


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (8): 492-502.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2019.08.002
• Lecture of science and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Zhao,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang( )
)
Received:2019-06-25
Online:2019-08-22
Published:2019-08-26
Contact:
Zheng-gang CUI
E-mail:cuizhenggang@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
CHEN Zhao,JIANG Jian-zhong,CUI Zheng-gang. Interactions between surfactants and nanoparticles and the construction of smart systems(II)Interaction of the nanoparticle with an oppositely charged ionic surfactant(i) Construction of switchable Pickering emulsions and Pickering foams via switch transference[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2019, 49(8): 492-502.

Fig. 7
Digital photographs and micrographs of n-octane-in-water emulsions stabilized by(A)silica nanoparticles solely at different concentrations, (B)CTAB solely at different concentrations, (C)1.0% silica nanoparticles plus CTAB at different concentrations, (a)3.0 mmol/L CTAB alone, (b)1.0% silica nanoparticles plus 0.01 mmol/L CTAB; (c)1.0% silica nanoparticles plus 0.1 mmol/L CTAB, and(d)1.0% silica nanoparticles plus 10 mmol/L CTAB, taken a week after preparation(Scale bar=100 μm)"
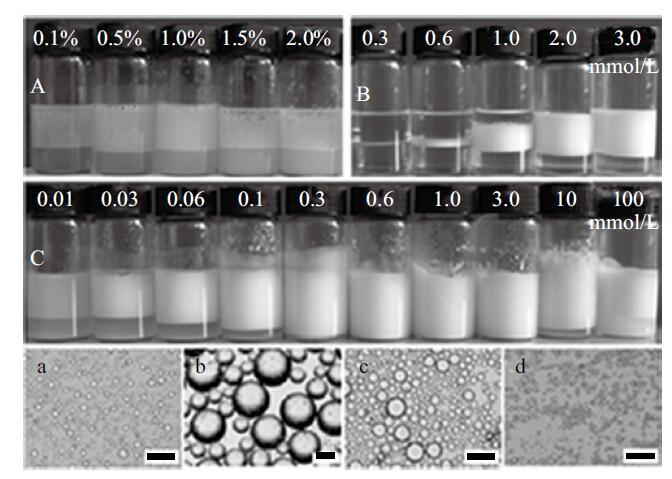
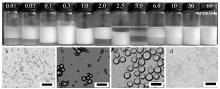
Fig. 8
Digital photographs and micrographs of n-octane-water emulsions stabilized by 0.1% silica nanoparticles in combination with diC12DMAB at different concentrations, taken a week after preparation.(a)3.0 mmol/L diC12DMAB;(b)1.0% silica nanoparticles plus 0.01 mmol/L diC12DMAB;(c)1.0% silica nanoparticles plus 2.5 mmol/L diC12DMAB; and(d)1.0% silica nanoparticles plus 30 mmol/L diC12DMAB(Scale bar=100 μm)"
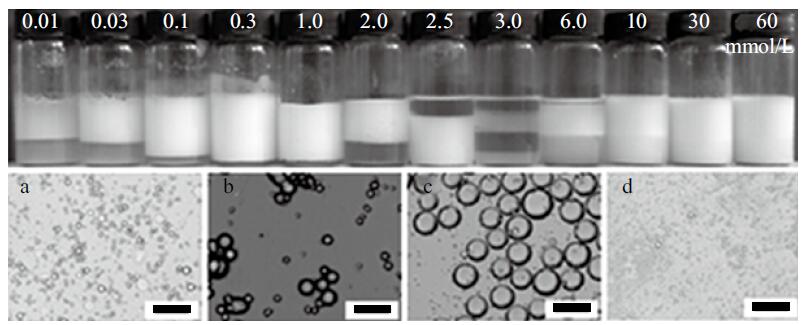
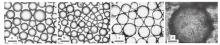
Fig. 12
Micrographs of emulsion droplets stabilized solely by CaCO3 nanoparticles taken 24 h after preparation.(a)toluene-in-water, 2% particles;(b)toluene-in-water, 3% particles;(c)n-octane-in-water, 2% particles;(d)n-octane-in-water, 3% particles(Scale bar is 500 μm for(a, b, c)and 50 μm for(d))"
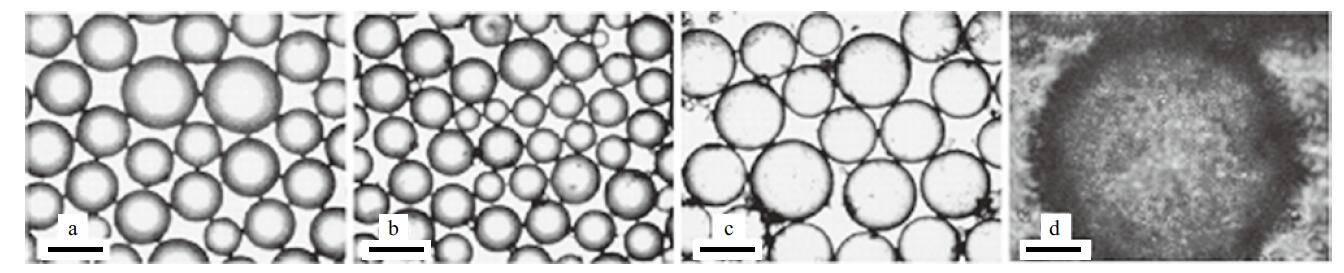
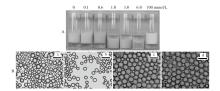
Fig. 13
Digital photographs(A)and micrographs(B)of toluene-water emulsions stabilized by 2 wt.% CaCO3 nanoparticles with SDS at different concentrations taken 24 h after preparation.(a)0.3 mmol/L SDS, O/W(1);(b)2 mmol/L SDS, W/O;(c)6 mmol/L SDS, O/W(2);(d)6 mmol/L SDS alone(Scale bar denotes 500 μm for a, b and 20 μm for c, d)"
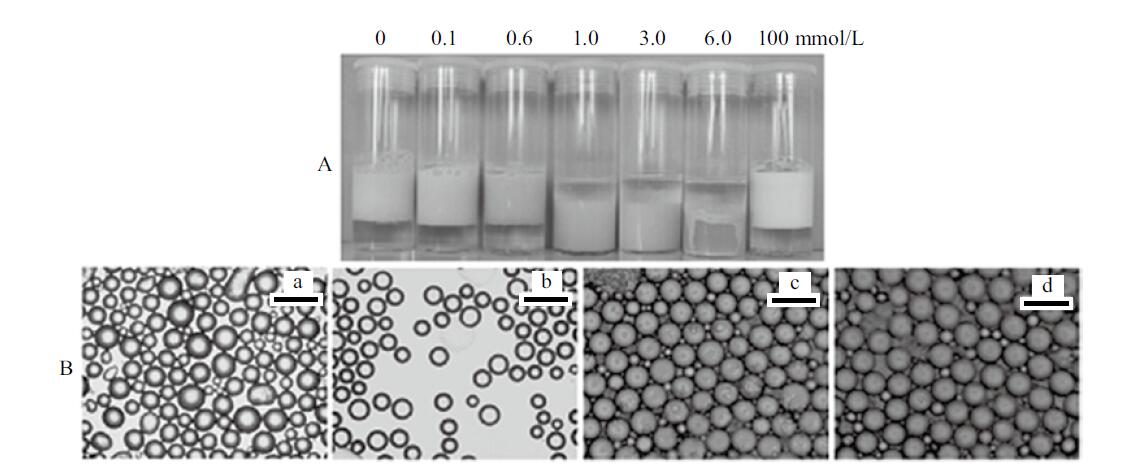

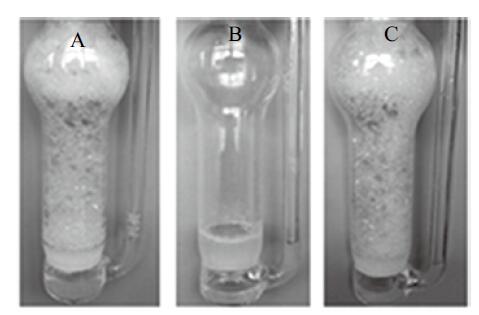
Fig. 17
