike micelles formed by an amine oxide surfactant [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2017, 47(6): 301-306. |
|