


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 757-764.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-2806.2023.07.004
• Development and application • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhou Lidan,Lu Yina( ),Yang Jifeng,Shi Xuemei,Xiong Yue,Zhang Lei
),Yang Jifeng,Shi Xuemei,Xiong Yue,Zhang Lei
Received:2022-12-19
Revised:2023-06-21
Online:2023-07-22
Published:2023-07-25
Contact:
*E-mail: inna_lu@jakabiotech.com.
CLC Number:
Zhou Lidan, Lu Yina, Yang Jifeng, Shi Xuemei, Xiong Yue, Zhang Lei. The protection mechanism of multi-herb extract CAP against exogenous cutaneous stimulation[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(7): 757-764.
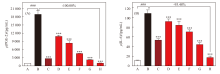
Fig. 1
CAP suppressed PGE-2 (A) and IL-6 (B) levels (estimated by ELISA) in NHEK cells A: Negative control group (NC, untreated group); B: Model control group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C); C: Positive control group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C)+1 μmol/L Dex; D-H: Test group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C)+0.125%, 0.25%, 0.5%, 1% and 2% CAP. *** indicated P<0.001 vs B; ### indicated P<0.001 vs A"
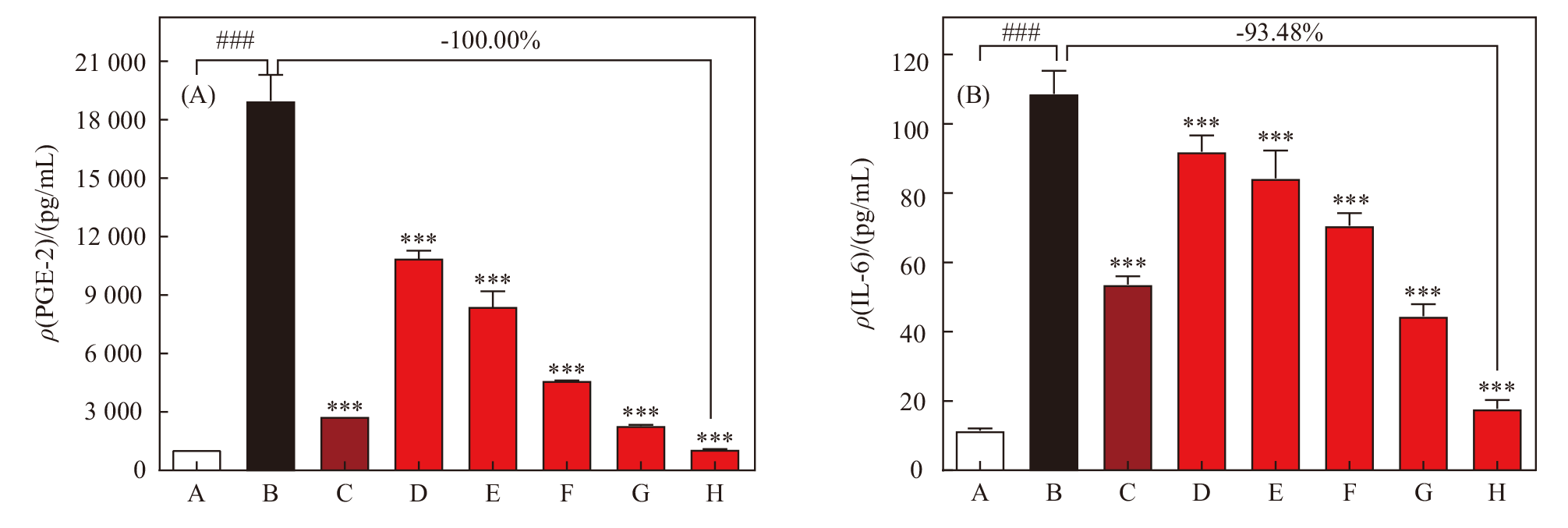
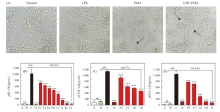
Fig. 2
CAP affected signal cytokines produced in THP-1 cells (A) THP-1 cells differentiate to M2 macrophages after PMA treatment. (Magnification: 100X); (B-D) ELISA estimation of IL-6, TNF-α and PGE-2 levels in PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells induced with LPS A: Negative control group (NC, untreated group); B: Differentiated cell control group, 50 ng/mL PMA ; C: Model control group, 1 μg/mL LPS+50 μg/mL PMA; D: Positive control group, 1 μg/mL LPS+50 μg/mL PMA +1 μmol/L Dex; E1-L1: Test group, 1 μg/mL LPS+50 μg/mL PMA +0.015%, 0.03%, 0.06%, 0.125%, 0.25%, 0.5%, 1% and 2% CAP. E2-H2: Test group, 1 μg/mL LPS+50 μg/mL PMA +0.25%, 0.5%, 1% and 2% CAP. E3-I3: Test group, 1 μg/mL LPS+50 μg/mL PMA+0.125%, 0.25%, 0.5%, 1% and 2% CAP. *** indicated P<0.001 vs C; ### indicated P<0.001 vs A"

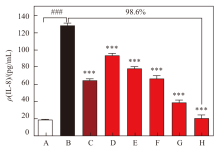
Fig. 3
CAP inhibited IL-8 level in C48/80-activated mast cells A: Negative control group (NC, untreated group); B: Model control group, 20 μg/mL C48/80; C: Positive control group, 20 μg/mL C48/80 +1 μmol/L Dex; D~H: Test group, 20 μg/mL C48/80 +0.125%, 0.25%, 0.5%, 1% and 2% CAP. ***indicated P<0.001 vs B; ### indicated P<0.001 vs A"