Digital photographs of n-octane-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized by 0.5 wt.% silica nanoparticles together with(a~h)0.3 mmol/L switchable surfactant undergoing switching or(i, j)0.1 mmol/L CTAB.(a)Emulsion with amidinium(10 mL:10 mL);(b)transferred to bubbling device;(c)bubbling N2 at 65 ℃ for 80 min;(d)transferred to vessel;(e)re-homogenized for 2 min, 24 h later;(f)one week later;(g)bubbling CO2 in ice bath for 50 min followed by re-homogenization for 2 min, one week later;(h)emulsion(7 mL∶7 mL)with amidinium kept at 65 ℃ for 24 h without bubbling N2;(i)Emulsion(7 mL∶7 mL)with CTAB, 24 h later;(j)emulsion with CTAB after bubbling N2 at 65 ℃ for 80 min, 24 h later"

Fig. 18
Digital photographs of aqueous foams stabilised by(A)0.5 wt.% silica nanoparticles alone; (B)N′-dodecyl-N, N-dimethylacetamidinium alone at different concentrations, and(C and D)0.5 wt.% silica nanoparticles in combination with N′-dodecyl-N, N-dimethylacetamidinium at different concentrations, taken immediately after shaking(A, B, C)and 24 h later(D); Surfactant concentrations in B, C, D from left to right are: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.6, 1, 2, 3 and 6 mmol/L"
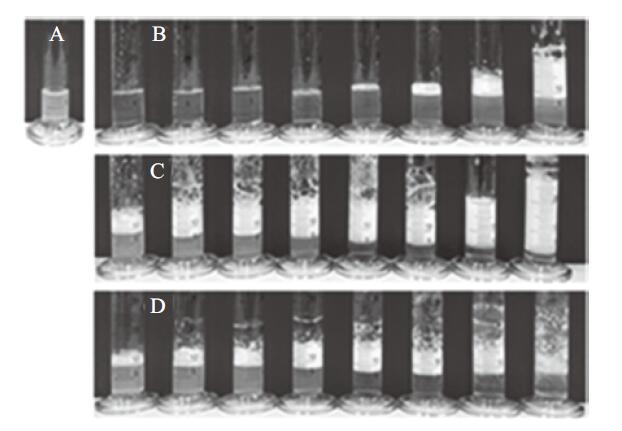
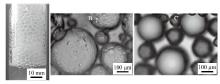
Fig. 19
(A)Photograph of the foam stabilized by 0.5 wt.% silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.3 mmol/L N′-dodecyl-N, N- dimethylacetamidinium, taken immediately after bubbling with N2 at room temperature for 5 min;(B)micrograph of the bubbles(produced by shaking)stabilized by 0.5 wt.% silica nanoparticles in combination with 1.0 mmol/L N′-dodecyl-N, N- dimethylacetamidinium;(C)micrograph of the bubbles stabilized by 1.0 mmol/L amidinium solely, taken immediately after shaking"
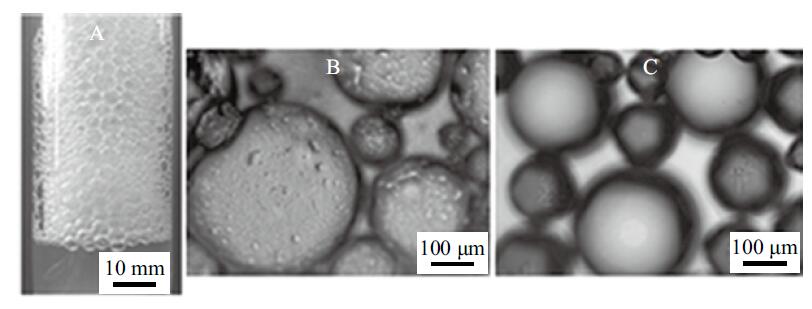
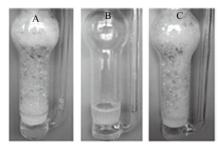
Fig. 20
Photographs of the dispersion of 0.5 wt.% silica nanoparticles in 0.3 mmol/L N′-dodecyl-N, N-dimethylacetamidinium aqueous solution in a bubbling device following bubbling with N2(160 mL/min)at 65 ℃ initially(A); bubbling with N2(160 mL/min)at 65 ℃ for 80 min(B)and then bubbling with CO2(160 mL/min)at 0-5 ℃ for 50 min(C)"
| [1] | Ramsden W . Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and ‘suspensions’[J]. Proc. Roy. Soc., 1903,72:156-164. |
| [2] | Pickering S U . Emulsions[J]. J. Chem. Soc., 1907,91:2001-2021. |
| [3] | Finkle P, Draper H D, Hildebrand J H . The theory of emulsification[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1923,45(12) : 2480-2788. |
| [4] | Briggs T R . Emulsions with finely divided solids[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1921,13(11) : 1008-1010. |
| [5] | Schulman J H, Leja J . Control of contact angles at the oil-water-solid interfaces: Emulsions stabilized by solid particles (BaSO4)[J]. Trans. Faraday Soc., 1954,50:598-605. |
| [6] | Levine S, Bowen B D, Partridge S J . Stabilization of emulsions by fine particles 1. Partitioning of particles between continuous phase and oil/water interface[J]. Colloid surf., 1989,38:325-343. |
