


China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (7): 639-647.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2021.07.009
• Development and application • Previous Articles Next Articles
Pan Xuen1,2,3,He Zhirong1,2,3,*,Lu Zhangshun1,2,3,Yang Guang1,2,3,Zhong An1,2,3,Huang Zhipeng1,2,3
Received:2020-10-10
Revised:2021-07-01
Online:2021-07-22
Published:2021-07-23
Contact:
Zhirong He
CLC Number:
Pan Xuen,He Zhirong,Lu Zhangshun,Yang Guang,Zhong An,Huang Zhipeng. Rapid classification of skin corrosion of detergents and disinfectants: a combined method of dye penetration and damage grading[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2021, 51(7): 639-647.
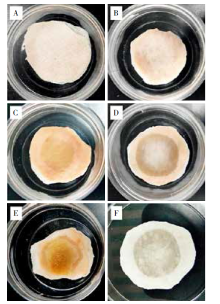
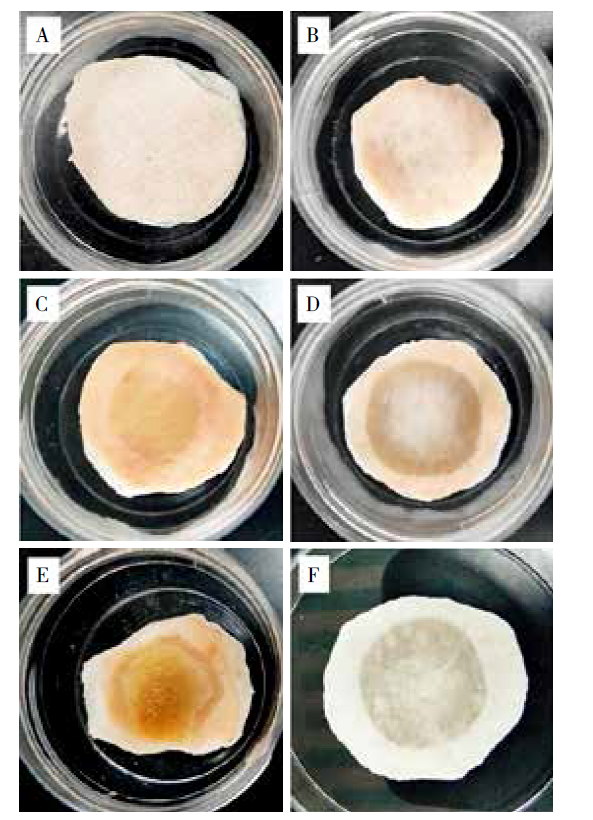
Fig. 1
Grading of the skin discs after the application of the test chemicals (A: Score-0 No obvious damage; B: Score-1 Slight patch and damage; C: Score-2 Well defined patch and damage; D: Score-3 Moderate to severe patch and damage, hyaline degeneration occurred; E: Score-4 Very severe patch and damage; F: Score-4 Patch and damage observed from the back side of the skin disc)"
Tab. 2
The RhB extraction efficiency of the tested skin under different extraction conditions"
| 提取条件 | 阴性对照 | 阳性对照 | 提取 效率 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 提取量 均值/μg | 下限/μg (95%CI) | 上限/μg (95%CI) | 提取量 均值/μg | 下限/μg (95%CI) | 上限/μg (95%CI) | |||
| 60℃静态提取过夜(16 h) | 36.79 | 27.16 | 46.41 | 80.21 | 59.81 | 100.60 | 2.18 | |
| 超声波提取9 min | 34.87 | 23.93 | 45.82 | 77.55 | 53.78 | 101.32 | 2.22 | |
| 超声波提取12 min | 42.04 | 24.68 | 59.40 | 89.74 | 63.81 | 115.66 | 2.13 | |
| 超声波提取15 min | 51.63 | 27.08 | 76.18 | 107.30 | 73.70 | 140.90 | 2.07 | |
Tab. 4
Comparison of classification results of skin corrosion of reference substances"
| 受试物 | CAS No. | 参考结果 | 实验结果 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GHS皮肤 腐蚀性分类 | 染药时间 | 皮肤损伤观察结果 | 评分 | 染色实验结果 | GHS皮肤腐蚀性分类 | ||
| 辛酸(正辛酸) | 124-07-2 | 1B/1C | 24 h | 轻微的色斑(3/3) | 1.0 | 阳性 | 1C |
| 四氯乙烯 | 127-18-4 | NC | 24 h | 无可见损伤(3/3) | 0.0 | 阴性 | NC |
| 4-氨基-1, 2, 4-三氮唑 | 584-13-4 | 2/NC | 24 h | 清晰的色斑(3/3) | 2.0 | — | 1C |
| 溴乙基苯 | 103-63-9 | NC | 24 h | 无可见损伤(3/3) | 0.0 | 阴性 | NC |
| N, N-二甲基亚二丙基三胺 | 10563-29-8 | 1A/1B | 1 h | 清晰的色斑(2/3) 透明变性(1/3) | 2.3 | — | 1B |
| 丙三醇 | 56-81-5 | NC | 24 h | 无可见损伤(3/3) | 0.0 | 阴性 | NC |
| 邻叔丁基苯酚 | 88-18-6 | 1B/1C | 24 h | 褐色的斑点(3/3) | 3.0 | — | 1C |
| 1, 2-丙二胺 | 78-90-0 | 1A | 1 h | 清晰的色斑(2/3) 透明变性(1/3) | 2.3 | — | 1B |
| 硬脂酸 | 57-11-4 | NC | 24 h | 无可见损伤(2/3) 轻微的色斑(1/3) | 0.3 | 阴性 | NC |
| 10%硫酸 | 7664-93-9 | 1B/1C | 1 h | 清晰的色斑(1/3) 透明变性(2/3) | 2.7 | — | 1B |
| 10%氢氧化钾水溶液 | 1310-58-3 | 1A | 5 min | 背面损伤(3/3) | 4.0 | — | 1A |
| 去离子水(阴性对照) | 7732-18-5 | NC | 24 h | 无可见损伤(3/3) | 0.0 | 阴性 | NC |
| 5%氢氧化钠水溶液 | 1310-73-2 | 1A | 5 min | 清晰的色斑(2/3) 透明变性(1/3) | 2.3 | — | 1A |