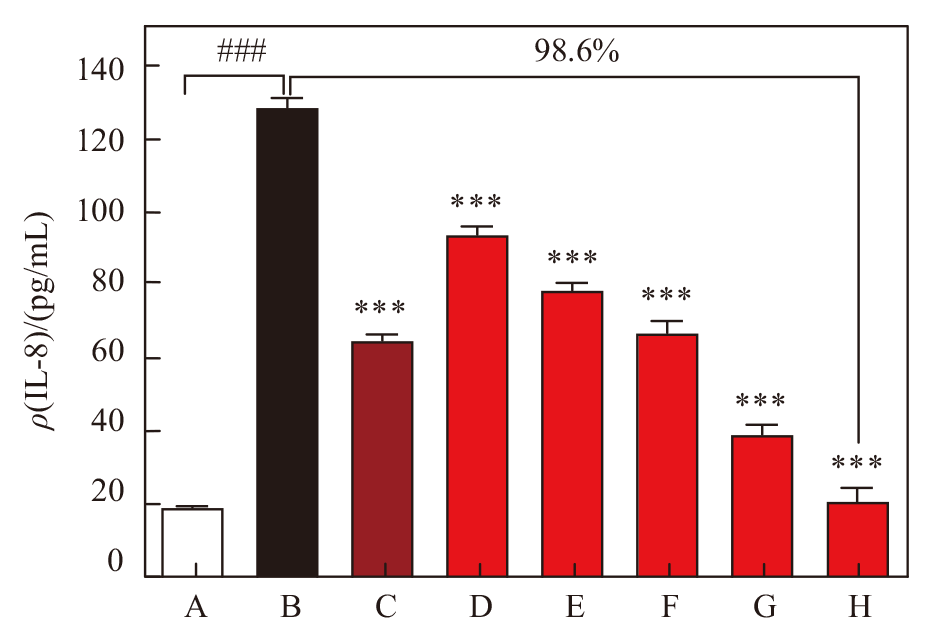
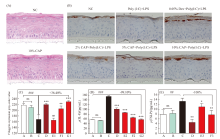
Fig. 4
Regulatory effect of CAP in EpiKutis. (A) Epikutis tissue structure assay by HE staining (400×). (B) Immunohistochemical staining of filaggrin expression in EpiKutis. CAP promoted poly (I:C)+LPS-induced filaggrin expression (400×). Filaggrin is stained brown and nuclei are stained blue. (C) Gray-scale analysis of filaggrin protein expression as revealed by immunohistochemical experiments. (D, E) ELISA estimation of IL-8 and TSLP levels in EpiKutis induced with poly (I:C) and LPS A: Negative control group (NC, untreated group); B: Normal control group:10% CAP; C: Model control group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C); D:Positive control group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C)+0.05% Dex; E1-G1: Test group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C)+2%, 5% and 10% CAP. E2-G2: Test group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C)+1%, 2% and 5% CAP. E3-F3: Test group, 100 μg/mL LPS+20 μg/mL poly (I:C)+1% and 2% CAP. ### indicated P<0.001 vs A. ***, **, * indicated P<0.001, 0.01, and 0.05 vs C"

| [1] | Boothby I C, Cohen J N, Rosenblum M D. Regulatory T cells in skin injury: at the crossroads of tolerance and tissue repair[J]. Sci. Immunol., 2020, 5 (47) : 9631. |
| [2] |
Jenei A, Kalló G, Dajnoki Z, et al. Detection of antimicrobial peptides in stratum corneum by mass spectrometry[J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22 (8) : 4233.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22084233 |
| [3] |
Qu R, Chen X, Hu J, et al. Ghrelin protects against contact dermatitis and psoriasiform skin inflammation by antagonizing TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9 (1) : 1348.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38174-2 pmid: 30718736 |
| [4] |
Xia S, Chen Z, Shen C, et al. Higher-order assemblies in immune signaling: supramolecular complexes and phase separation[J]. Protein Cell, 2021, 12 (9) : 680-694.
doi: 10.1007/s13238-021-00839-6 |
| [5] |