| [7] | Levine S, Bowen B D, Partridge S J . Stabilization of emulsions by fine particles II: Capillary and van der Waals forces between particles[J]. Colloids Surf., 1989,38:345-364. |
| [8] | Tambe D E, Sharma M M . Factors controlling the stability of colloid-stabilized emulsions. I: An experimental investigation[J]. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993,157:244-253. |
| [9] | Tambe D E, Sharma M M . The effects of colloid particles on fluid-fluid interfacial properties and emulsion stability[J]. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 1994,52:1-63. |
| [10] | Aveyard R , Binks B P and Clint J H. Emulsions stabilized solely by solid colloid particles[J]. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003,100:503-546. |
| [11] | Binks B P , Particles as surfactants—similarities and differences[J]. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 2002,7:21-41. |
| [12] | Binks B P, Horozov T S. Colloid particles at liquid interfaces[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006. |
| [13] | Chevalier Y, Bolzinger M A . Emulsion stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions[J]. Colloid Surf. A, 2013,439:23-34. |
| [14] | Schrade A, Landfester K, Ziener U . Pickering-type stabilized nanoparticles by heterophase polymerization[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013,42:6823-6839. |
| [15] | Tang J, Quinlan P J, Tam K C . Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: recent advances and potential applications[J]. Soft Matter, 2015,11:3512-3529. |
| [16] | Toor A, Feng T, Russell T P . Self-assembly of nanomaterials at fluid interfaces[J]. Eur. Phys. J. E, 2016,39(5) : 57. |
| [17] | Wu J, Ma G H . Recent studies of Pickering emulsions: particles make the difference[J]. Small, 2016,12:4633-4648. |
| [18] | Yang Y, Fang Z, Chen X , et al. An overview of Pickering emulsions: solid-particle materials, classification, morphology, and applications[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2017,8:287. |
| [19] | Shi S, Russell T P . Nanoparticle assembly at liquid-liquid interfaces: from the nanoscale to mesoscale[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018,30:1800714. |
| [20] | Hunter T N, Pugh R J, Franks G V , et al. The role of particles in stabilizing foams and emulsions[J]. Adv. Colloid Interface. Sci., 2018,137:57-81. |
| [21] | Tadros T F. Surfactants[M]. London: Academic Press, 1984. |
| [22] | Cui Z G, Yang L L, Cui Y Z , et al. Effects of surfactant structure on the phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by mixtures of silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2010,26:4717-4724. |
| [23] | Cui Z G, Li W, Qi J J , et al. Individual and mixed adsorption of alkylcarboxylbetaines and fatty amide ethoxylates at Daqing sandstone/water interface[J]. Colloids Surf. A, 2012,414:180-189. |