| 25%盐酸(阳性对照) | 7647-01-0 | 1B | 1 h | 背面损伤(3/3) | 4.0 | — | 1B |
| 0.9%氯化钠水溶液 | 7647-14-5 | NC | 24 h | 无可见损伤(3/3) | 0.0 | 阴性 | NC |
| 40%乙烯利水溶液 | 16672-87-0 | 1C | 24 h | 透明变性(2/3) 背面损伤(1/3) | 3.3 | — | 1C |
Tab. 5
Classification results of skin corrosion of detergents and disinfectants"
| 受试物 | 主要成分 | pH | GHS皮肤腐蚀性分类 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 评分结合 染色方法 | TG430 | |||
| 4.8%对氯间二甲苯酚消毒液 | 水、对氯间二甲苯酚、表面活性剂 | 9.91 | NC | NC |
| 84消毒液(有效氯4.3%) | 水、次氯酸钠、表面活性剂 | 12.45 | 1C | C |
| 50%柠檬酸消毒液 | 柠檬酸、水、其他有机酸 | 1.02 | 1C | C |
| 4.5%过氧乙酸消毒液 | 水、乙酸、过氧化氢、过氧乙酸 | <1.00 | 1B | C |
| 物品表面消毒液 | 水、乙醇、异丙醇 | 8.35 | NC | NC |
| 洗衣机槽清洁剂 | 过碳酸钠、表面活性剂、缓蚀剂 | 10.36(10%水溶液) | 1C | C |
| 洗衣粉 | 表面活性剂、生物酶制剂、水软化剂、香精 | 10.95(10%水溶液) | NC | NC |
| 洗洁精 | 水、表面活性剂、氯化钠、EDTA二钠、甲基异噻唑啉酮、香精 | 7.82 | NC | NC |
| [1] | OECD. Test No. 404: Acute dermal irritation/corrosion [EB/OL]. ( 2015-07-28)[2020-09-20]. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-404-acute-dermal-irritation-corrosion_9789264242678-en. |
| [2] | Song Bing, Gu Jixiu, Wang Yongfeng, et al. Research on alternative technology of laboratory animals[J]. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica, 2020,28(5) : 680-687. |
| [3] | Cheng Shujun. Research progress of alternative technologies in animal experiments[J]. Science Technology Review, 2017,35(24) : 40-47. |
| [4] |
Lewis D I. Animal experimentation: implementation and application of the 3Rs[J]. Emerging Topics in Life Sciences, 2019,3(6) : 675-679.
doi: 10.1042/ETLS20190061 |
| [5] | Ge Shanzhen, Niu Yuntong, Lu Tao. Progress of research on the skin irritation test alternative models[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2015,15(1) : 167-170. |
| [6] | Zeng Can, Yang Ting, Xiao Ying. Application and new development of alternative model of skin irritation tests[J]. Medical Information, 2011,24(6) : 2483-2484. |
| [7] | Robinson M, Perkins M. Handbook of cosmetic science and technology[M]. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc., 2005: 95-106. |
| [8] | OECD. Test No. 430: In vitro skin corrosion: transcutaneous electrical resistance test method (TER)[EB/OL]. ( 2015-07-28)[2020-09-20]. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-430-in-vitro-skin-corrosion-transcutaneous-electrical-resistance-test-method-ter_9789264242739-en. |
| [9] | Chen Yurong, An Xinglan, Wang Zhengzhu, et al. Research progress on pigs as human disease models[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine, 2020,30(7) : 110-119. |
| [10] | Wang Jieying, Sun Jiaqi, Ning Bo. Overview on the application of the minipig model in medical research[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2019,38(5) : 91-95. |
| [11] |
Mahl J A, Mireille B E V, Court, et al. The minipig in dermatotoxicology: Methods and challenges[J]. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology, 2006,57(5) : 341-345.
doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2006.03.004 |
| [12] |
Qvist M H, Hoeck U, Kreilgaard B, et al. Evaluation of Göttingen minipig skin for transdermal in vitro permeation studies[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Official Journal of the European Federation for Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2000,11(1) : 59-68.
doi: 10.1016/S0928-0987(00)00091-9 |
| [13] | Qiu Bo, Wang Yan, Hu Jianting, et al. Comparison of skin histology between SD rats and BAMA minipig [J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine, 2012,22(6): 14-15, 20, 85-86. |
| [14] | National Health Commission of the PRC. Diagnostic criteria of occupational chemical skin burns [EB/OL]. ( 2009- 03- 16)[2020-11-02]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/pyl/201807/31f659a 256914ac4b1a6c35b88661222.shtml. |
| [15] |
Hakan A, Zeki A K. Rare chemical burns: review of the literature[J]. International Wound Journal, 2019,16(6) : 1330-1338.
doi: 10.1111/iwj.v16.6 |
| [16] | Yin S. Chemical and common burns in children [J/OL]. Thousand Oaks: Clinical Pediatrics, 2017,56(5S): 8-12 [2020-11-02]. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0009922817706975. |
| [17] | Le Xiaohong, Zhang Minquan. An clinical analysis of mechanism and treatment for chemical burn[J]. Journal of Ningbo University(NSEE), 2000,13(4) : 101-104. |
| [18] | Dave Allen, Mike D Waters. Reducing, refining and replacing the use of animals in toxicity testing [M]. London: RSC Publishing, 2013: 221-223. |
| [19] | European Chemicals Agency. Table of harmonised entries in Annex VI to CLP [EB/OL]. [2020-09-20]. https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/annex-vi-to-clp. |
| [1] | Jingxuan Liu, Jianming Jin, Hua Wu. Botanical cosmetic ingredients (VII)Research and development of plant antifungal [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 259-266. |
| [2] | Cuicui Hu, Daihong Zhou, Xinwan Chen, Jialing Zhong, Canquan Mao. Efficacies and mechanisms of a formula of Chinese medicinal plants (MHC-20) against Streptococcus pyogenes [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 282-289. |
| [3] | Wu Bi, Xiaohong Pan, Xiaoqin Tu, Shuai Yin, Hui Sun. Analysis of the mechanism of anti-sensitive skin effect of cosmetic raw material Stephania tetrandra based on network pharmacology [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 305-312. |
| [4] | Yaoyao Li. Study on the anti-aging and antioxidant effects of isosinensetin [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 313-319. |
| [5] | Wanping Zhang, Qi Peng, Dongmei Zhang, Shilian Zheng, Wen Jiang, Lihao Gu. Mechanism and research progress of chemical leukoderma induced by 4-substituted phenols [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 320-328. |
| [6] | Mengran Xu, Hua Zhao. Research progress on the evaluation methods of cosmetic after-sun repair efficacy [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 329-336. |
| [7] | Na Ta, Mengxin Feng, Jiamin Gao, Fenglan Zhang, Gangli Wang. Supervision and use analysis of sunscreen with potential endocrine disruption risk [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 337-343. |
| [8] | Wenrui Zhou, Jianbiao He, Qian Jiao, Zidi Wang, Qianqian Su, Yan Jia. Research progress of the correlation between sensory evaluation and instrumental analysis of cosmetics in O/W emulsion system [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 344-352. |
| [9] | Liyuan Zhang, Linqi Yan, Qiaoyuan Cheng, Lvye Qi, Rong Wang, Liuqian Huang. Determination of 14 kinds of α-hydroxy acids and hydroxy esters in cosmetics [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 353-359. |
| [10] | Wei Xu, Po Zou, Changyu Li, Ming Yang, Yan Lu, Huiliang Li. Determination of 36 stimulants in cosmetics by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(3): 360-368. |
| [11] | Kangfu Zhou, Yixuan Zhi, Feifei Wang, Yazhuo Shang. New emulsion system and its application in cosmetics (VI)Microemulsion [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 139-148. |
| [12] | Hongling Zhang, Lin Cheng, Haiyan Wang, Feiya Luo, Huiliang Zhang, Lei Sun. Using DPRA alternative method to evaluate the skin sensitization of 3 coumarins [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 156-160. |
| [13] | Zhen Xie, Wei Huang, Jinsong Zhang, Shuhuai Chen, Linji Qu, Rong Kuang. Study on biomarkers of corneal injury in the evaluation of eye irritation of cosmetics [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 161-167. |
| [14] | Huiyi Li, Yue Zhou, Qian Wu, Lidi Du, Jiaying Xie, Jianhua Tan. Evaluation of cosmetics in melanin inhibition efficacy [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 168-174. |
| [15] | Xinyu Peng, Haiyan Liang, Zixian Wen, Meiting Li, Xin Li, Xiaofeng Qiu. Impact of rheology modifiers on Bag-on-valve spray products [J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2024, 54(2): 181-187. |
|