Sun Z, Pan Y, Qu J, et al. 17β-Estradiol promotes trained immunity in females against sepsis via regulating nucleus translocation of RelB[J]. Front. Immunol., 2020, 11: 1591.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01591 pmid: 32793229 |
| [6] |
Chen J, Gao K, Wang R, et al. Prediction and mitigation of mutation threats to COVID-19 vaccines and antibody therapies[J]. Chem. Sci., 2021, 12 (20) : 6929-6948.
doi: 10.1039/d1sc01203g pmid: 34123321 |
| [7] |
Hou X X, Chen G, Hossini A M, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulates the expression of TNF-α and IL-8 in Human sebocytes via the MyD88-p65NF-κB/p38MAPK signaling pathways[J]. J. Innate. Immun., 2019, 11 (1) : 41-51.
doi: 10.1159/000491029 |
| [8] |
Haidari G, Cope A, Miller A, et al. Combined skin and muscle vaccination differentially impact the quality of effector T cell functions: the CUTHIVAC-001 randomized trial[J]. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7 (1) : 13011.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13331-1 pmid: 29026141 |
| [9] |
Merches K, Schiavi A, Weighardt H, et al. AHR signaling dampens inflammatory signature in neonatal skin γδ T Cells[J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21 (6) : 2249.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21062249 |
| [10] | Sumpter T L, Balmert S C, Kaplan D H. Cutaneous immune responses mediated by dendritic cells and mast cells[J]. Jci. Insight., 2019, 4 (1) : 123947. |
| [11] |
Kalesnikoff J, Rios E J, Chen C C, et al. Roles of RabGEF1/Rabex-5 domains in regulating Fc epsilon RI surface expression and Fc epsilon RI-dependent responses in mast cells[J]. Blood., 2007, 109 (12) : 5308-5317.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-067363 pmid: 17341663 |
| [12] |
Gandhi GR, Neta MTSL, Sathiyabama RG, et al. Flavonoids as Th1/Th2 cytokines immunomodulators: A systematic review of studies on animal models[J]. Phytomedicine., 2018, 44: 74-84.
doi: S0944-7113(18)30092-8 pmid: 29895495 |
| [13] | Man M Q, Yang B, Elias P M. Benefits of hesperidin for cutaneous functions[J]. Evid-Based Compl. Alt. Med., 2019: 2676307. |
| [14] |
Zhang F, Wang Y, Liu P, et al. Puerarin exhibits antiinflammatory properties in gunpowder smog-induced acute lung injury in rats via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system and the NFκB signaling pathway[J]. Exp. Ther. Med., 2021, 22 (2) : 809.
doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10241 pmid: 34093765 |
| [15] |
Deng Y, Liu Z, Geng Y. Anti-allergic effect of Artemisia extract in rats[J]. Exp. Ther. Med., 2016, 12 (2) : 1130-1134.
pmid: 27446332 |
| [16] |
Celebi Sözener Z, Cevhertas L, Nadeau K, et al. Environmental factors in epithelial barrier dysfunction[J]. J. Allergy Clin. Immun., 2020, 145 (6) : 1517-1528.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.024 |
| [17] |
Kashem S W, Haniffa M, Kaplan D H. Antigen-presenting cells in the skin[J]. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 2017, 35: 469-499.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052215 pmid: 28226228 |
| [18] |
Tsepkolenko A, Tsepkolenko V, Dash S, et al. The regenerative potential of skin and the immune system[J]. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol., 2019, 12: 519-532.
doi: 10.2147/CCID |
| [19] |
Cabeza-Cabrerizo M, Cardoso A, Minutti C M, et al. Dendritic cells revisited[J]. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 2021, 39: 131-166.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-061020-053707 pmid: 33481643 |
| [20] |
Balan S, Saxena M, Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cell subsets and locations[J]. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol., 2019, 348: 1-68.
doi: S1937-6448(19)30067-X pmid: 31810551 |
| [21] |
Daigneault M, Preston J A, Marriott H M, et al. The identification of markers of macrophage differentiation in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells and monocyte-derived macrophages[J]. PLoS One., 2010, 5 (1) : 8668.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008668 pmid: 20084270 |
| [22] |
Ullmann T, Luckhardt S, Wolf M, et al. High-throughput screening for CEBPD-modulating compounds in THP-1-derived reporter macrophages identifies anti-inflammatory HDAC and BET Inhibitors[J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22 (6) : 3022.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22063022 |
| [23] |
Tsuge K, Inazumi T, Shimamoto A, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying prostaglandin E2-exacerbated inflammation and immune diseases[J]. Int. Immunol., 2019, 31 (9) : 597-606.
doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxz021 pmid: 30926983 |
| [24] |
Mukai K, Tsai M, Saito H, et al. Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors[J]. Immunol. Rev., 2018, 282 (1) : 121-150.
doi: 10.1111/imr.12634 pmid: 29431212 |
| [25] |
Galli S J, Gaudenzio N, Tsai M. Mast cells in inflammation and disease: Recent progress and ongoing concerns[J]. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 2020, 38: 49-77.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-071719-094903 pmid: 32340580 |
| [26] |
Elieh A K D, Wöhrl S, Bielory L. Mast cell biology at molecular level: a comprehensive review[J]. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol., 2020, 58 (3) : 342-365.
doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08769-2 |
| [27] |
Kany S, Vollrath J T, Relja B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease[J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20 (23) : 6008.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20236008 |
| [28] |
Kim Y, Lim K M. Skin barrier dysfunction and filaggrin[J]. Arch. Pharm. Res., 2021, 44 (1) : 36-48.
doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01305-x pmid: 33462753 |
| [29] | Adhikary P P, Tan Z, Page B D G, et al. TSLP as druggable target-a silver-lining for atopic diseases?[J]. Pharmacol. Ther., 2021, 217: 107648. |
| [30] | Wang S H, Zuo Y G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin in cutaneous immune-mediated diseases[J]. Front Immunol., 2021, 12: 698522. |
| [1] | LI Rui,ZHANG Nan,YAO Lei,LI Yu-hong. Study on the hair growth promotion effect of lavender essential oil and Asian mint essential oil [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2020, 50(8): 536-541. |
| [2] | LIU Ting-qiang,YAN Ze-min,HOU Dong-mei,ZHOU Hua-feng,DUAN Ming-xing. Effect of low molecular weight peptides extract from Earthworm on cell viability and synthesis of collagen in cultured human skin cells [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2016, 46(3): 168-172. |
|