| [24] | Binks B P, Rodrigue J A, Frith W J . Synergistic interaction in emulsions stabilized by a mixture of silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2007,23:3626-3636. |
| [25] | Lan Q, Yang F, Zhang S , et al. Synergistic effect of silica nanoparticle and cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide on the stabilization of O/W emulsions[J]. Colloids Surf. A, 2007,302:126-135. |
| [26] | Chen Zhao , Cui ChenFang, Cui ZhengGang. Interaction between silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactants and thereby induced double phase inversion of n-octane-water emulsions[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2010,31:2246-2253. |
| [27] | Binks B P, Rodrigues J A . Double inversion of emulsions by using nanoparticles and a di-chain surfactant[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007,46:5389-5392. |
| [28] | Cui Z G, Shi K Z, Cui Y Z , et al. Double phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by a mixture of CaCO3 nanoparticles and sodium dodecyl sulphate[J]. Colloids Surf. A, 2008,329:67-74. |
| [29] | Cui Z G, Cui C F, Zhu Y , et al. Multiple phase inversion of emulsions stabilized by in situ surface activation of CaCO3 nanoparticles via adsorption of fatty acids[J]. Langmuir, 2012,28:314-320. |
| [30] | Xu M D, Zhang W Q, Pei X M , et al. CO2/N2 triggered switchable pickering emulsions stabilized by alumina nanoparticles in combination with a conventional anionic surfactant[J]. RSC Advances, 2017,7:29742-29751. |
| [31] | Cui Z G, Cui Y Z, Cui CF , et al. Aqueous foams stabilized by in situ surface activation of calcium carbonate nanoparticles via adsorption of anionic surfactant[J]. Langmuir, 2010,26:12567-12574. |
| [32] | Liu Y, Jessop P G, Cunningham M , et al. Switchable surfactants[J]. Science, 2006,313:958-960. |
| [33] | Jiang J Z, Zhu Y, Cui Z G , et al. Switchable Pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ by a switchable surfactant[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013,52:12373-12376. |
| [34] | Zhu Y, Jiang J Z, Cui Z G , et al. Responsive aqueous foams stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a switchable surfactant[J]. Soft Matter, 2014,10:9739-9745. |
| [1] | Pei Liu, Ting Pan, Xiaomei Pei, Binglei Song, Jianzhong Jiang, Zhenggang Cui, Bernard P. Binks. Dual-responsive oil-in-water emulsions co-stabilized by a nonionic-anionic Bola surfactant and silica nanoparticles [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | Ding Zhengqing, Wu Yingyi, Wang Weiyun, Huang Xujuan, Cai Zhaosheng. Study on Pickering emulsion stabilized by hydroxyethyl cellulose/nanocellulose and its rheological properties [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(3): 245-252. |
| [3] | Chen Ningru, Zhang Ruoqi, Han Xu, Shang Yazhuo. New emulsion system and its application in cosmetics (III)Pickering emulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(11): 1257-1265. |
| [4] | Shen Jiajun,Huan Jingjing,Wang Bijia,Sui Xiaofeng. Properties of oleogel-in-water Pickering emulsion stabilized by nano-chitin [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(8): 844-850. |
| [5] | Zhang Qianjie,Shen Xingliang,Sheng Taotao,Zhang Wanping,Xu Jianying. The interaction of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide-pearl powder and its stabilization of the double phase inversion in emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(5): 468-475. |
| [6] | Xie Xin,Wang Weihao,Liu Huanyu,Sun Mengmeng,Li Qinyuan,Jia Lufan,Meng Tao. Study on the Pickering emulsion stabilized by Alg@TiO2 microspheres for sunscreen formulation [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(3): 229-236. |
| [7] | Chen Yunbo,Li Xinyi,Mao Zhiping,Xu Hong,Sui Xiaofeng. Fabrication of phase change microcapsules via nano-chitin stabilized Pickering emulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(12): 1286-1292. |
| [8] | Huan Jingjing,Wang Bijia,Mao Zhiping,Sui Xiaofeng. Rapid preparation of nano-chitin for stabilizing Pickering emulsions [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2022, 52(10): 1081-1087. |
| [9] | Shen Yongqiang,Sun Yajuan,Yang Cheng,Wang Jing. Study on the preparation and emulsifying properties of peach seed protein isolate nanoparticles [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(9): 809-816. |
| [10] | Yu Hui,Zhu Yongfeng,Hui Aiping,Yang Fangfang,Wang Aiqin. Advances in the application of attapulgite in Pickering emulsion preparation [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(7): 670-678. |
| [11] | GONG Cheng-yi,YU Hao,WANG Qi-qi,SUN Ji-yong,SONG Ai-xin. Progress on stimulus-responsive Pickering emulsions and their applications [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 554-563. |
| [12] | FANG Zhen-xing,WANG Xi-ying,WU Jing,ZENG Ying,PAN Hong,XIE Zhen-hua. Preparation of Pickering emulsion from volcano mud and its pH stability [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(6): 506-512. |
| [13] | HE Yi-jing,XU Hu-jun. Preparation of Pickering emulsion stabilized by lauroyl lysine [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(5): 413-420. |
| [14] | CHEN Feng-feng,TAO Sheng-nan,GONG Sui-jing,ZHANG Sheng-wei,SUN Ya-juan,YANG Cheng,LI Yun-xing. Cosmetic emulsions and new technologies of emulsification (I) Fundamental principles of Pickering emulsions and their applications in cosmetics [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(2): 89-97. |
| [15] | Hu Jiawen,Fan Ye,Fang Yun,Wang Hong. Aqueous two-phase Pickering emulsions stabilized by the CLAA@CaCO3 nanoparticles [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(12): 1186-1191. |
|